Saturn, the second-largest planet in our solar system and often described as the jewel of the night sky, presents a fascinating study of atmospheric phenomena. As a gas giant, Saturn’s climate is not only vastly different from Earth’s but also filled with astonishing characteristics that elicit intrigue and scientific investigation. This encapsulation of the planet’s atmospheric dynamics reveals both the beauty and complexity of its climatic systems.
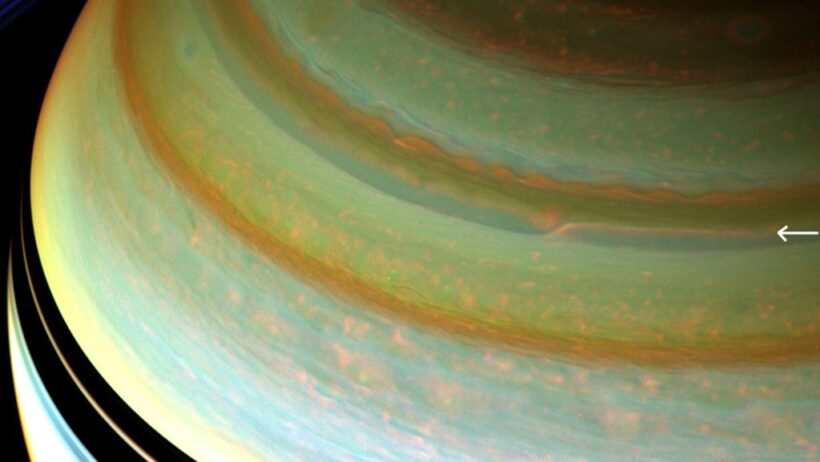
At first glance, images of Saturn showcase its spectacular rings and streaks of golden and brown cloud bands. These are not merely aesthetic features; they indicate a dynamic and tumultuous atmosphere driven by various meteorological processes. The planet’s primary composition, predominantly hydrogen and helium, is critical in shaping its atmospheric conditions, leading to a variety of weather phenomena.
Wind speeds on Saturn are among the highest in the solar system. They can reach up to 1,100 miles per hour (approximately 1,800 kilometers per hour) at the equator. Such extreme velocities create turbulent systems that generate storms and disturbances across vast distances. The juxtaposition of these high-speed winds with the planet’s immense size amplifies the strength and scale of the storms, creating an environment where cyclones can develop into colossal formations.
One of the most notable meteorological phenomena on Saturn is its immense storms. These storms, some of which can rival the size of Earth, exhibit features similar to hurricanes, such as eye walls and spiraling wind patterns. Observations have documented storms lasting for months, and some are categorized as polynya, characterized by their elongated shapes and sustained energy. These turbulent systems provide a vivid illustration of Saturn’s chaotic nature. Their formation remains a topic of ongoing research, shedding light on the interplay between the planet’s rotation and atmospheric conditions.
Another riveting aspect of Saturn’s climate is its striking seasonal changes. Saturn experiences seasons akin to Earth due to its axial tilt of approximately 26.7 degrees; however, the lengthy orbital period of 29.5 Earth years means each season lasts about seven Earth years. Anthropogenic-like effects can be studied in these seasons, such as variations in temperature and atmospheric circulation patterns. As Saturn moves through its orbital cycle, dramatic changes occur in cloud patterns, and storm activity can increase, leading scientists to ponder the underlying mechanisms driving such fluctuations.
The planet’s rings, while not directly part of its atmosphere, play an intriguing role in its climate system. The rings, composed primarily of ice particles and rocky debris, interact with Saturn’s atmosphere in unique ways. For instance, the particles can influence atmospheric temperatures and contribute to complex weather patterns. Herein lies a paradox: these beautiful rings are not merely visual spectacles but integral components of Saturn’s climatic interplay.
Temperature fluctuations across Saturn’s atmosphere are profound and showcase a complexity that continues to baffle researchers. The upper atmosphere, where auroras paint the sky with dazzling light shows, reveals a stark contrast to the lower levels. Temperatures in the cold atmosphere can drop to around -218 degrees Celsius (-360 degrees Fahrenheit) for the upper layers, yet the deeper layers can reach scorching temperatures of over 11,700 degrees Celsius (over 21,000 degrees Fahrenheit) due to the immense pressure. This temperature gradient contributes to layering of dense clouds, which in turn affects the radiative and convective processes at play. The examination of these phenomena can unravel insights into not only Saturn’s weather dynamics but also those of other gas giants across the universe.
Beyond the extraordinary storms and temperature shifts, Saturn’s atmosphere hosts a complex composition of atmospheric constituents. Ammonia, methane, and various hydrocarbons present a diverse chemical environment, leading to the rich colors observed in the planet’s cloud tops. The interaction of sunlight with these gases results in intricate cloud formations and vibrant hues, further enhancing its visual allure. The differential rotation of Saturn contributes to the layering of clouds that exhibit opaque and translucent characteristics, providing a canvas of ever-changing atmospheric art.
The exploration of Saturn’s climate has implications that extend beyond planetary curiosity. Understanding its atmospheric processes can offer valuable insights into broader questions regarding climate systems, both in our solar system and in exoplanetary research. The dynamics observed in Saturn’s atmosphere may mirror potential weather patterns found on distant celestial bodies, facilitating a deeper comprehension of atmospheric science.
As scientists continue to probe the secrets of Saturn’s tumultuous climate, the exploration not only enhances our understanding of gas giants but also emphasizes the significance of studying diverse planetary atmospheres. There’s a peculiar allure in the distinct and frenetic weather patterns that characterize Saturn—a continuous dance between chaotic storms, robust winds, and breathtaking beauty. This ever-evolving atmosphere sparks curiosity and invites further exploration, ensuring Saturn remains a subject of fascination and wonder within the tapestry of our solar system.
In conclusion, Saturn’s climate represents a vivid tapestry woven from extreme winds, massive storms, and dazzling displays of color and light. Each of these elements contributes to an ongoing narrative of scientific inquiry, situating Saturn not merely as a distant planet, but as a vital piece of the larger cosmic puzzle. As we learn more about its atmospheric intricacies, we gain clearer insights into the fundamental processes that govern not just Saturn, but ultimately the diverse climates that exist beyond our own planet Earth.