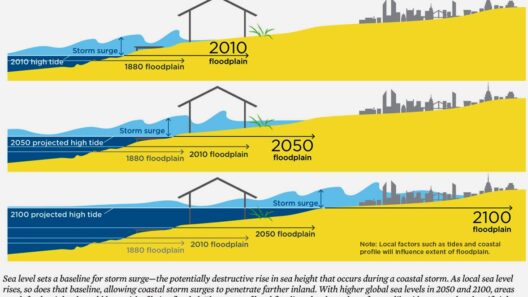
Rising sea levels present a formidable challenge for global society, manifesting in a myriad of environmental, social, and economic consequences. As the planet warms, glaciers and polar ice caps melt, and thermal expansion of seawater contribute to the steadily increasing sea levels that encircle our coastlines. This issue does not merely threaten picturesque beach destinations; its impact is comprehensive, reverberating through ecosystems, communities, and economies worldwide.
Understanding the nuances of rising sea levels requires delving into the specific environmental consequences that serve as harbingers of change. One of the most glaring effects is coastal erosion, a natural process exacerbated by the encroaching tide. As sea levels rise, shorelines are gradually altered, with significant loss of land in low-lying areas. This erosion transforms not just the geography but also the habitats of countless species. Dunes, wetlands, and estuaries, which serve as essential buffers against storm surges and natural disasters, are being compromised. Consequently, the biodiversity that relies on these ecosystems grows increasingly vulnerable, ultimately leading to habitat loss and shifts in species distribution.
Moreover, the intrusion of saltwater into freshwater sources is a critical issue, affecting both ecosystems and human communities. The salinization of aquifers undermines the quality of drinking water and agriculture, which relies on fresh water supply for irrigation. Saline intrusion poses a severe threat to food security in regions where agriculture has thrived for generations. In turn, diminished agricultural output furthers the cycle of vulnerability and scarcity that beleaguers many coastal communities.
As environmental detriments manifest, the social consequences associated with rising sea levels become unmistakable. Communities situated along coastlines face displacement, often referred to as “climate refugees.” The term denotes populations forced to vacate their homes due to the encroaching sea and increased frequency of extreme weather events. This forced migration strains urban infrastructures and social services in inland areas, leading to potential conflicts and exacerbating existing societal inequities. Relocation is not merely a movement of people; it entails a significant cultural upheaval, as communities grapple with a loss of heritage and identity.
Furthermore, the impact of rising sea levels on human health cannot be understated. Increased flooding exacerbates health risks through waterborne diseases, necessitating a robust examination of public health infrastructure. Vulnerable populations may lack access to health services, making them more susceptible to ailments related to these changes. As stagnant water becomes a breeding ground for pathogens, there is an urgent need for investments in preventive health measures, especially in frontline communities.
The economic ramifications of rising sea levels are equally staggering. Coastal towns heavily reliant on tourism industry are witnessing tangible declines as beaches erode and landscapes change. The real estate market also feels the tremors of this shift, with property values in high-risk areas plummeting. Insurance premiums rise as risks associated with flooding become widely recognized. In turn, local governments must contend with reduced tax revenue, limiting their capacity to address infrastructure issues or to fortify defenses against rising waters.
Significantly, the long-term outlook for global commerce is altered in light of rising sea levels. Ports and shipping lanes, which are vital components of international trade, face threats from increased flooding and hurricanes. Therefore, businesses must adapt to changing conditions, requiring investment in climate-resilient infrastructure. Logistics and supply chains may be disrupted, with potential cascading effects across markets that reverberate well beyond coastal territories.
To combat the multifaceted challenges posed by rising sea levels, adaptive strategies are imperative. Governments must prioritize sustainable urban planning that incorporates climate change preparedness, ensuring infrastructure is fortified to withstand increased flooding. Green spaces, such as wetlands and mangroves, can serve as natural defenses against sea-level rise, while also providing vital ecosystems that enhance biodiversity.
Engagement with local communities is crucial in crafting effective policies to mitigate the impacts of rising sea levels. Education and awareness initiatives can foster a sense of responsibility and encourage proactive measures that reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Collective action, especially among vulnerable communities, can galvanize support for policies that prioritize resilience and sustainability.
As global temperatures continue to rise, the necessity of understanding and addressing the consequences of rising sea levels cannot be ignored. Awareness and action are key to safeguarding our coastal environments and the communities that depend on them. The intricate interplay of environmental, social, and economic factors requires a comprehensive approach that not only addresses immediate concerns but also embraces long-term solutions.
Ultimately, rising sea levels are not merely a distant theoretical problem; they are a present-day reality that necessitates an urgent response. As we work towards sustainable practices and innovative solutions, it becomes evident that the fight against climate change cannot be won in isolation. It is a collective journey that will define the resilience of our planet and the future of generations to come.