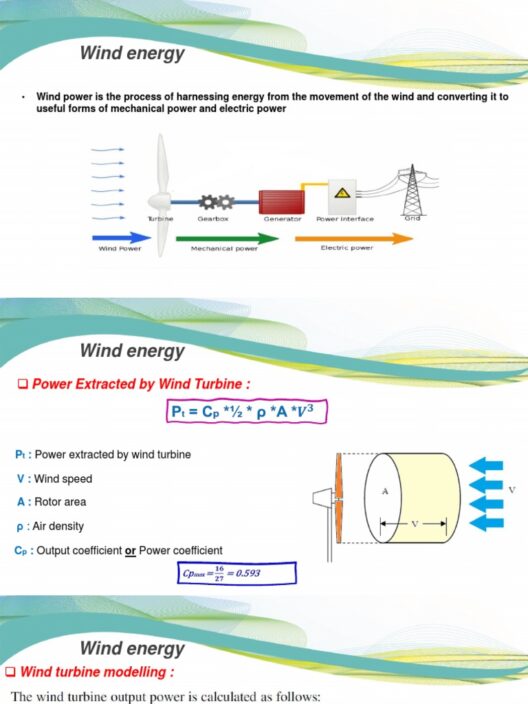
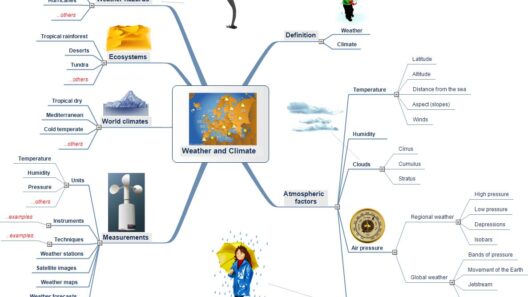
Neptune, the eighth planet in our solar system, stands as an enigmatic sentinel shrouded in deep azure hues. This gas giant, often referred to as an “ice giant,” captivates scientists and stargazers alike. But what constitutes the climate of such a distant world? A profound exploration into Neptune’s atmospheric phenomena reveals not only the intricate workings of its meteorological systems but also underlines our fascination with this unique celestial body.
The climate of Neptune is characterized by its frigid temperatures, fast-moving winds, and complex atmospheric dynamics. Observations reveal that Neptune’s atmosphere is predominantly composed of hydrogen, helium, and methane. The presence of methane is crucial; it absorbs red light, imparting the planet’s striking blue appearance. However, the atmospheric composition is merely one facet of Neptune’s climatic tapestry.
Temperatures on Neptune are staggering, with averages plummeting to around -214 degrees Celsius (-353 degrees Fahrenheit). This chilling environment raises questions: how does Neptune generate such extreme temperatures? Researchers speculate that, despite its distance from the Sun—approximately 30 times farther than Earth—Neptune radiates more internal heat than it receives from solar radiation. This internal energy contributes significantly to the planet’s dynamic weather systems.
The most remarkable feature of Neptune’s climate is its supersonic winds. Winds can reach speeds of up to 2,100 kilometers per hour (1,304 miles per hour), making them some of the fastest in the solar system. Such atmospheric turbulence is a subject of ongoing study, as it challenges our understanding of planetary atmospheres. The origins of these fierce winds remain somewhat elusive, but they are believed to be driven by the planet’s rapid rotation and the heat emanating from its core. This intriguing interplay between internal energy and rotational dynamics creates chaotic weather patterns that continue to bewilder astronomers.
Neptune’s weather is not just a matter of wind speed; it is also marked by violent storms and dynamic cloud formations. Observations have recorded massive storms, akin to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot, but distinctly clouded by methane. These storms can emerge from seemingly tranquil conditions and can last for many years, illustrating Neptune’s volatile temperament. The intricate dance of clouds in Neptune’s atmosphere is a spectacle of intertwining hues, revealing a world that is both beautiful and tempestuous.
One of the most striking phenomena observed on Neptune is the presence of large, dark spots within its atmosphere. These are believed to be storm systems that can evolve rapidly, appearing unexpectedly and sometimes dissipating just as quickly. The appearance of these spots is a prominent reminder of the planet’s ever-changing climate. Their unpredictability cultivates a sense of mystery, further deepening human curiosity about the processes at work on this remote world.
Furthermore, the seasonal changes on Neptune are a remarkable aspect worth mentioning. As Neptune orbits the Sun, its axial tilt allows for varying seasonal patterns, resembling the seasonal changes experienced on Earth, but on a much larger scale. Each season lasts approximately 40 Earth years due to Neptune’s long orbital period of 165 Earth years around the Sun. This prolonged cycle invites scientists to ponder the implications of such extended weather patterns on the planet’s atmospheric dynamics.
While Neptune is situated in a frigid realm, it harbors a rich and complex climate that invites inquiry into the broader aspects of planetary science. The ongoing study of Neptune’s atmospheric characteristics has far-reaching implications, not only for our understanding of gas giants, but also for the enlightenment it brings to climatological processes across the universe. How do the dramatic climatic conditions on Neptune compare to those on other planets? What universal principles govern the atmospheres of distant worlds? Each discovery regarding Neptune’s climate echoes in the corridors of planetary sciences and enhances our comprehension of celestial dynamics.
The fascination with Neptune transcends mere scientific inquiry; it speaks to a deeper yearning to comprehend the vast complexities of our universe. Observing such extreme climates invites reflections on climate processes that shape our own planet. The study of Neptune can serve as a lens through which we consider the implications of climate change on Earth. Indeed, the relationship between internal processes and external conditions mirrors the challenges posed by climate change within our own atmosphere. The rapid changes observed on Neptune may mirror the alarming rate at which our climate is evolving.
In conclusion, the climate of Neptune represents a labyrinth of complexities and wonders—a stark contrast to the serene beauty we perceive from afar. The interplay of icy temperatures, ceaseless winds, and vibrant storms not only defines this ice giant but compels humanity to look both inward and outward. As guardians of our own planet’s future, it becomes increasingly essential to appreciate the vastness and variability of climates beyond Earth. Understanding Neptune’s atmosphere and its mysteries provides not only insights into planetary science but also urges a deeper commitment to preserving the delicate atmospheric balance here at home. Our journey of exploration continues, as does our responsibility to foster a sustainable environment on our own blue planet.