The phenomenon of the greenhouse gas effect is a critical component of our understanding of climate change and global warming. This effect, while a natural part of Earth’s atmospheric processes, is increasingly being influenced by human activities. It’s a topic that encapsulates both scientific nuances and societal implications, making it vital to explore both the mechanics and the consequences of greenhouse gases and their interaction with our climate.
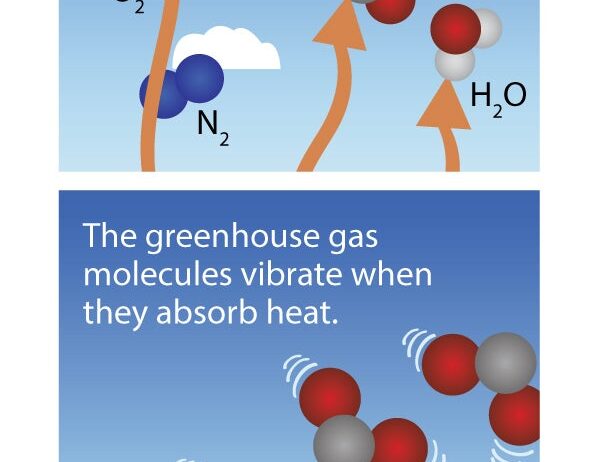
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are primarily composed of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor. They are essential for maintaining the Earth’s temperature by trapping heat in the atmosphere. Without these gases, our planet would be inhospitably cold. However, the escalating concentrations of GHGs due to industrial activities, deforestation, and other anthropogenic factors are enhancing this natural greenhouse effect, leading to alarming changes in our climate.
The Mechanism of Heat Trapping
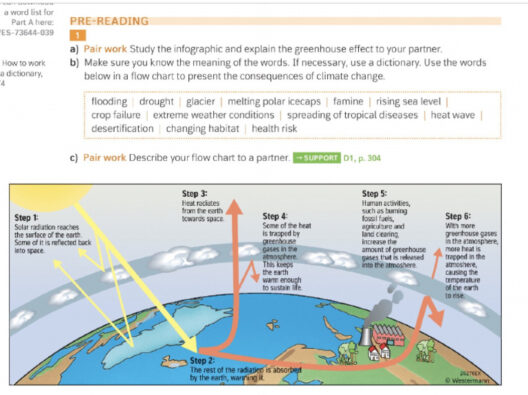
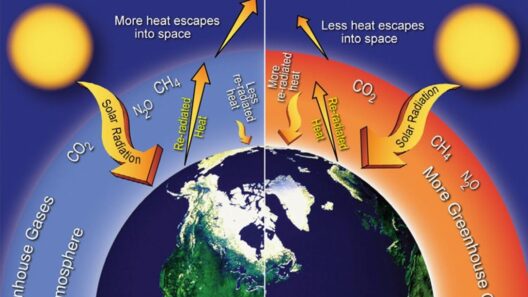
To understand the greenhouse gas effect, it’s essential to first grasp how GHGs operate within the Earth’s atmosphere. When solar radiation reaches our planet, a portion of it is absorbed by the Earth’s surface, warming it. The Earth then radiates this energy back into the atmosphere in the form of infrared radiation, or heat. GHGs absorb some of this outgoing radiation, preventing it from escaping into space. This is akin to the way a blanket retains body heat, providing a warm and stable temperature for life to flourish.
This process is a delicate balance. In a naturally occurring state, the concentrations of GHGs in the atmosphere maintain a stable climate. However, human activities, particularly since the Industrial Revolution, have drastically increased the levels of these gases. For example, burning fossil fuels releases significant amounts of CO2. Land-use changes and agricultural practices contribute to emissions of methane and nitrous oxide, both potent GHGs, which exacerbate the greenhouse gas effect.
The Impact of Elevated Greenhouse Gas Levels
The ramifications of increased greenhouse gas concentrations are manifold and profound. One of the most pressing issues is global warming, a direct consequence of the enhanced greenhouse gas effect. Average global temperatures have been rising, leading to a plethora of environmental changes.
As the Earth warms, we see more frequent and severe weather events. Heatwaves, droughts, and heavy rainfall are becoming increasingly common, altering local climates and disrupting ecosystems. This transition can lead to habitat loss for many species, pushing them towards extinction. Coral reefs, for instance, are particularly sensitive to temperature changes, and rising sea temperatures contribute to coral bleaching, threatening marine biodiversity.
The impacts extend beyond just temperature fluctuations. The melting of polar ice caps and glaciers is contributing to rising sea levels, which threaten coastal communities and infrastructure. This phenomenon is another critical aspect of climate change, as it enhances the risk of flooding and erosion, prompting displacement of populations and economic instability.
Mitigating Greenhouse Gas Emissions
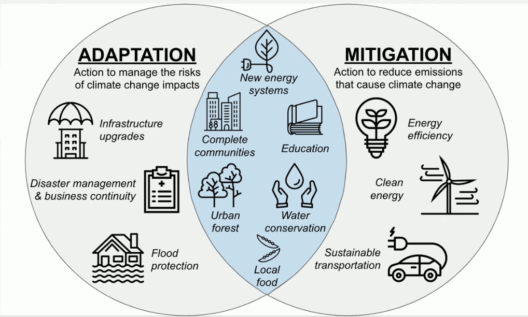
Understanding the greenhouse gas effect ultimately leads us to the imperative of mitigating its impacts. Reducing emissions requires a multi-faceted approach that combines technological innovation, policy changes, and societal shifts. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, can significantly diminish reliance on fossil fuels and subsequently reduce CO2 emissions.
Agricultural practices also need reform. Implementing sustainable farming methods can lower methane and nitrous oxide emissions. Techniques such as precision farming, which optimizes the use of resources, and agroforestry, which combines agriculture and forestry practices, can enhance carbon sequestration and biodiversity while minimizing emissions.
At an individual level, lifestyle changes can contribute to emission reductions. Reducing meat consumption, embracing public transport, and minimizing waste can collectively lead to a significant decrease in one’s carbon footprint. Advocacy for climate-friendly policies also plays a critical role; supporting local and national legislation aimed at reducing GHG emissions can help create a larger impact.
Education and awareness are vital in this fight against climate change. Promoting understanding of the greenhouse gas effect and its implications enables individuals and communities to make informed choices and advocate for systemic changes. The more we comprehend the intricacies of GHGs and their impact on our planet’s health, the better equipped we become to tackle the challenges posed by climate change.
In conclusion, the greenhouse gas effect is a crucial mechanism that sustains life on Earth, but its enhancement due to human activities poses significant threats to our climate. Understanding, mitigating, and adapting to these changes is essential. The path forward involves a collective effort spanning technological advancements, individual actions, and robust policy frameworks designed to curtail greenhouse gas emissions. By working together, we can strive for a sustainable future, ensuring that the delicate balance of our climate is preserved for generations to come.