The climate of the Northeast region of the United States is characterized by a diverse array of weather phenomena, seasonal transformations, and coastal influences that together create an intricate tapestry of environmental conditions. Ranging from the warm, humid summers to the frigid, snow-laden winters, the Northeast’s climate presents a captivating study in contrasts and variances shaped by geographical and natural elements.
Firstly, a hallmark feature of Northeast temperate climate is its four distinct seasons. Spring emerges with a rejuvenating freshness, generally in March, inviting flora and fauna to emerge from their winter dormancy. The melting of snow and the increasing warmth foster an environment rich with budding trees and blossoming flowers. However, this period also gives way to unpredictable weather patterns, often characterized by fluctuating temperatures and unexpected late-season snowstorms. The variability can at times be surprising for residents, echoing a complex interplay between lingering winter influences and the incipient warmth of prolonged sunlight.
As spring cedes to summer, the Northeast experiences a formidable rise in temperatures. June through August signifies a time when humidity levels soar, resulting in sweltering days that can culminate in intense thunderstorms. The prevalence of these storms is largely attributable to the coastal weather patterns, which are driven by the Atlantic Ocean’s temperate waters. These storms can be both awe-inspiring and treacherous, creating a vivid contrast to the serene summer days. It is during this season that the natural splendor of the region is on full display, with bustling beaches and verdant parks drawing both locals and tourists alike.
Transitioning into fall, the climate of the Northeast takes on a picturesque quality as foliage transforms into vibrant hues of red, orange, and yellow. September through November brings cooler temperatures and the first indications of frost. This seasonal metamorphosis is not only a visual spectacle but also serves as a reminder of the cyclical nature of the environment. Autumn harvests, particularly in rural areas, celebrate agricultural productivity and resilience, showcasing local crops. This profound interaction between the seasons and agriculture underscores the intrinsic link between climate and community.
Winter in the Northeast can be formidable, characterized by cold temperatures, significant snowfall, and arctic air masses sweeping down from Canada. December through February envelops the region in its chilling embrace, with snowstorms called Nor’easters blanketing cities and countryside alike. These storms can create hazardous conditions, impacting transportation, infrastructure, and daily life. Yet, there lies an intrinsic beauty in the starkness of winter; the stillness and serene landscapes evoke a sense of solitude and introspection.
Each season harbors its own set of perplexing weather patterns shaped by numerous coastal influences. The Atlantic Ocean plays an integral role, affecting temperatures and precipitation levels through its currents and proximity. The Gulf Stream, in particular, moderates the climate along the coastal areas, contributing to milder winters and warmer summers. Conversely, coastal regions may also bear the brunt of extreme weather events, including hurricanes, which can wreak havoc on communities. The ocean’s temperamental nature serves as a reminder of the forces wielded by the natural world.
The interplay between land and sea is paramount. The northeastern coastline features a distinctive topography that includes cliffs, sandy beaches, and salt marshes. These geographical features not only influence local climatology but also serve as critical ecosystems that support diverse marine and terrestrial life. Coastal marshes, in particular, serve as valuable buffers against erosion and flooding, showcasing the intricate interactions between climate, ecology, and community resilience.
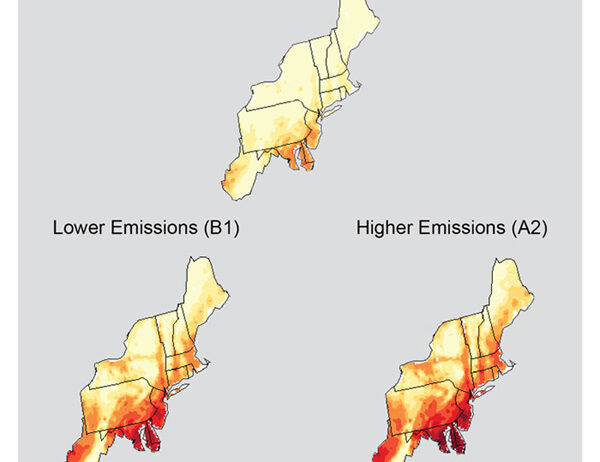
This relationship is further complicated by climatic shifts stemming from global phenomena such as climate change, which introduces new dynamics into the established climate patterns of the Northeast. Rising sea levels threaten coastal communities, while increased temperatures may alter precipitation patterns and the timing of seasonal events, known as phenology. Observations of changing flowering times or migratory patterns reflect the sensitivity of the ecosystem to these alterations. Moreover, warmer winters can lead to reduced snowfall, impacting water resources and altering hydrology across the region.
One also cannot overlook the social and cultural implications of these climatic changes. The Northeast has a rich historical context that intertwines with its climate, from indigenous practices of seasonal harvesting to today’s urban gardens and local food movements. Communities are compelled to adapt as climatic changes force them to reevaluate historical practices and embrace sustainability. The fascination with the Northeast’s climate goes beyond mere observation; it delves into the challenges faced and the resilience demonstrated by its inhabitants in the face of formidable environmental changes.
Consequently, the climate of the Northeast is not merely a stagnant feature to be cataloged; it is a dynamic entity that undergoes continual transformation. From the harsh realities of winter to the vibrant life of summer, the region’s climate serves as a profound reflection of broader ecological phenomena. Understanding these intricate interactions offers valuable insights, not only into the natural world but also into humanity’s place within it, ultimately reminding us of the interdependence between our actions and the environment that sustains us.
In conclusion, the diverse climate of the Northeast presents an engaging subject that encompasses seasonal changes and coastal influences. Each season bestows a unique character upon this region, while also representing an ongoing dialogue between human life and environmental conditions. These interactions serve as a testament to the beauty and complexity of our world, urging a contemplative approach to understanding and addressing the challenges posed by a changing climate.