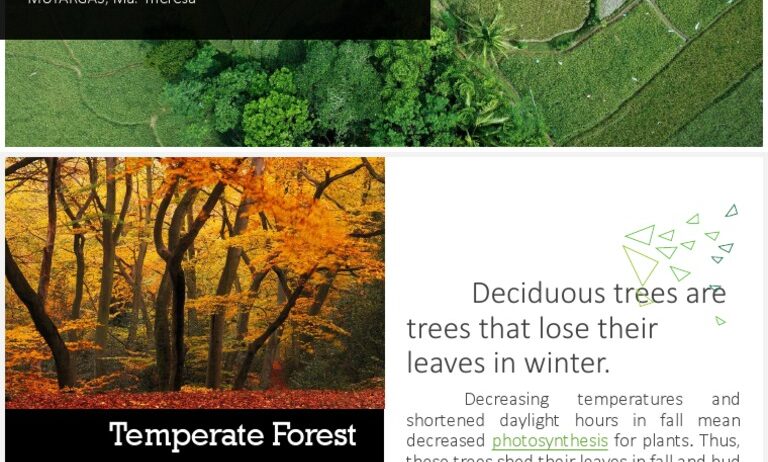
Temperate forests are among the most diverse and lush ecosystems on our planet. They are found in areas that experience four distinct seasons, characterized by temperate climates that typically present mild winters and warm summers. But have you ever wondered what makes their climate so unique? Let’s delve into the intricacies of the climate in a temperate forest, exploring the seasonal transitions, temperature variations, and other pivotal elements that contribute to its vibrant health.
The climate in temperate forests is defined by its moderate temperatures and adequate precipitation, making it a perfect habitat for a myriad of plant and animal species. Generally, these forests experience an annual temperature ranging from -30°F in the coldest months to as much as 86°F in the hottest months. This temperature variation is crucial, as it dictates the growth cycles of flora and fauna alike.
As one contemplates the seasonal characteristics, spring emerges as a poignant time of rejuvenation. During spring, temperatures begin to rise, facilitating an explosion of life. The frost recedes, enabling the blooming of various wildflowers and the budding of trees. This season stretches from March to June and often brings with it unpredictable weather patterns; occasional rain showers help to nourish the burgeoning plant life. Can you envision witnessing a carpet of enchanting wildflowers unfurling right before your eyes? It’s during this period that the forest becomes a playground of fresh green hues and the sounds of awakening wildlife fill the air.
However, this beauty comes with a challenge: spring can also usher in unpredictable storms, which might cause damage to newly sprouted vegetation. The biodiversity in these forests has adapted to such fluctuations, showcasing resilience by employing various survival strategies. For instance, many plants have developed deep root systems that help them withstand turbulent weather and extract moisture from deeper soil layers.
As we transition into summer, typically lasting from June to September, temperatures in temperate forests peak. Average temperatures may rise to around 70°F to 85°F, and the days stretch long, allowing ample sunlight to invigorate the thriving greenery. During this time, deciduous trees like oaks, maples, and beeches are in full foliage, creating a verdant canopy that provides habitat for countless species. Moreover, summer rainstorms often occur in the form of sudden, intense bursts, helping replenish the nutrients in the soil.
Yet, with increased temperatures comes the potential for droughts. How do these ecosystems combat such adverse conditions? Many temperate forest species, particularly trees, have adapted to conserve water through specialized mechanisms. Some trees have evolved thicker bark that helps to reduce water loss, while others can enter a state of dormancy during extreme heat, ultimately preserving their life force for better days. Their ability to adapt is astonishing and serves as a testament to the wonders of nature.
As summer wanes, the enchantment of autumn unfolds from September to November. This season signifies decay and rebirth, a beautiful metamorphosis as trees shed their vibrant leaves, creating a riot of color across the landscape. Average temperatures begin to decline, hovering around 60°F to 70°F. The fading sunlight and declining temperatures kickstart the nutrient recycling process, as fallen leaves contribute organic matter to the soil. This cycle not only enriches the ground but also supports new life the following spring.
Yet, this picturesque autumnal spectacle poses its own set of challenges. The falling leaves can create a thick blanket on the forest floor, which, if left unchecked, may lead to increased moisture retention and fungal growth, impacting the ecosystem negatively. Forest management strategies often involve controlled burns or selective harvesting to mitigate such issues while still preserving the forest’s integrity.
Winter descends from December to February, enveloping temperate forests in a tranquil silence. Average temperatures can drop to 20°F to 40°F, with snowfall creating a picturesque scene; a blanket of white transforms the lush greenery into a serene wonderland. The colder climate compels many animals to hibernate or migrate to warmer regions, showcasing the adaptability of life within these ecosystems.
During this austere season, one might wonder how life persists amid harsh conditions. The answer lies in dormancy. Many trees and plants enter a dormant state to reduce metabolic processes and conserve energy. Some species, like the red maple, can survive extended periods of cold, thanks to the natural antifreeze substances in their sap. Nature’s ingenuity continuously astounds us.
As we contemplate the climate of temperate forests, it is evident that each season presents a unique set of circumstances and challenges. From the vibrant blooms of spring to the stillness of winter, every phase serves a purpose in the grand tapestry of life. While the climate may evoke beauty, it also calls for stewardship. How can humans mitigate the challenges posed by climate change that threaten these delicate ecosystems? The interplay between human action and environmental health will dictate the future of temperate forests, making it imperative for us to engage in sustainable practices today.
In conclusion, the climate in a temperate forest is a dynamic amalgamation of temperatures and precipitation patterns that create a rich tapestry of life. By understanding and appreciating the delicate balance of this environment, we can foster a deeper connection to our planet and advocate for its preservation. The temperate forest climate is not just a backdrop; it is a vibrant character in the story of our world, full of intrigue and wonder. Will you take up the challenge to protect these vital ecosystems?