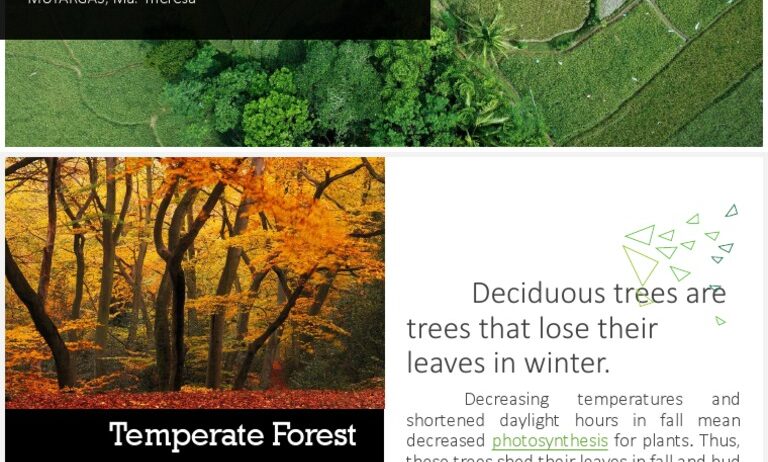
Temperate forests are remarkable ecosystems, characterized by a unique climate that fosters rich biodiversity. But what exactly defines the climate of a temperate forest? Let’s embark on a journey to explore these mild weather phenomena, teeming with life, whilst posing a playful question: How does the temperate forest manage to sustain such an array of flora and fauna despite its seemingly unpredictable weather? Along the way, we might uncover a challenge that these forests face today.
Temperate forests exist in regions where mild weather is the norm, providing a distinct environmental framework conducive to a plethora of species. This climate is typically marked by four distinct seasons: a warm summer, a cool autumn, a frigid winter, and a rejuvenating spring. The annual temperature in these areas usually ranges from about 30°F (-1°C) in the winter to 80°F (27°C) in the summer. These temperatures create a unique microhabitat—one that does not experience extreme heat or cold. The moderation in temperature plays a pivotal role in supporting an ecological equilibrium that fosters diversity.
The precipitation level in temperate forests is another critical aspect of their climate. Generally, these regions receive between 30 to 60 inches (76 to 152 cm) of rainfall annually, distributed relatively evenly throughout the year. This regular rainfall contributes to the rich soil, which is composed of a mix of decaying organic material, nutrients from decomposed plants, and minerals. The moisture levels are vital for the growth of a diverse array of plant species, including deciduous trees, conifers, and understory plants. This intricate interplay of precipitation and temperature creates a vivacious ecosystem where life thrives.
The biodiversity within temperate forests is astonishing. Home to numerous species of trees, such as oaks, maples, and birches, these areas also house a myriad of understory plants, shrubs, and grasses. As you wander through these woodlands, you may notice vibrant wildflowers blooming in the spring, a variety of fungi emerging from the forest floor during the damp months, and the bold colors of leaves transitioning in autumn. This seasonal transformation not only adds to the beauty of the landscape; it also supports myriad wildlife species, ranging from mammals like deer and foxes to birds such as woodpeckers and warblers.
Speaking of wildlife, temperate forests offer a myriad of habitats, from dense canopies that serve as nesting sites to open forest floors that provide foraging grounds. The interplay between different species and their habitats leads to complex food webs and ecosystems. For instance, a single tree may support countless species, from saprophytic fungi that decompose fallen leaves to the migratory birds that nest in its branches. This intricate dance highlights the interdependence of species and the importance of conserving these ecosystems.
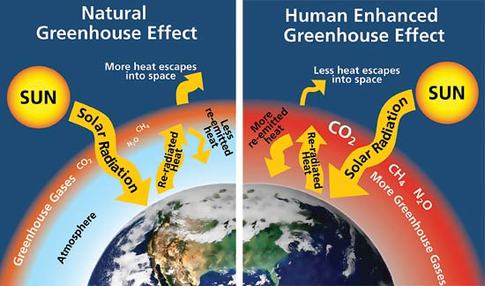
Despite the allure and complexity of temperate forests, these ecosystems are not without challenges. Climate change presents a formidable threat, reshaping weather patterns and altering precipitation levels. As global temperatures rise, forests face the possibility of increasingly severe droughts or torrential downpours. Forest health becomes compromised when such shifts occur, potentially leading to more frequent wildfires or tree diseases. This transition raises a pertinent question: How can we effectively mitigate the impacts of climate change on these vibrant ecosystems, ensuring their survival for future generations?
Furthermore, the encroachment of urbanization and agriculture further complicates the situation. As human populations expand, habitats are lost or fragmented. This habitat destruction poses a risk to the delicate balance of these ecosystems. Fragmentation can isolate wildlife populations, making it challenging for species to find mates or access resources. What might happen to these forests if their resources dwindle and biodiversity declines? The web of life that thrives in temperate forests hinges on the conservation of these spaces, making it crucial for individuals and communities to rally in their defense.
As we consider the future of temperate forests, we must reflect on the role of community action and education in protecting these vital ecosystems. Initiatives to restore habitats, reforestation projects, and sustainable land-use practices can all contribute to enhancing the resilience of temperate forests. By fostering a deeper understanding of the intricacies of these ecosystems, we can spur action that prioritizes conservation and sustainability.
In conclusion, the climate of temperate forests, characterized by its mild weather and rich biodiversity, encapsulates a world that is both enchanting and vulnerable. Understanding the delicate balance of temperature, precipitation, and seasonal changes is pivotal for appreciating these ecosystems’ complexity. Yet, as we revel in their beauty, we must also confront the pressing challenges they face, particularly in the wake of climate change and industrial expansion. So, as we ponder the question posed earlier about the sustainability of such vibrant ecosystems, let us also commit ourselves to action—ensuring the survival of temperate forests and the myriad forms of life they harbor.