The complexities surrounding climate change frequently lead to misunderstandings, particularly when it comes to the terms “greenhouse effect” and “global warming.” Both concepts are undeniably linked and often used interchangeably by the public. However, they encapsulate different phenomena within the broader discourse of environmental science. This article aims to delineate these two crucial concepts and unravel their interconnections and implications on our planet.
Understanding the Greenhouse Effect: Nature’s Thermostat
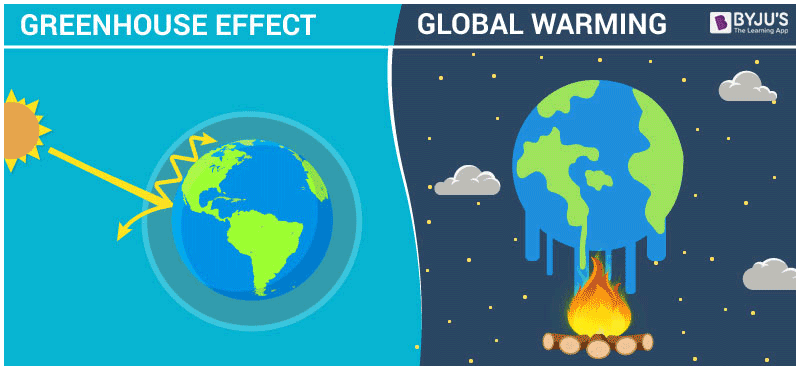
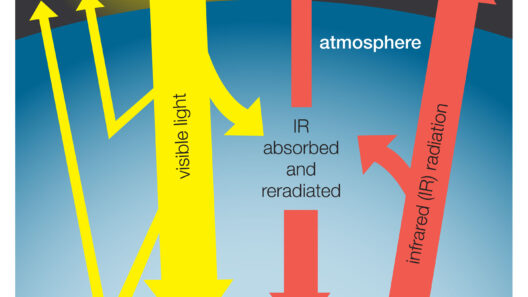
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. When the Sun’s energy reaches the planet, certain gases in the atmosphere trap heat, preventing it from escaping back into space. These gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor. Collectively, they are termed greenhouse gases (GHGs) due to their crucial role in maintaining the Earth’s temperature.
Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth would be inhospitably cold, with average surface temperatures plummeting to about -18 degrees Celsius (0 degrees Fahrenheit). The atmospheric layers, particularly those rich in greenhouse gases, act like a blanket, keeping the planet warm enough to sustain life. This delicate balance is essential for ecological systems, agriculture, and human societies. Over millennia, the greenhouse effect has allowed life to flourish by shaping climates and weather patterns.
Yet, this natural process becomes problematic once human activities emit excess greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, mainly through the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial activities. Understanding this balance is critical, as the uncontrolled increase of GHGs leads us to the core of another perilous reality—global warming.
The Phenomenon of Global Warming: The Escalation of Climate Crisis
Global warming refers specifically to the long-term rise in Earth’s average surface temperature, primarily due to human-induced increases in greenhouse gas concentrations. While the greenhouse effect is natural, global warming is largely anthropogenic, meaning it arises from human actions. The phenomenon has become a clarion call for urgent environmental action, serving as a stark reminder of the repercussions of our industrialized lifestyles.
Since the late 19th century, the Earth’s average temperature has risen about 1.2 degrees Celsius (2.2 degrees Fahrenheit), with most of the increase occurring in the last few decades. The processes driving global warming usually stem from excessive emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse gases, which significantly amplify the greenhouse effect.
The consequences of global warming are increasingly alarming. From severe weather changes—from heatwaves to hurricanes—to the melting of polar ice caps, the ramifications affect every continent and ecosystem on Earth. Rising sea levels threaten coastal cities and biodiversity, while heatwaves compromise agricultural productivity and human health. Social and economic structures are now under threat, making global warming not just an environmental issue but a pressing global concern.
Distinguishing Between Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming: A Clarion Call for Clarity
While both the greenhouse effect and global warming are connected through greenhouse gases, distinguishing the two is paramount for fostering understanding and motivation toward climate action. The greenhouse effect is a necessary mechanism that maintains life, whereas global warming acts as a buzzing alarm bell, signaling that humanity is pushing this natural equilibrium beyond its limits.
One might compare the greenhouse effect to a car’s heating system. While it provides warmth during cold weather, an excessive output—much like harnessing fierce fossil fuels—could lead to overheating, rendering not just the car but also its occupants uncomfortable or even in peril. Recognizing this semblance clearly illustrates the intricate dynamic between natural processes and human influence.
The Environmental Challenge: The Road Ahead
As the debate intensifies over climate change policies and their implications for future generations, addressing the difference between the greenhouse effect and global warming serves as a stepping stone toward effective action. Education and awareness play vital roles in catalyzing movement toward solutions. Understanding that the greenhouse effect, while natural and necessary, can morph into global warming under certain conditions instills a sense of responsibility in individuals and policymakers alike.
Efforts worldwide are ramping up to mitigate these threats. Renewable energy sources, carbon capture technologies, afforestation, and implementing more efficient energy use showcase humanity’s capacity to tackle the challenges of climate change. However, overcoming the inertia may require a shift in our perception and values. By transcending the barriers of confusion surrounding these terms, there exists an opportunity for collective action—and this can lead toward a sustainable future.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between the greenhouse effect and global warming is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world implications. As the planet grapples with escalating climate crises, grasping these concepts provides clarity. It empowers individuals, communities, and nations to think critically about their contribution to the larger ecological narrative. The discourse surrounding climate change is complex yet remarkably vital. Individuals who engage with and advocate for climate literacy stand at the forefront of the fight against global warming, bridging the gap between knowledge and action. As the urgency amplifies, so must our resolve to effect change for the Earth and generations to come.