Sea level rise is a pressing issue in the contemporary environmental discourse. This phenomenon occurs due to a combination of factors, primarily related to climate change, but also influenced by natural processes. Understanding the causes of this rise is paramount for developing effective strategies and policies to combat its consequences. This article delves into the main contributors to the rising oceans, exploring their implications and potential solutions.
Climate Change: The Underlying Catalyst
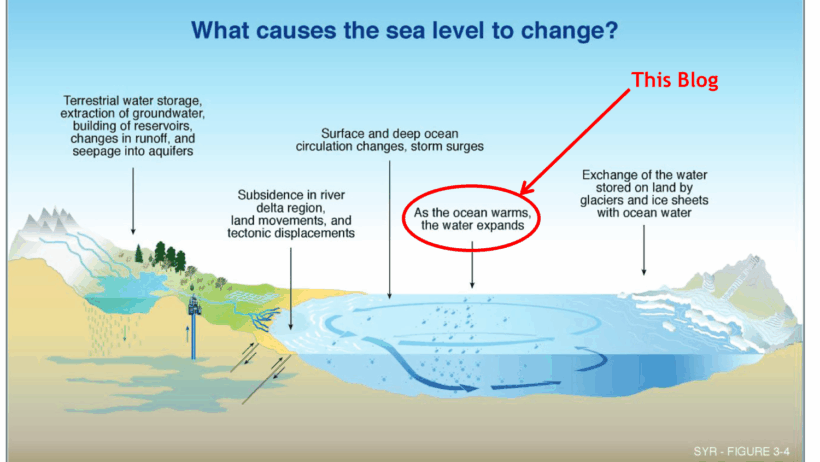
Among the myriad factors that affect sea levels, climate change reigns supreme. It drives two principal mechanisms leading to elevated ocean levels: thermal expansion and melting ice sheets. As global temperatures escalate, seawater warms and expands, occupying more space. This thermal expansion accounts for approximately half of the observed sea level rise. Meanwhile, glaciers and polar ice caps continue to undergo extensive melting, adding significant amounts of freshwater to the oceans.
Moreover, the acceleration of ice mass loss is alarming. The Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets, vital for maintaining global sea levels, are melting at unprecedented rates. Scientists observe that these massive ice reserves are thinning and retreating dramatically, contributing to a potent rise in sea levels. Recent studies indicate that Greenland alone shed about 3.8 trillion tons of ice between 1992 and 2018, a harrowing figure that underscores the urgency of addressing climate change.
The Role of Human Activity
Human actions exacerbate the natural processes contributing to sea level rise, particularly through greenhouse gas emissions. The combustion of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial activities release carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the atmosphere, intensifying the greenhouse effect. As these gases accumulate, they trap heat, resulting in a warming planet.
Deforestation also plays a crucial role in climate change and subsequently affects sea levels. Trees act as natural carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 and mitigating climate impacts. However, widespread deforestation for agriculture, urban development, and other purposes leads to increased carbon emissions, accelerating global warming and sea level rise.
Additionally, land use changes and urbanization further complicate the sea level rise scenario. Coastal cities, often densely populated and economically important, are particularly vulnerable. As urban areas expand, wetlands and other natural buffers are often destroyed, reducing the landscape’s ability to absorb floodwaters and worsening flooding during high tide or storm surges.
Melting Glaciers: A Ticking Clock
Glaciers around the world are in rapid decline, significantly impacting sea levels. These dynamic ice formations serve as freshwater reservoirs, and their melting contributes directly to the rising oceans. Glaciers traditionally discharge freshwater into oceans and rivers slowly; however, increased melting accelerates this process.
The consequences are dire, especially for low-lying island nations and coastal communities. Places such as the Maldives and Tuvalu face existential threats from encroaching shorelines. As sea levels rise, saltwater intrusion into freshwater aquifers becomes more frequent, endangering drinking water supplies and agricultural viability.
Moreover, glacier retreat causes sediment release, altering coastal geology. These changes ultimately disrupt local ecosystems and the livelihoods of communities dependent on these environments for fishing, tourism, or other economic activities.
Ocean Currents and Atmospheric Pressure
Understanding sea level rise requires not just examining isolated variables but also comprehending the broader environmental interplay. Ocean currents significantly influence regional sea levels. Variations in ocean circulation can lead to localized sea level changes and can exacerbate rise in certain areas, making some coastlines more susceptible to flooding than others.
Additionally, barometric pressure fluctuations can temporarily affect sea levels. A drop in atmospheric pressure can result in a rise in sea level in specific areas, while a high-pressure system can have the opposite effect. These phenomena are typically short-term but illustrate the complexities involved in sea level dynamics.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Confronting the challenge of rising seas requires immediate action. A two-pronged approach focusing on both mitigation and adaptation is essential for effectively addressing this crisis. Mitigation involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions through increased reliance on renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and implementing carbon capture technologies.
In conjunction with mitigation, adaptation strategies are equally vital. Coastal fortification measures such as seawalls and storm surge barriers can offer immediate protection to vulnerable areas. Additionally, natural solutions like restoring mangroves and wetlands can enhance resilience against rising seas while also providing habitat for diverse species.
Education and community engagement are crucial in addressing the impacts of sea level rise. Policymakers must work to communicate these challenges effectively, empowering local populations to understand the risks and take constructive action. Public awareness campaigns and participatory planning can drive community-led responses, fostering adaptive capacity.
Looking Forward: A Call to Action
The issue of sea level rise encapsulates the urgent need for collaborative global action. Scientific research continues to refine our understanding of this critical phenomenon, equipping communities and governments with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions.
The negative implications of ignoring sea level rise are profound. If proactive measures are not taken, the risks of displacement, economic loss, and environmental degradation will escalate. The time for action is now, and an integrative approach that combines scientific research, policy reform, and community engagement is crucial in combating this existential threat posed by rising oceans.
In summary, sea level rise is a complex issue with various contributing factors ranging from climate change to human activity. A multifaceted strategy that prioritizes mitigation and adaptation is essential for confronting this challenge and safeguarding vulnerable communities worldwide.