The concept of the Law of Conservation of Energy is a cornerstone of understanding the universe. This principle asserts that energy cannot be created or destroyed—it merely transforms from one form to another. This central tenet weaves through every aspect of our existence, from the mundane actions of daily life to the grand orchestration of celestial phenomena. But have you ever pondered what this might mean for your everyday activities? Could it be possible that you are, in a sense, a steward of energy flows in your own life?
The exploration of this law opens up an intellectual playground filled with opportunities for reflection on personal habits, technological innovations, and the ecological consequences of energy consumption. The implications are profound, and delving into them reveals not just the mechanics of energy but also their philosophical and ethical dimensions.
Let us embark on this journey to dissect the Law of Conservation of Energy, its significance, and its omnipresent influence on various facets of the cosmos.
The Historical Context of Energy Conservation
Understanding the Law of Conservation of Energy requires a trip through scientific history. In the 19th century, physicists such as James Prescott Joule and Hermann von Helmholtz solidified this concept, providing a formal framework that would become foundational in physics. Joule’s empirical studies on converting mechanical work into heat brought clarity to the idea that all forms of energy were interchangeable. Helmholtz extended these notions, proposing that energy remains constant in an isolated system.
The foundation laid by these pioneers has become integral to the laws of thermodynamics, which govern the behavior of energy and matter. First, it challenges our conventional understanding of energy as a finite resource; rather, it emphasizes the continuous cycling of various energy forms. From kinetic energy to potential energy, from thermal energy to chemical energy, the universe operates within this elaborate ballet of transformations.
The Implications of Energy Transformation
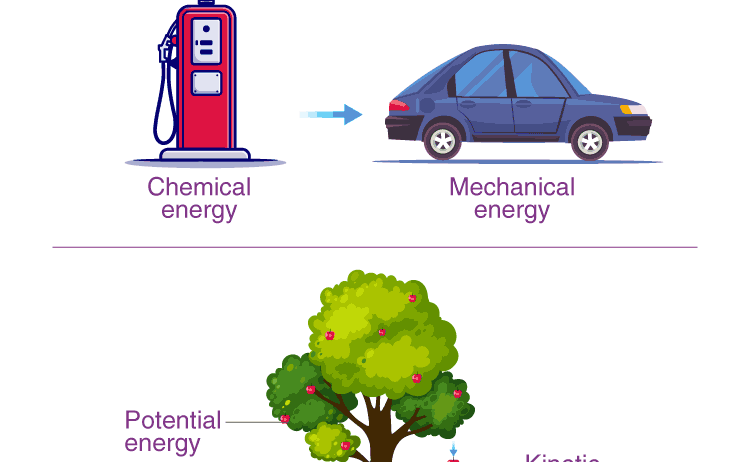
As we unearth the implications of energy conservation, it becomes evident how this principle governs countless phenomena in nature. Take, for instance, the photosynthesis process. In this remarkable biochemical reaction, plants convert solar energy into chemical energy, which sustains nearly all life on Earth. Simply put, sunlight is transformed into the energy stored in glucose, which in turn fuels growth, reproduction, and ultimately, the food chain.
This bioenergetics paradigm elegantly illustrates energy’s metamorphosis—from radiant light captured by leaves to the potential energy stored in organic compounds. The Law of Conservation of Energy contextualizes the ecological balance; energy flows through living systems, influencing growth, decay, and regeneration. In this sense, plants act as fundamental energy converters within ecosystems, dictating the flow and availability of energy resources.
Example of Energy Transition: From Fossil Fuels to Renewable Sources
In the modern world, the ramifications of energy transformation are especially pertinent in discussions surrounding fossil fuels and renewable energy sources. The combustion of coal, oil, or natural gas releases stored chemical energy, thus transforming the energy stored within these fossilized remnants of ancient flora and fauna into usable work for humanity. However, this process is not without consequences. Each transformation involves losses—primarily in the form of heat—due to inefficiencies in energy conversion. This inefficiency contributes to climate change, illustrating the delicate balance between energy consumption and ecological impact.
The transition to renewable energy sources presents a significant challenge and opportunity under the umbrella of energy conservation. Solar panels, wind turbines, and hydroelectric systems are also reliant on energy transformation principles, albeit in less polluting forms than fossil fuels. As we grapple with global warming and the depletion of finite resources, the Law of Conservation of Energy invites us to think critically about our energy choices and to innovate in ways that sustain the environment.
Everyday Life: Energy Stewardship
On a more personal level, the Law of Conservation of Energy challenges individuals to reconsider their energy stewardship. Every time you flip a light switch or start your car, you are engaging in energy transformations. Understanding how these operations function can empower you to make conscious decisions about energy use. Do you allow your devices to idle, leaking energy into the void of inefficiency? Or do you seek to harness energy more responsibly, opting for practices that reduce waste and conserve resources?
Consider this playful quandary: If energy cannot disappear, where does your wasted energy go? The thermodynamic aftermath of energy negligence has tangible consequences on both our wallets and the planet. This introspection urges us to rethink our role as active participants in the energy ecosystem—advocates for sustainability and conscious consumers.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The Law of Conservation of Energy elucidates the intricate interplay that governs our universe. From grand cosmic systems to individual lifestyles, energy transitions shape the fabric of reality. Embracing this principle invites a heightened awareness of our responsibility in energy conservation, whether at a global policy level or an intimate household routine. In an age marked by ecological uncertainty, this knowledge calls us to innovate, adapt, and challenge ourselves to be the best custodians of energy we can be.
By recognizing the immutable law of energy conservation, we foster a climate of responsibility that resonates deeply within our communities. Thus, each action taken can create ripples in the vast ocean of existence—after all, we are all inherently interwoven in the tapestry of energy.