Wind energy, an ever-evolving source of sustainable power, epitomizes the intricate relationship between nature and technology. As a clean and renewable energy source, it harnesses the invisible force of the wind, which is generated through the simple principles of atmospheric dynamics. But where exactly does wind power originate? This inquiry leads us into the fascinating world of meteorological science, energy conversion, and the potential for a greener future.
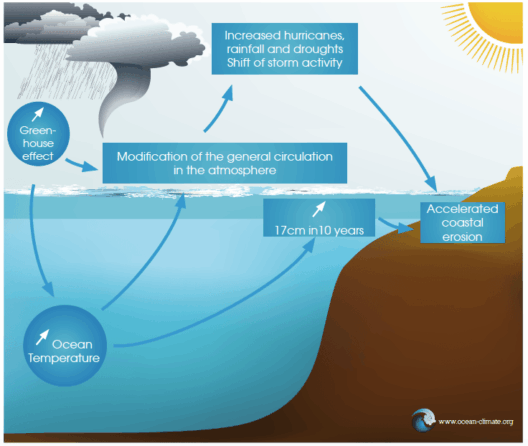
The genesis of wind energy is deeply rooted in the sun’s influence on the Earth. The sun’s rays, upon striking the surface of the planet, do not heat it uniformly. Different surfaces, including oceans, forests, and urban areas, absorb and release heat at varying rates. This differential heating causes air masses of differing pressure to form, creating wind. Essentially, wind is the movement of air from high-pressure regions to low-pressure regions.
To delve deeper, let’s explore the fundamental mechanics that contribute to the formation of wind.
The Role of Temperature Variations
Fundamental to the existence of wind is the temperature differential created by the sun’s interaction with our planet. When the sun warms the Earth, warm air rises, creating a void that must be filled by cooler air moving in from surrounding areas. This movement orchestrates the currents of wind, which vary in intensity and speed based on geographic and climatic factors. The interactions between land and sea also significantly impact local wind patterns. Sea breezes, for instance, arise as a result of the differential heating of sand and water, leading to characteristic daily wind flows that can be harnessed for energy.
Geographical Influences on Wind Patterns
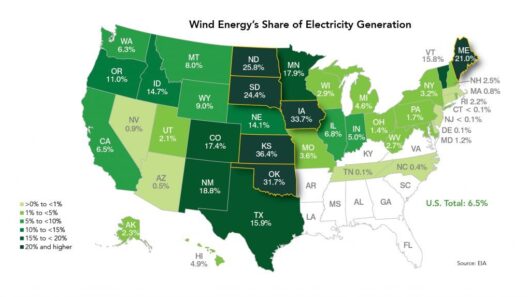
Geography plays a significant role in determining wind energy potential. Coastal areas, mountains, and flat plains exhibit distinctive wind patterns due to the topography of the land. For instance, coastal regions often benefit from consistent sea breezes, while mountainous terrains can funnel winds through passes, creating powerful gusts suited for energy generation. Furthermore, open plains experience fewer obstructions, allowing winds to flow unobstructed over vast distances. Understanding these geographical influences is crucial for optimizing wind farm placements, thus maximizing efficiency and energy output.
How Wind Energy is Captured
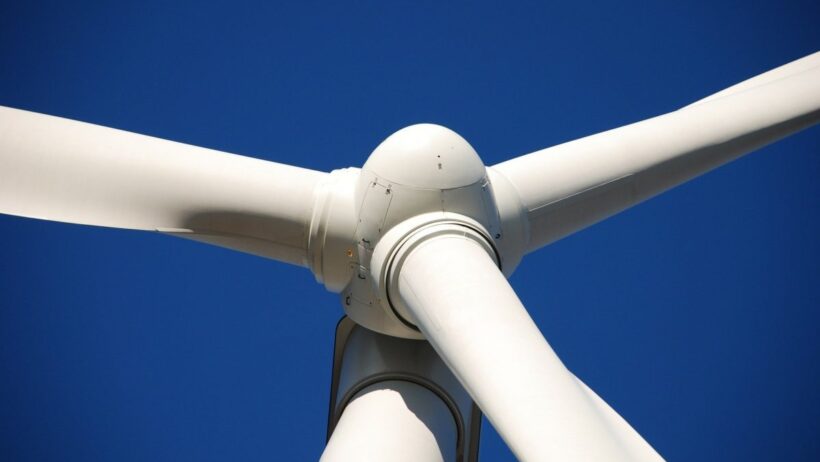
Once we understand the source of wind energy, the focus shifts to how this kinetic energy is captured and converted into usable electricity. The technology used to harness wind power typically involves wind turbines. These towering structures are designed to convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical energy, which can then be transformed into electrical energy. A wind turbine consists of several key components, including rotor blades, a rotor hub, a generator, and a tower.
The rotor blades, usually engineered with lightweight materials and aerodynamic shapes, are engineered to turn in the wind. As wind flows over the blades, it creates lift, causing them to rotate. This rotational movement is transferred to the generator, where mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. The design and placement of wind turbines are critical, as they must be strategically positioned to capture wind most efficiently.
The Advantages of Wind Power
Wind energy comes with a plethora of advantages. It is inherently renewable, as wind is an inexhaustible resource, unlike fossil fuels. Moreover, the carbon footprint associated with wind energy is minimal. The operational phase of wind farms produces no greenhouse gas emissions, making them a vital player in combating climate change. Additionally, advancements in technology have led to increased efficiency, lowering the cost of electricity generated from wind considerably in recent years.
Moreover, wind energy contributes positively to local economies. The establishment of wind farms creates jobs, from the initial construction phase through ongoing maintenance and operation. It also offers a sustainable income stream for landowners who lease their land for turbine installations, thereby fostering community engagement in renewable energy initiatives.
The Challenges of Wind Energy
Despite its many advantages, wind energy is not without challenges. The intermittency of wind can create inconsistencies in energy supply. Wind does not blow consistently, which can lead to periods of low energy production. Consequently, energy grid stability can be affected, necessitating advancements in storage technologies or supplementary energy sources to bridge the gaps in power generation.
Another consideration is the environmental impact of wind farms on local wildlife, particularly birds and bats. While various studies suggest that the benefits of wind energy far exceed these impacts, it remains a point of contention among environmental stakeholders. Ongoing research is essential to continue mitigating these effects through improved turbine designs and siting strategies that respect natural habitats.
Looking to the Future of Wind Energy
The future of wind energy appears bright as technological innovations continue to emerge. Enhanced turbine designs, larger capacities, and the integration of artificial intelligence for predictive analytics in energy generation are just a few advancements poised to revolutionize the wind power sector. Offshore wind farms also present an exciting frontier, leveraging the vast and windy expanses of oceans to produce substantial amounts of energy with less land use conflict.
In conclusion, the source of wind energy stems from complex atmospheric interactions influenced by solar radiation and land-sea dynamics. As society continues to grapple with climate change and the need for sustainable energy solutions, wind power remains a vital player in the transition to a cleaner, more resilient energy future. Understanding its origins, capturing its power, and addressing its challenges will be critical as we forge ahead in making wind energy an integral part of our global energy landscape.