Global warming is a term that evokes a sense of urgency, drawing attention to one of the most critical challenges faced by humanity today. At its core, global warming refers to the gradual increase in the Earth’s average surface temperature due to the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This phenomenon, while complex, can be understood through a series of fundamental concepts that shed light on its dire implications for our planet.
Understanding the mechanics behind global warming reveals how it intertwines with the broader tapestry of climate change. It is essential to unravel the relationship between greenhouse gases, human activity, and the delicate balance of our environment.
The Greenhouse Effect: Nature’s Insulation
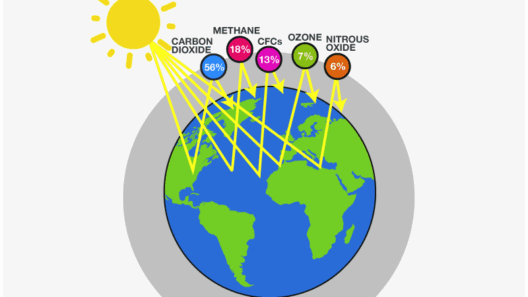
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. When the sun’s energy reaches the Earth, some of it is reflected back into space while the rest is absorbed, warming the planet. To maintain a stable climate, the Earth radiates some of this energy back to space. However, certain gases in the atmosphere trap a portion of this energy, acting like a blanket around the Earth. These gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor.
This phenomenon is akin to a well-designed greenhouse that fosters plant growth. The crucial difference lies in the accelerated accumulation of greenhouse gases due to human activities. Industrialization, fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and agricultural practices have all significantly increased these gases in the atmosphere, enhancing the greenhouse effect beyond natural levels.
The aesthetic allure of Earth’s natural systems belies the underlying peril posed by this increased warming. When the balance is tipped, the consequences reverberate throughout ecosystems, weather patterns, and ultimately human well-being.
Causal Factors: The Anthropogenic Influence
Human activities are the principal contributors to the alarming rise in greenhouse gas concentrations. Industrialization sparked a revolution in production methods, which, while boosting economic growth, led to rampant fossil fuel use. Burning coal, oil, and natural gas for energy releases vast amounts of CO2. This is not just an environmental issue; it translates to palpable changes that affect all inhabitants of our planet.
Additionally, deforestation exacerbates the situation. Trees play a vital role in sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. When forests are cleared for agriculture or urban development, not only is this carbon sink diminished, but the act of burning or decomposing wood releases more CO2. Furthermore, agriculture itself emits greenhouse gases through livestock emissions and the use of chemical fertilizers.
More than an abstract concept, these practices manifest in tangible shifts in climate and biodiversity, leaving scars on the landscape that are both striking and sorrowful.
Consequences: A Global Reality Check
The impacts of global warming are profound and multifaceted, stretching from localized phenomena to global events. One of the most immediate effects is the increase in global temperatures, which leads to severe weather patterns. Heatwaves, droughts, and torrential rains are becoming more prevalent, disrupting ecosystems and endangering agricultural productivity.
Rising sea levels present another striking reality. As polar ice melts and ocean waters warm, the volume of water in the oceans increases, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems. The aesthetic beauty of coastal landscapes may soon face the harsh reality of erosion and habitat loss.
Moreover, global warming has far-reaching repercussions on biodiversity. Many species are facing extinction as they struggle to adapt to rapid changes in their habitats. The dissolving of ecosystems—once vibrant and teeming with life—calls into question the very fabric of our environmental heritage.
Addressing Global Warming: A Call for Action
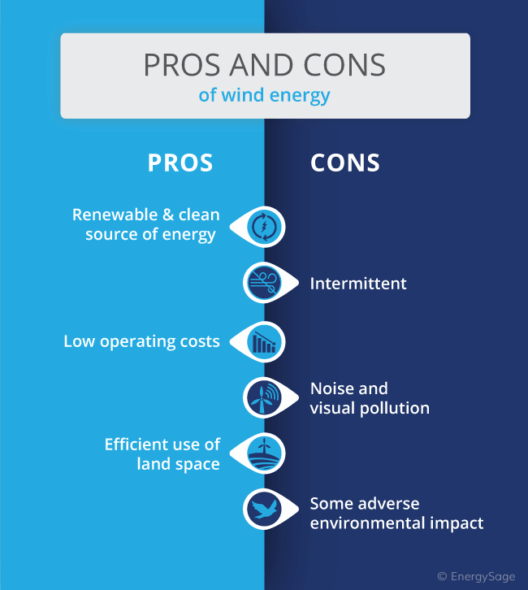
Combating global warming calls for a concerted effort from individuals, governments, and organizations worldwide. Transitioning to renewable energy sources—such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power—is paramount in reducing dependence on fossil fuels. Energy efficiency, conservation efforts, and sustainable urban planning can also contribute significantly to mitigating emissions.
Moreover, reforestation and responsible land management are pivotal strategies. By restoring forests and maintaining biodiversity, we can enhance the Earth’s natural defenses against climate change. This not only combats global warming but also restores some of the aesthetic grandeur of natural landscapes that humanity often takes for granted.
As communities come together to educate, innovate, and advocate for change, the possibility emerges for a more sustainable future. Understanding the simplicity of global warming prompts further inquiry, revealing layers of complexity that demand our attention and action.
In conclusion, global warming is not merely a phenomenon to be studied— it is a clarion call for immediate action. By fostering awareness and promoting sustainable practices, we can embrace a transformative journey toward a healthier planet. This journey is both an ethical obligation and an opportunity to restore the balance between humanity and the natural world, reminding us of our interconnectedness with all living beings. In doing so, we can hope to create a legacy characterized by resilience and harmony—a legacy that honors the intrinsic beauty of our planet.