The Law of Conservation of Energy is a fundamental principle in physics and a cornerstone of our understanding of the natural world. This law stipulates that energy cannot be created or destroyed but merely transformed from one form to another. It resonates deeply within various fields, from mechanical systems to ecological processes, shaping the way we perceive energy dynamics in our daily lives.
As humans, we engage with energy in multifaceted ways, often taking its presence for granted. For some, the intrigue lies in the ceaseless transformation of energy forms around us. Why does a car’s engine convert fuel into motion? How does a tree transform sunlight into the energy that sustains life? These examples prompt us to reflect on our energy consumption practices, urging a deeper understanding and appreciation of conservation.
Exploring the ubiquitous manifestations of the Law of Conservation of Energy reveals not only scientific marvels but also practical implications for energy conservation in our modern world.
Transformation and Transience: Energy in Motion
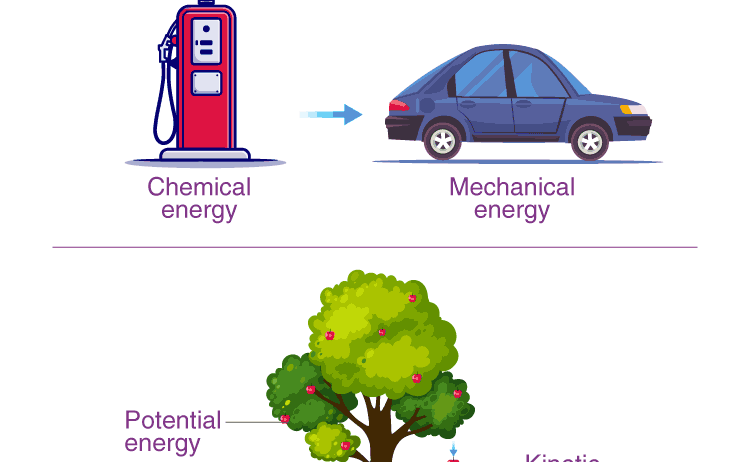
One of the most palpable illustrations of energy conservation can be seen in mechanical systems, where kinetic and potential energy interchange seamlessly. Consider a roller coaster: as the car ascends, kinetic energy is converted into potential energy, reaching a peak. Upon descent, potential energy metamorphoses back into kinetic energy, propelling the riders with thrilling velocity. This cycling between energy forms is a testament to the steadfast law that governs such systems.
In everyday applications, automobiles serve as commonplace entities embodying this conservation principle. Gasoline fuels a car, and in essence, the chemical energy stored in the fuel is transformed into kinetic energy as the vehicle accelerates down the highway. However, not all of that energy is utilized effectively; friction and other forces dissipate some energy, which is why energy-efficient vehicles are becoming increasingly vital. They are designed to maximize energy transformation efficiency, reducing overall consumption and environmental impact.
A Breach into Biology: Photosynthesis as an Energy Alchemist
Shifting from mechanical to biological systems, we find another remarkable illustration of the Law of Conservation of Energy in the process of photosynthesis. This complex biochemical reaction occurs in plants, wherein solar energy is harnessed to transform carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. In essence, the radiant energy from the sun is transmuted into chemical energy stored in the bonds of glucose molecules, a food source for the plant and other organisms in the food chain.
This transformation showcases a crucial aspect of energy conservation—a phenomenon vital for life on Earth. Plants serve as the foundation of terrestrial ecosystems, directly capturing solar energy and converting it into a usable form for countless life forms. The energy thus accumulated keeps the ecological wheels turning, underpinning interactions between species, from herbivores to apex predators.
Urban Insights: The Shift from Conventional to Renewable Energy
The implications of energy conservation extend beyond natural phenomena into the urban landscape. Cities and communities are now recognizing the need to adopt renewable energy sources to mitigate environmental degradation. Wind and solar energy epitomize this shift from conventional fossil fuels to more sustainable forms of energy harnessed from nature’s bounty.
Wind energy illustrates the conservation principle beautifully. Wind turbines convert kinetic energy from wind into mechanical energy, which in turn generates electricity. This transition from mechanical to electrical energy showcases how environmental resources can be transformed rather than consumed entirely. Furthermore, the shift towards renewable energy not only epitomizes the conservation of energy but also highlights the necessity for sustainable practices to reduce carbon footprints and conserve the planet’s natural resources.
Behavior and Energy: Daily Practices and Conservation Measures
On a more personal level, everyday actions such as turning off lights and unplugging devices when not in use exemplify the broader concept of energy conservation. While these actions may seem trivial, they contribute to a larger tapestry of energy efficiency in households. Each time individuals take proactive steps to manage their energy consumption, they play an integral role in conserving energy on a global scale.
Energy-efficient appliances, such as LED light bulbs and ENERGY STAR-rated devices, further embody this principle. By providing the same level of service while consuming less energy, they illustrate the effectiveness of conservation measures. Adopting such technologies encourages a cultural shift towards responsible energy consumption, fostering a deeper appreciation for the finite nature of energy resources.
The Interconnectedness of Energy Conservation and Environmental Sustainability
The discussion surrounding the Law of Conservation of Energy inevitably leads to the crucial topic of environmental sustainability. As more individuals and communities embrace practices that prioritize energy conservation, they contribute to the health of the planet. Understanding the intricacies of energy transformation not only cultivates awareness of individual behaviors but also inspires collective action—spurring innovations in technology, policies, and lifestyle changes that promote sustainability.
The interplay between convenience and conservation is at the core of modern living. As more renewable energy sources become mainstream, the fabric of energy consumption will inevitably shift, ushering in an era where conservation becomes an inherent value. The recognition that energy is not merely available for the taking, but a resource that must be carefully managed, catalyzes the quest for more ingenious solutions to energy challenges.
In conclusion, the Law of Conservation of Energy serves as a guiding principle that transcends scientific inquiry, manifesting in numerous real-world applications. From the kinetic dances of roller coasters to the transformative powers of photosynthesis, this law shapes our interactions with energy in profound ways. By recognizing and embracing energy conservation practices, individuals can not only educate themselves about sustainable living but also become active participants in safeguarding the planet for future generations.