Nicaragua, a country characterized by its stunning natural beauty, is often celebrated for its breathtaking landscapes, rich biodiversity, and significant geological features, including an array of volcanoes. However, its climatic conditions form a critical backdrop for understanding the nation’s ecology, economy, and social fabric. This enchanting Central American nation exhibits a tropical climate, which is primarily influenced by its geographical location, elevation, and topography. Navigating through the climatic intricacies of Nicaragua reveals not just a tapestry of weather patterns but also the broader implications of climate change on the region.
The tropical climate of Nicaragua is fundamentally categorized into two distinct seasons: the dry season and the rainy season. The dry season, known locally as “verano,” typically spans from November to April. During these months, the sun reigns supreme, with minimal precipitation and balmy temperatures. Coastal areas bask in the warm embrace of the sun, while the interior experiences a blistering heat that can exceed 35 degrees Celsius (95 degrees Fahrenheit). Surfers flock to the Pacific beaches, where consistent waves provide an adrenaline rush against the backdrop of the fiery sun. Visitors are often enamored by the tropical breezes that relieve the intensity of the heat, particularly along the coastline.
Conversely, the rainy season, which stretches from May to October, dramatically transforms Nicaragua’s landscape. It’s a time when the heavens unleash their bounty, cloaking the verdant hills and rainforest with life-giving rain. This season witnesses a surge in humidity, and average temperatures hover around 28 degrees Celsius (82 degrees Fahrenheit), creating a lush environment that thrives on moisture. The dramatic transition from searing sunlight to torrential downpours alters the rhythm of life—for both the people and the environment. Agricultural activities ramp up, as farmers sow seeds, relying on the nourishing rains to cultivate staples like beans, maize, and coffee.
The coastal lowlands and equatorial regions of Nicaragua exhibit significant climatic variation due to topography. The Pacific lowlands experience hotter temperatures than the cooler Caribbean side, largely due to the trade winds that sweep in from the Pacific. This disparity lends itself to a unique microclimate, especially on the Caribbean coast, where rainfalls are more abundant and unpredictable. Here, the humidity blankets the atmosphere, creating an ecosystem rich in biodiversity, harboring rare species of flora and fauna that are only found in the lush, tropical rainforests.
Moreover, Nicaragua’s topographical diversity—from mountains and valleys to lakes and plains—contributes to its complex climatic conditions. The central highlands, particularly around cities like Matagalpa and Jinotega, benefit from a cooler temperate climate, creating ideal conditions for agriculture and coffee cultivation, as they’re situated at higher altitudes. With elevations over 1,200 meters (about 4,000 feet), these regions experience a different climate dynamic, influencing both local culture and economy. The famous Nicaraguan coffee, known for its rich flavor, thrives in this cooler, mountainous terrain, offering local farmers an economic lifeline.
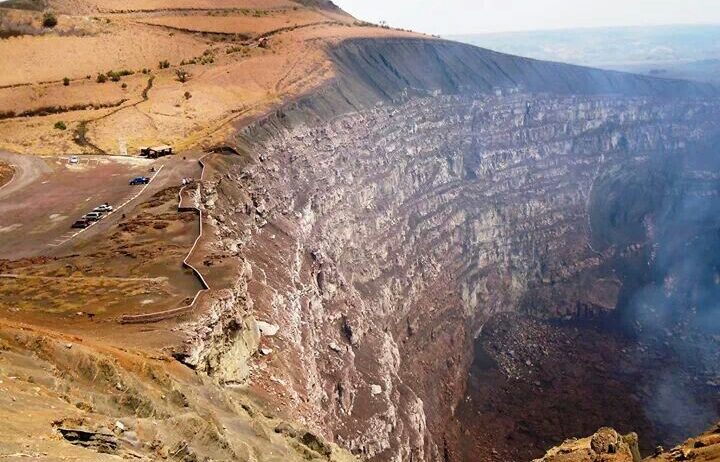
Significantly, Nicaragua is also home to several active volcanoes, including the iconic Masaya Volcano, which have a direct impact on local weather patterns. Volcanoes contribute to the fertility of the soil, giving rise to flourishing agriculture around their bases. However, volcanic activity can also lead to sudden changes in the climate by altering air quality and local temperatures. The eruptions can inject ash and sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere, leading to phenomena such as acid rain, which can have detrimental effects on both human health and agriculture. Such conditions create unique challenges that communities must navigate, making resilience a necessary quality for those living in the shadow of these geological giants.
The interplay between Nicaragua’s tropical climate and its volcanic activity has also introduced a delicate relationship between nature and human endeavors. With climate change looms large globally, Nicaragua faces pressing challenges, including rising temperatures, shifting precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events. These factors jeopardize the agricultural sector, which is predominantly rain-fed and highly susceptible to climate variability. The government and various organizations are now endeavoring to integrate sustainable practices and modern agricultural techniques that will bolster food security and mitigate the adverse effects of climate change.
Besides the immediate implications on agriculture and the economy, climate change poses dire threats to biodiversity and ecosystems in Nicaragua. Coral reefs along the Caribbean coast are at risk due to ocean acidification and rising temperatures, which could spell disaster for marine life and local fishermen who rely on healthy ecosystems for their livelihoods. Inland, shifting weather patterns may disrupt the delicate balance of tropical rainforests, highly sensitive to even slight temperature changes, leading to irrevocable losses in flora and fauna population.
In summation, the climate in Nicaragua—defined by its tropical breezes and volcanic mists—encapsulates a rich, dynamic interplay between environmental factors and human existence. As this nation navigates the dual challenges of preserving its stunning landscapes while confronting climate change, understanding the intrinsic links between climate and human activities is paramount. By recognizing the unique climatic attributes of Nicaragua, one gains not only a deeper appreciation of its geographical splendor but also insight into the urgent need for sustainable practices that champion the environment while fostering resilience in the face of inevitable climate-related challenges.