The greenhouse effect is a crucial mechanism that influences Earth’s climate by regulating temperatures and creating a stable environment conducive to life. While it is a natural phenomenon, human activities have exaggerated this effect, leading to global consequences. Understanding the intricacies of the greenhouse effect is essential for comprehending how it shapes Earth’s climate.
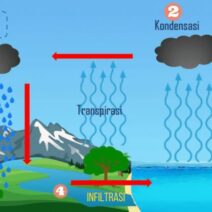
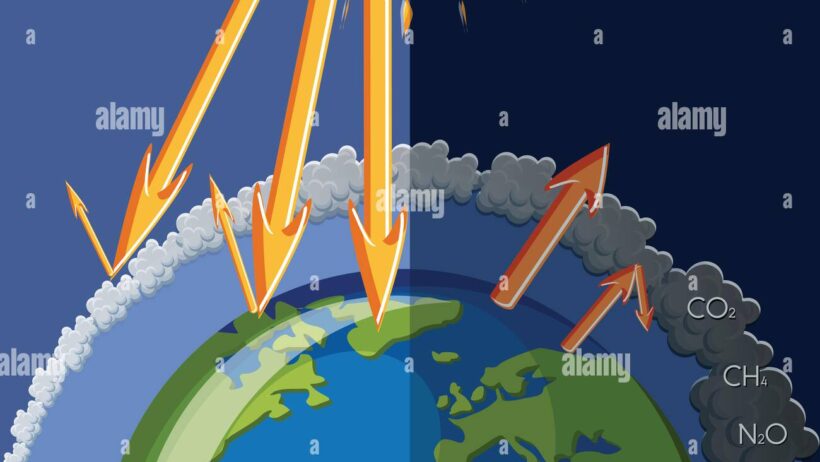
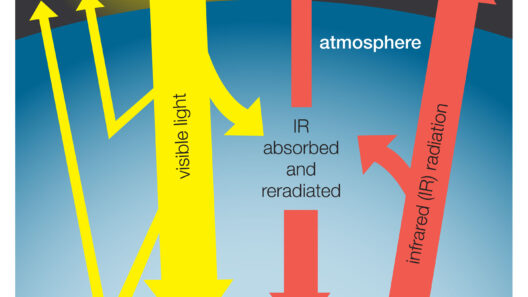
At its core, the greenhouse effect involves the planet’s atmosphere capturing and retaining heat from the sun. This process is vital, preventing the Earth from becoming a frozen wasteland. The sun emits solar radiation, which passes through the atmosphere and reaches the surface of the Earth, warming it. Some of this heat is then re-radiated back into space. However, certain gases in the atmosphere—known as greenhouse gases—act like a barrier, retaining a portion of this heat and hence warming the planet. This balance is essential, but it can be disrupted.
Understanding Greenhouse Gases: The Key Players in Climate Regulation
Carbon dioxide is perhaps the most recognized greenhouse gas. It is released through processes such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and various industrial processes. Surprisingly, while CO2 has a significant impact on climate change, its concentration in the atmosphere is only one part of the puzzle. Methane, although less prevalent, is arguably more potent. Its ability to trap heat is over 25 times that of CO2 over a 100-year period. Methane emissions arise from agricultural practices, landfills, and livestock management.
Nitrous oxide emerges from agricultural activities, particularly the use of synthetic fertilizers. Additionally, water vapor is often overlooked, but it is the most abundant greenhouse gas and plays a pivotal role in the natural greenhouse effect by amplifying the effects of other gases. Understanding the sources, concentrations, and effects of these gases is critical in grasping the broader implications of climate change.
The Mechanics of the Greenhouse Effect: How Heat is Captured
This dynamic creates a natural insulation layer around the planet, stabilizing temperatures throughout the year. The critical aspect of this process lies in the balance of incoming solar energy and outgoing infrared energy. Without greenhouse gases, Earth’s average temperature would plummet to around -18 degrees Celsius (0 degrees Fahrenheit), rendering the planet inhospitable.
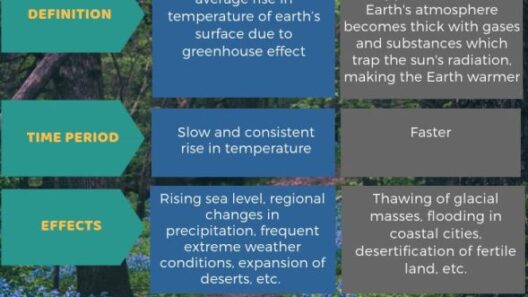
However, the increasing concentration of greenhouse gases due to human activities has intensified this effect, leading to what is commonly referred to as anthropogenic climate change. The rise in global temperatures is not uniform, manifesting through extreme weather events, changing precipitation patterns, and melting polar ice caps.
The Dire Consequences of an Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
Additionally, an altered climate exacerbates weather patterns, leading to more intense storms, droughts, and heatwaves. Agricultural sectors face significant challenges as crops become vulnerable to unpredictable weather conditions, threatening food security across the globe. The impact of climate change is not just an environmental concern; it is a socio-economic issue that affects livelihoods, health, and international stability.
Moreover, biodiversity is under threat. As ecosystems struggle to adapt to rapid climate changes, species extinction rates are escalating. The delicate balance of life is threatened, demanding immediate action to mitigate these changes and protect our planet’s ecological heritage.
Strategies for Mitigating Climate Change: A Collective Responsibility
For individuals, lifestyle changes such as reducing waste, using public transportation, and consuming locally sourced foods can make a significant impact. Community engagement and education play a vital role in fostering an informed public that advocates for sustainable practices and policies.
International cooperation is paramount. Global accords like the Paris Agreement aim to unite nations in combating climate change, emphasizing the need for collective action. Adopting policies to limit greenhouse gas emissions and enhance carbon sequestration techniques—such as afforestation—can help restore the balance that sustains life on Earth.
The greenhouse effect is intricately linked to the well-being of our planet. It fosters life but requires careful stewardship. Acknowledging the delicate balance between natural processes and human influences is crucial in shaping a sustainable future for generations to come. Understanding the greenhouse effect empowers us to take informed actions, urging society to embrace innovative solutions that mitigate its impacts, ensuring a healthier planet for all.