The concept of the greenhouse effect is pivotal for understanding climate change and its implications on our planet. In this guide, we delve into various dimensions of the greenhouse effect, utilizing a comprehensive Quizlet resource as a learning tool. This article offers structured insights on what constitutes the greenhouse effect, its mechanisms, impacts, and relevance in today’s environmental discourse.
Understanding the Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that plays a crucial role in warming the Earth’s atmosphere. It occurs when certain gases, known as greenhouse gases (GHGs), trap heat emitted from the Earth’s surface. This trapped heat is essential for sustaining life, as it keeps our planet at a temperate level. Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be inhospitable, lacking the warmth necessary to support diverse ecosystems.
Key greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor. Each of these gases contributes differently to the overall warming effect but collectively functions to maintain thermal balance within the atmosphere. The detrimental aspect arises from human activities, such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes, which have amplified greenhouse gas concentrations, leading to significant climate destabilization.
Mechanics of the Greenhouse Effect
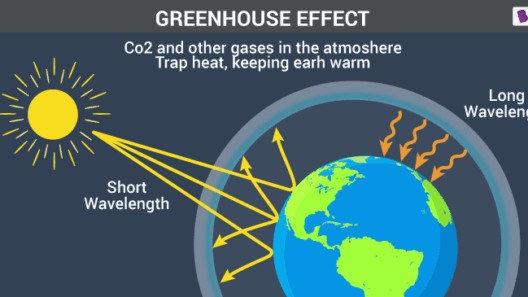
The greenhouse effect operates through a series of intricate processes. Initially, solar radiation reaches the Earth’s surface, warming it. Subsequently, this energy is re-radiated back into the atmosphere in the form of infrared radiation. However, greenhouse gases absorb a portion of this re-emitted energy, trapping heat in the atmosphere and creating a warming layer. This phenomenon can be succinctly described through the analogy of a blanket: just as a blanket retains body heat, greenhouse gases hold onto the Earth’s warmth.
It is imperative to note that not all solar radiation is absorbed equally. Different surfaces absorb varying amounts of sunlight, which is why urban areas bask in heat compared to the cooler conditions of expansive natural landscapes. As GHG concentrations rise, the volume of heat retained escalates, causing shifts in climatic patterns worldwide. This warming effect contributes to extreme weather events, as well as longer-term trends like rising sea levels and altered precipitation patterns.
Impacts of the Greenhouse Effect
The implications of an intensified greenhouse effect are profound and multifaceted. A prominent consequence is global warming, which leads to rising average temperatures across the globe. This rise affects weather patterns in significant ways, resulting in unpredictable storms, heatwaves, and flooding. Such climatic disturbances can devastate agricultural productivity, leading to food insecurity and economic instability.
Additionally, ecosystems face great stress as species struggle to adapt to rapidly changing environments. Polar bears, for instance, are emblematic of the impact of climate change, as melting ice drastically reduces their hunting grounds. Biodiversity loss accelerates when species fail to adapt or migrate effectively to new suitable habitats.
The human footprint is also profoundly affected. Increased frequencies of natural disasters place immense pressure on infrastructure and public health systems. Vulnerable communities, particularly in developing nations, are disproportionately impacted, facing challenges in resilience and adaptation. This reinforces existing inequalities and poses ethical questions regarding environmental responsibility.
Utilizing Quizlet for Greenhouse Effect Learning
For individuals seeking to understand the greenhouse effect more thoroughly, Quizlet offers a plethora of resources. These include flashcards, diagrams, and quizzes that elucidate complex concepts in manageable formats. One effective way to engage with this content is through visual aids, such as the greenhouse effect diagram available on Quizlet. This diagram meticulously outlines the flow of energy, the role of greenhouse gases, and the consequent warming effects. Visual learning can reinforce and complement textual study, catering to diverse learning styles.
In addition to diagrams, the interactive learning quizzes on Quizlet serve as a valuable tool for self-assessment. They effectively gauge comprehension, ensuring that users can track their understanding of the material. Engaging with the content actively fosters retention and encourages a deeper exploration of related topics, such as climate policies and renewable energy solutions.
Navigating the Layers of the Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is not merely a standalone phenomenon; it intertwines with various environmental and socio-political matrices. It underscores the urgency of transitioning to sustainable practices and advocating for policy reforms aimed at curbing GHG emissions. Global efforts, such as the Paris Agreement, exemplify collaborative international endeavors to address climate change repercussions. These frameworks seek to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, a goal that necessitates collective action and commitment.
Moreover, individual actions play a critical role in mitigating climate change. Simple lifestyle alterations, such as reducing energy consumption, promoting public transport, and embracing renewable energy sources, contribute substantially to GHG reduction. Public awareness campaigns aim to empower individuals and communities to engage in sustainable practices, fostering a collective environmental stewardship.
Conclusion: An Ongoing Journey Towards Awareness
Understanding the greenhouse effect is foundational for grasping the broader narrative of climate change. Utilizing platforms like Quizlet can enhance knowledge acquisition and retention regarding this crucial subject. As we navigate an increasingly warming world, it is essential to recognize our role in either exacerbating or alleviating its effects. The time for action is now, and informed individuals can be change agents in the quest for a sustainable future.