In the southwestern corner of Europe lies Portugal, a nation renowned for its stunning landscapes, rich history, and delectable cuisine. But perhaps the most alluring aspect is its climate, which graces its inhabitants and visitors alike with a delightful Mediterranean persona. When one thinks of Portugal, it conjures images of sun-drenched beaches bordering the Atlantic, yet there’s much more beneath the surface. What makes Portugal’s climate unique, and how does it embrace its Iberian charm?
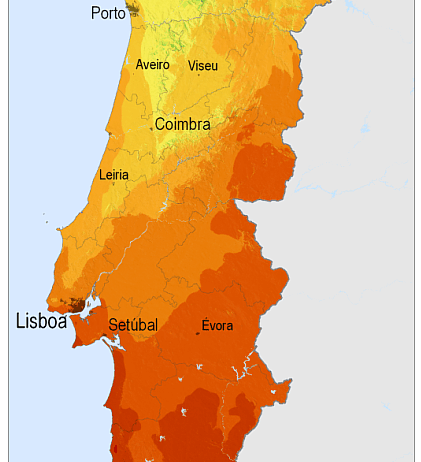
The climate in Portugal varies dramatically by region, influenced by both geographical features and ocean currents. Generally, the country can be classified into two predominant climatic zones: the Mediterranean climate to the south and the temperate maritime climate to the north. This dichotomy gives rise to diverse environmental phenomena that affect local flora, fauna, and human activities.
The southern region, particularly the Algarve, is characterized by a warm Mediterranean climate. Summers are typically hot and arid; temperatures frequently reach above 30 degrees Celsius (86 degrees Fahrenheit). The winters are mild, rarely dipping below 10 degrees Celsius (50 degrees Fahrenheit). Are you ready to bask in nearly 3,000 hours of sunshine per year? This region offers an enticing playground for beach lovers and sun-seekers. However, what happens when the sun becomes unrelenting, and the water levels begin to recede?
Conversely, the northern parts of Portugal, including Porto and Braga, experience a more temperate maritime climate. Here, winters can be cold and wet, and summers are often warm but moderated by the cooler Atlantic breezes. Rainfall is significantly higher in these areas, particularly between October and March, contributing to the lush green landscapes that Portugal is known for. The contrast between the arid south and the verdant north is striking, and one must wonder: how does this disparity affect the cultural practices and agriculture in each region?
Speaking of agriculture, it’s essential to appreciate how the climatic variations foster diverse agricultural practices throughout Portugal. The nation boasts a plethora of agricultural products ranging from olives and cork oak trees in the Alentejo to the famous Port wines of the Douro Valley. The idyllic weather conditions facilitate the growth of distinct crops, contributing to Portugal’s economic sustainability. As climate change progressively threatens agriculture worldwide, how can Portuguese farmers adapt to shifting weather patterns while maintaining their heritage?
Portugal’s coastline is another vital aspect influenced by its climate. Stretching over 800 kilometers (497 miles), it varies from the rugged cliffs of the Algarve to sandy bays and estuaries. The Atlantic Ocean plays a crucial role in tempering temperatures, renewable energy generation, and promoting biodiversity. Yet, the increasing frequency of extreme weather events such as storms and rising sea levels presents a formidable challenge. Are coastal communities prepared for the potential ramifications of climate-induced shoreline erosion?
Portugal’s climate not only showcases natural beauty but also supports a diverse array of ecosystems. Its unique geographical position at the confluence of continental and maritime influences creates habitats for numerous species, including the iconic Iberian wolf and endangered marine life. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these species, yet human encroachment and global warming threaten their existence. How can a balance be struck between development and ecological preservation?
Moreover, Portugal has begun taking steps towards sustainability by investing in renewable energy sources. With its abundant sunlight and wind, the country is a leader in renewable energy generation. Approximately 30% of its electricity comes from wind power, while solar energy has surged in recent years. However, the ambitious goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 presents a complex challenge. Can Portugal sustain its progress while tackling the socio-economic implications of such a revolutionary shift?
In terms of tourism, Portugal remains a magnet for travelers drawn by its favorable climate. From historical landmarks to vibrant nightlife, alongside its pristine beaches, the country attracts millions annually. These visitors contribute significantly to the economy, but there lies a heightened responsibility to manage tourism sustainably. How can Portugal continue to welcome tourists without compromising its cultural identity and environmental integrity?
As one explores the intricacies of Portugal’s climate, it becomes evident that it is a double-edged sword. The bountiful sun and moderate winters provide a rich environment for agriculture, tourism, and biodiversity, yet these benefits are accompanied by challenges like climate change and environmental degradation. Engaging local communities, government initiatives, and scientific research is paramount to developing effective strategies that safeguard the integrity of Portugal’s climate and its myriad advantages.
In conclusion, as we delve deeper into the nuances of what constitutes the climate in Portugal, we unveil layers of complexity that encompass both natural and human elements. While the sunny shores entice with promises of relaxation and exploration, the underlying challenges require thoughtful navigation. The journey toward a sustainable future for Portugal’s climate is an ongoing endeavor, and as stewards of our environment, the question remains: how committed are we to protecting the delicate balance that sustains this Iberian charm?