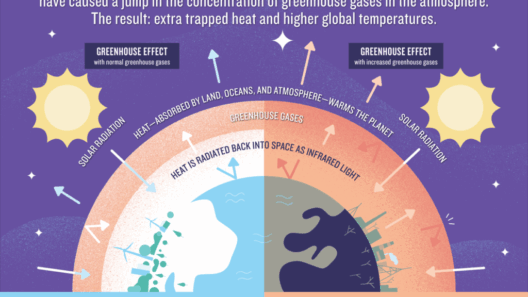
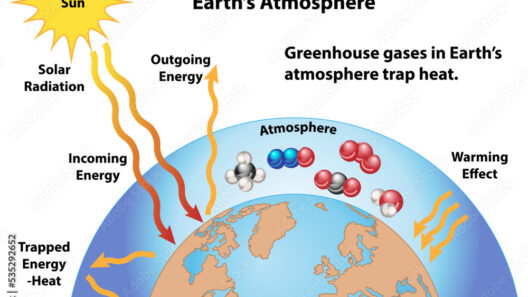
The greenhouse effect is one of the most critical natural phenomena influencing our planet’s climate and ecosystems. It is produced by a complex interplay of greenhouse gases (GHGs), which trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, thereby regulating temperatures conducive to life. Understanding the mechanics of this effect, particularly in the context of growing concerns about climate change, is essential for policymakers, environmental advocates, and the general public alike.
Greenhouse gases are constituents of the atmosphere that have the unique ability to absorb and emit infrared radiation, leading to the greenhouse effect. The most prevalent GHGs include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). Each of these gases plays a distinctive role in trapping heat and contributes differently to climate change. The warming capacity of these gases is measured through a metric known as global warming potential (GWP), which compares the warming potential of a gas relative to CO2 over a specified time period.
As the concentration of these gases increases due to anthropogenic activities, the balance of the natural greenhouse effect is disrupted, leading to warming trends that are detrimental to our environment.
Understanding the fundamental mechanics of the greenhouse effect and its impact on our climate is imperative. Here we unravel the layers of this phenomenon to reveal how greenhouse gases operate and their implications on global warming.
Grasping the science behind the greenhouse effect provides clarity on how human activity exacerbates climate instability. Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth would be inhospitably cold, but with excessive levels of greenhouse gases, we’ve entered a perilous state of overheating. Our planet’s average surface temperature has already risen, stressing the need for comprehensive understanding and urgent measures to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
The role of carbon dioxide in climate regulation cannot be understated. It is primarily emitted through the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and various industrial processes. In addition to its natural presence in the atmosphere, the anthropogenic contribution has elevated CO2 levels significantly. This increase leads to a stronger greenhouse effect, enhancing global warming and resulting in climate phenomena such as extreme weather events, sea-level rise, and shifts in biodiversity.
Methane, on the other hand, is a potent greenhouse gas that, although shorter-lived than CO2, is considerably more effective at trapping heat—over 25 times more potent in a 100-year time horizon. Major sources of methane include agriculture (especially livestock), landfills, and the oil and gas industry. The rise in global temperatures accelerates the release of methane from natural sources, such as permafrost and clathrates, further exacerbating the issue and creating a feedback loop that accelerates climate change.
It is also essential to highlight nitrous oxide, predominantly emitted from agricultural processes and the combustion of fossil fuels. While it constitutes a smaller fraction of greenhouse gases compared to CO2 and methane, it possesses a GWP almost 300 times greater than that of CO2. This signifies that even small increases in nitrous oxide can have pronounced effects on the greenhouse effect, underscoring the intricacies of agricultural practices that may unwittingly contribute to climate change.
The dynamics of greenhouse gases extend beyond mere presence in the atmosphere; they interact with other environmental phenomena. Their cumulative effect not only leads to higher global temperatures but also exacerbates ocean acidification, disrupts agricultural patterns, and induces species migration. The implications are far-reaching, affecting human livelihoods, ecosystems, and overall planetary health.
As awareness surrounding the greenhouse effect and climate change grows, key buyer concerns emerge about energy consumption, agricultural practices, and corporate accountability. There is a pressing need for transparency from businesses regarding their carbon footprints and initiatives aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable practices are increasingly becoming focal points of consumer demand. Buyers are more inclined to favor companies and products that adopt eco-friendly practices and demonstrate a commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Policy initiatives aiming to curb greenhouse emissions are gaining momentum globally. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, serve as a framework for countries to commit to reducing their carbon footprints. Governments are encouraged to invest in renewable energy sources, enhance energy efficiency, and promote sustainable agriculture and forestry practices. Public engagement and education play a crucial role in galvanizing support for these measures, building pressure on corporations and governments to act.
The discourse around renewable energy has significantly escalated in recent years. Transitioning to solar, wind, and other renewable energies can substantially decrease reliance on fossil fuels, thereby mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. The evolution of technology and innovation will be critical to developing solutions that harness clean energy and thus significantly reduce the GHG burden.
Ultimately, addressing the greenhouse effect and its associated challenges requires a multifaceted approach. Increased public awareness, supportive regulatory frameworks, and a commitment to sustainable practices from both individuals and corporations will pave the way for meaningful change. Continuing research into innovative solutions while fostering collective awareness can perhaps fashion an effective response to one of the most pressing issues of our time: climate change.
In conclusion, comprehending the greenhouse effect not only elucidates the mechanics of climate change but also underscores a collective responsibility to act decisively. The interplay of greenhouse gases poses a threat not just to biodiversity but to human existence. By promoting sustainability and holding stakeholders accountable, we can forge a path toward a healthier planet.