The Invisible Engine: Harnessing the Power of the Wind
Wind energy stands as a quintessential metaphor for harnessing nature’s untamed spirit. It is the silent engine of modern energy production, transforming invisible gusts into tangible power. With ever-increasing urgency around climate change, its role in the global energy mix cannot be overstated. So, what exactly is wind energy used for? The applications are as diverse as the landscapes across which the wind sweeps, each harnessing its potential to meet the demands of a rapidly evolving world.
Generating Electricity: The Backbone of Renewable Power
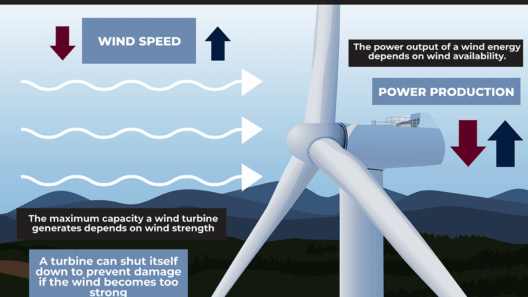
At the heart of wind energy’s myriad applications lies its most prominent use: the generation of electricity. Wind turbines stand like sentinels across fields and coastlines, converting kinetic energy from moving air into electrical energy. This electric output can power everything from homes in sprawling suburbs to massive industrial complexes. As wind farms proliferate, they grow to resemble vast fields of modern-day windmills, capturing the breeze with their colossal blades.
The integration of wind energy into the national grid signifies an essential shift toward sustainability. In many regions, especially those with expansive open spaces and favorable winds, wind farms can contribute significantly to a community’s or even a country’s overall energy needs. This conversion is not merely beneficial; it is vital for reducing reliance on fossil fuels, thereby mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change. For many nations, transitioning to wind power is akin to planting seeds for a healthier environmental future.
Offshore Solutions: Pioneering the Blue Frontier
As land-based wind farms begin to saturate prime locations, attention has turned to the world’s oceans—an untapped reservoir of windswept potential. Offshore wind farms are akin to great shipbuilders setting sail to conquer the waves, harnessing the relentless oceanic winds that flow unhindered over water. These installations present unique advantages, particularly their ability to generate more consistent and powerful wind energy due to the lack of land obstacles.
Offshore wind energy isn’t merely a logistical challenge; it is also an engineering marvel. Floating turbines, anchored far from the shore, can now reach depths once deemed impractical for traditional structures. This innovation broadens the horizon for wind power, proposing new strategies for meeting large-scale energy demands. Beyond energy generation, offshore wind farms are beginning to play a role in local economies, creating jobs and providing communities with clean, reliable electricity.
Heating Applications: Beyond Electricity Production
The utilization of wind energy extends well beyond simply generating electricity. Harnessing wind power for direct heating applications is a lesser-known yet practical solution that deserves attention. Energy sourced from wind can be utilized to produce and circulate hot air within homes and industrial facilities. This practice, often referred to as ‘wind heating’, employs mechanical systems to transfer energy collected by wind-driven turbines directly to thermal applications.
Moreover, when coupled with systems designed for thermal accumulation, wind energy can serve as a sustainable source for heating water. Such applications reinforce the idea that wind energy is not just a phase in the renewable energy revolution—it is an intricately woven thread that can contribute to everyday life. When we think about harnessing wind for heating, it’s like transforming a gentle breeze into a warm hearth, comfortingly defying the chill of the winter months.
Fueling Transportation: The Advent of Green Mobility
The transportation sector is undergoing a metamorphosis with the integration of renewable energy sources. Wind energy plays a pivotal role in this transition, particularly in the production of green fuels. Wind-derived electricity can be employed in the generation of hydrogen through a process known as electrolysis. This hydrogen can then serve as fuel for vehicles, ships, and even aircraft, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions associated with travel and transport.
The advent of hydrogen as a wind-powered fuel can be compared to finding a new river flowing through an arid landscape—an abundant resource that can, if harnessed wisely, support entire communities and industries. As technology advances and infrastructure develops, wind energy’s role in the transport sector may redefine how we travel, making the journey not only cleaner but also more sustainable.
Supporting Agriculture: A Breezy Ally
Wind energy’s applications have even infiltrated the sacred fields of agriculture. Farmers have begun to adopt wind turbines on their lands, leveraging the powerful gusts to reduce their operational costs. The energy generated can help power irrigation systems, machinery, and farm-related equipment, decreasing reliance on traditional energy sources and increasing productivity.
Moreover, wind turbines can play a role in providing additional revenue streams for farmers. This practice is akin to nurturing a second crop; while they harvest their primary yield, they also reap benefits from the energy harvested from the winds that sweep across their property. As climatic shifts force farmers to rethink traditional practices, wind energy is emerging as an unwavering ally, providing stability in a time of uncertainty.
The journey to fully realize the potential of wind energy is ongoing, as its many applications continue to evolve. From powering homes and industries to revolutionizing transport and agriculture, the uses of wind power are as dynamic and far-reaching as the very winds that generate it. The invisible engine driving our quest for cleaner energy is not merely a fleeting trend; it is a cornerstone of a sustainable future, solidly anchored in the hopes and aspirations of a planet striving to flourish anew. In acknowledging its capabilities, we take critical strides toward an eco-friendlier tomorrow.