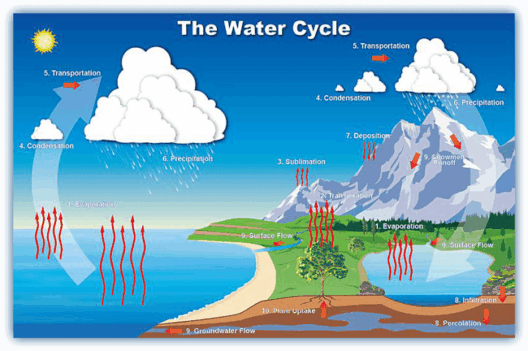
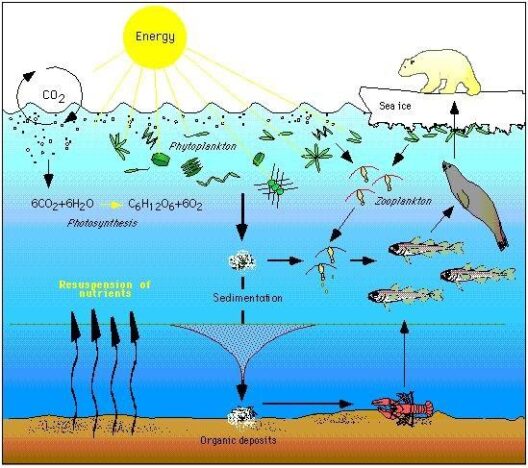
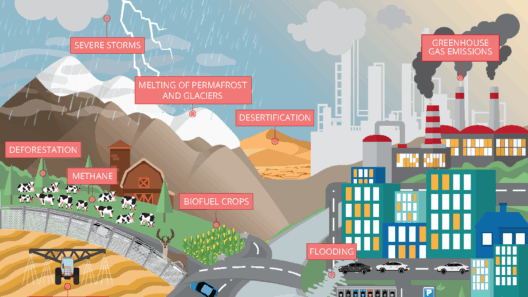
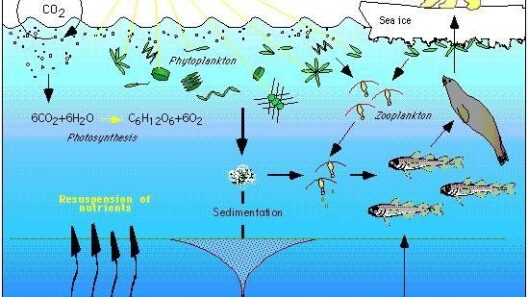
The acknowledgment of climate change as an existential threat catalyzed a surge in governmental action across the globe, with the year 2025 serving as a crucial juncture for evaluating the initiatives undertaken by various nations. Diverse schemes and agreements, often characterized by their ambitious targets, have emerged. This review meticulously examines the multifaceted strategies employed by governments in their quest to mitigate climate change, each offering distinct elements and insights.
At the crux of governmental efforts lies the adoption of international treaties aimed at curbing greenhouse gas emissions. Notably, the Paris Agreement remains a landmark accord stipulating that signatory nations commit to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, striving for 1.5 degrees where feasible. In 2025, many countries have pledged to update their nationally determined contributions (NDCs), reflecting more rigorous emission reduction targets. Nations have begun implementing sector-specific frameworks to align with these targets, such as transitioning to renewable energy sources and enhancing energy efficiency within industrial sectors.
Moreover, the implementation of carbon pricing mechanisms has gained prevalence. Such frameworks include both carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems, effectively assigning a financial cost to carbon emissions. By incentivizing corporations and individuals to reduce their carbon footprints, these mechanisms are positioned as pivotal tools in driving down emissions. Governments across Europe and North America have increasingly relied on these financial levers, facilitating a transition toward greener alternatives. As industries grapple with the additional costs associated with carbon emissions, innovation becomes imperative, fostering advancements in clean technologies and sustainable practices.
In recent years, substantial investments have been funneled into renewable energy projects. Governments have primarily targeted solar, wind, and hydropower initiatives, recognizing their potential to displace reliance on fossil fuels. For instance, ambitious offshore wind projects have emerged in coastal regions, transforming how energy is sourced and generated. Governments have also forged public-private partnerships to accelerate research and development in renewable technologies, underscoring the recognition that collaboration is essential to achieving net-zero goals.
Beyond energy production, governments have turned their attention to enhancing climate resilience and adaptation measures. As extreme weather events become more pervasive due to climate change, policies addressing infrastructural resilience have become paramount. In 2025, various nations implemented strategies to reinforce urban infrastructure, such as improving drainage systems to mitigate flooding and constructing buildings designed to withstand increasingly volatile weather conditions. These adaptations are vital to safeguard both human life and economic stability in the face of ecological upheavals.
The agricultural sector has not been left untouched, with governments increasingly recognizing the interplay between farming practices and climate dynamics. Sustainable agriculture initiatives have been introduced, promoting practices that bolster soil health, reduce methane emissions from livestock, and encourage crop diversity. Governments have offered financial incentives for farmers adopting regenerative practices, fostering a symbiotic relationship between food production and environmental stewardship. This integration holds the promise of not only enhancing crop yields but also contributing to carbon sequestration efforts.
However, governmental action cannot be assessed in isolation from the social dimension of climate change policies. The implications of such initiatives ripple through communities, often necessitating a careful balancing act between economic interests and environmental responsibilities. In 2025, the emphasis on a just transition has become salient, highlighting the importance of ensuring that those most affected by climate policies—typically marginalized communities—receive the necessary support and opportunities to participate in the green economy.
Education and public awareness campaigns have surged, aiming to cultivate a climate-conscious populace. Governments have launched initiatives to educate citizens about the urgency of climate action, encouraging grassroots movements and fostering community involvement. The recognition that societal engagement is critical to the success of climate policies underpins these efforts, demonstrating a comprehensive approach to generating momentum for climate initiatives.
Critically, technological advancements have played a transformative role in how governments address climate change. The proliferation of innovative technologies, from smart grids and energy storage solutions to carbon capture and storage (CCS) mechanisms, has revitalized governmental efforts. These technologies facilitate the efficient distribution and consumption of energy while concurrently reducing the carbon intensity of various sectors. As governments continue to prioritize research and development, the potential for sustainable technological breakthroughs becomes increasingly pronounced.
Nonetheless, challenges persist as governments navigate the complexities of climate action. Disparities in policy implementation and financing pose significant hurdles to achieving cohesive global progress. The need for equity in addressing climate change is paramount, as developing nations often face barriers in financial resources and technological access compared to their developed counterparts. This necessitates international cooperation and support mechanisms that enable all nations to contribute meaningfully to combating climate change.
As the year unfolds, it becomes increasingly evident that governments are undertaking a multitude of initiatives aimed at addressing climate change comprehensively. From international agreements to local adaptation strategies, the spectrum of actions reflects a growing recognition of the urgency of the climate crisis. Progress has been made, yet the scale of the challenge ahead demands an unwavering commitment to innovation, collaboration, and inclusivity. It is through a concerted effort that lasting change can be realized, ensuring a sustainable and resilient planet for future generations.