The Mediterranean climate is a distinctive and captivating climatic zone, widely acknowledged for its sun-drenched summers and mild winters. Occupying regions located around the Mediterranean Sea and extending to various parts of the world, including parts of California, Chile, South Africa, and Australia, this climate is notable for its unique characteristics. Understanding the Mediterranean climate involves examining its temperature patterns, rainfall distribution, ecological significance, and cultural implications.
At the heart of the Mediterranean climate is its seasonal temperature contrast. Summers tend to be hot and dry, characterized by long days bathed in abundant sunshine. Average daytime temperatures during summer frequently surpass 30 degrees Celsius (86 degrees Fahrenheit), pushing residents and visitors alike to seek respite in shaded areas or through the azure waters of nearby seas. Nights, conversely, offer a pleasant respite, with cooler temperatures that provide a comfortable environment for outdoor evening pursuits, making summer evenings in Mediterranean regions particularly enchanting.
Winters in the Mediterranean climate are notably mild, with average temperatures hovering around 10 to 15 degrees Celsius (50 to 59 degrees Fahrenheit). Although winter is the wet season for these locales, the general character remains temperate compared to harsher climates elsewhere. Precipitation during the winter months is essential, as it replenishes the water supply and sustains the lush landscapes for the following growing season. Snow is a rarity in most areas; however, in certain elevated regions, occasional snowfalls can create a transient winter wonderland, adding an unexpected layer of beauty to the climate’s overall character.
Rainfall distribution plays a pivotal role in shaping the Mediterranean climate. The hallmark of this climatic zone is the highly seasonal nature of precipitation. Most of the annual rainfall occurs during the winter months, while summers are often characterized by aridity. This seasonal precipitation pattern results from geographic and meteorological influences, including prevailing winds and oceanic currents. The contrast between the wet winters and dry summers supports a diverse range of flora and fauna, adapted to these alternating conditions.
The ecological tapestry of Mediterranean climates is replete with resilience and adaptation. The vegetation predominant in these regions often includes drought-resistant species—such as olive trees, grapevines, and various aromatic herbs—that thrive despite the harsh summer conditions. The so-called “Mediterranean scrub,” or maquis, boasts a rich biodiversity with endemic species that have adapted uniquely to this environment. Such ecosystems importantly contribute to regional biodiversity and are vital for sustaining local wildlife. Furthermore, the ecology of these climates supports a plethora of human activities, such as agriculture and viticulture, that have become intrinsic to the cultural identity of the Mediterranean basin.
The cultural significance associated with the Mediterranean climate cannot be overstated. The predictable weather patterns and fertile soils of this region have historically encouraged human settlement and agricultural development. Rich crops of olives, grapes, and citrus fruits are emblematic of the agricultural heritage and are deeply intertwined with the culinary traditions of Mediterranean societies. The propensity for wine production, in particular, has rendered the Mediterranean region synonymous with wine culture, impacting everything from gastronomy to social rituals.
Furthermore, the Mediterranean climate has been a muse for artists, writers, and travelers throughout history. Endless horizons, vibrant landscapes, and a bounty of sunshine have inspired countless works. Beaches, quaint villages, and coastal views have drawn people from all walks of life, seeking both relaxation and adventure. The romantic allure of the Mediterranean is frequently encapsulated in the notion of “la dolce vita” – the sweet life, a concept that captures the essence of leisurely enjoyment found in these sun-kissed lands.
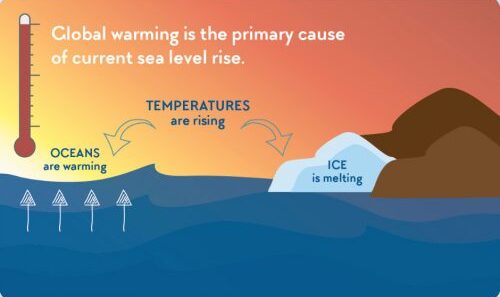
Nevertheless, amidst the charm of the Mediterranean climate, there are pressing concerns related to climate change and environmental sustainability. The warming planet poses significant challenges, leading to increasing temperatures and unpredictable rainfall patterns. Prolonged droughts and intense heatwaves have become more prevalent, threatening the delicate balance of ecosystems and the livelihoods dependent on agriculture. The risk of wildfires, which are exacerbated by hot, dry conditions, has elevated dramatically in Mediterranean regions, endangering both nature and human communities.
Addressing these challenges necessitates a convergence of local and global efforts to promote sustainable land use practices, increase water conservation, and encourage renewable energy initiatives. Furthermore, raising awareness about the fragility of these unique ecosystems is crucial for fostering public appreciation and engagement in conservation efforts.
As we navigate the implications of climate change, a deeper appreciation of the Mediterranean climate’s beauty and its inherent challenges highlights the need for action. With its captivating seasons and diverse ecosystems, the Mediterranean climate stands as a testament to the interplay between nature and humanity. Embracing its nuances can foster a greater sense of responsibility towards preserving this remarkable environment for generations to come. Understanding the delicate balance of this climate will not only enhance our appreciation for these sun-drenched regions but also empower us to advocate for their preservation in an era of burgeoning environmental change.