Wind power energy is a compelling testament to humanity’s quest for sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels. Utilizing the inexhaustible force of the wind, this form of renewable energy has garnered substantial attention in recent years. However, beneath the surface lies a plethora of engineering marvels and ecological implications that merit scrutiny.
As the world continues to grapple with climate change, the fascination with wind energy springs not only from its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also from the intricate mechanics that facilitate its generation. Understanding these mechanics reveals why wind power is not merely a fleeting trend but a cornerstone in the transition toward sustainable energy systems.
The science behind wind energy is as captivating as the technology that harnesses it. This article delves into the fundamentals of wind power, exploring the mechanics involved in transforming kinetic energy into electricity, while highlighting its advantages and challenges.
Understanding the Basics: What Is Wind Power?
Wind power refers to the process of converting wind energy, which originates from the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface by solar radiation, into electricity. This transformation occurs through a series of mechanical and electrical processes, culminating in the generation of usable electrical power. The size and design of wind turbines play a pivotal role in maximizing efficiency, as does their placement in optimal wind corridors.
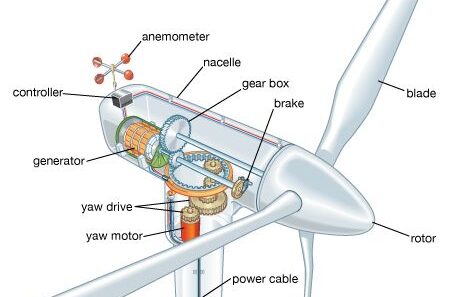
At its core, the wind turbine operates on the principle of lift and drag. When wind strikes the blades of the turbine, it causes them to rotate. The rotation of the blades is then transmitted through a shaft to a generator, which translates the mechanical motion into electrical energy. The basic components of a wind turbine include the rotor, nacelle, tower, and foundation, each engineered to withstand the forces exerted by the wind.
The rotor, typically equipped with two or three blades, is designed to capture as much wind as possible. The nacelle houses the generator and other critical mechanical components. Rising above the ground on a tower, the turbine must align itself with prevailing winds, necessitating strategic placement in open fields, coastal regions, or elevated terrain.
Bridging Physics and Engineering: The Mechanics Behind Wind Power Generation
To further appreciate the intricacies of wind power generation, it is essential to understand the relationship between wind speed and energy production. Wind energy production follows a cubic relationship; this means that a mere doubling of wind speed results in an eightfold increase in energy output. Consequently, wind turbines are equipped with sophisticated sensors and control systems to optimize performance and safety during extreme weather conditions.
Modern wind turbines utilize advanced materials and technology to enhance efficiency and durability. Composite materials, for example, allow for lighter and stronger blades that can capture more wind energy without succumbing to physical wear. Additionally, gearless designs, such as direct-drive turbines, have emerged as practical solutions to reduce maintenance and enhance reliability.
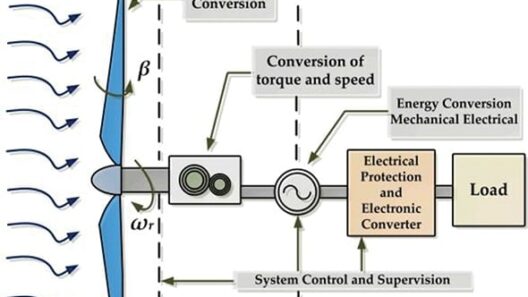
Electromagnetic principles also come into play. The generator inside the nacelle converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by creating a magnetic field that induces current flow. The effectiveness of this process relies on seamless interaction between mechanical components and electrical systems, drawing on the foundation of electromechanical engineering.
The Role of Wind Farms in Power Generation
Wind farms, often comprising numerous interconnected turbines, play a crucial role in harnessing wind energy efficiently. These farms are strategically located in sites with high average wind speeds to optimize their energy production. A single wind turbine can generate sufficient power for hundreds of homes, while a collective wind farm can significantly contribute to a region’s energy needs.
In addition to generating electricity, wind farms bolster local economies by providing job opportunities ranging from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and operation. Furthermore, their relatively low environmental footprint positions them as desirable alternatives compared to conventional energy sources.
Challenges and Considerations: The Other Side of Wind Energy
Despite its advantages, wind energy is not without challenges. Variability in wind patterns can result in inconsistent electricity generation, necessitating a robust storage system or backup energy source to ensure reliability in a power grid. While battery technology is advancing, the quest for scalable and efficient energy storage remains critical for broader wind energy integration.
Noise pollution and visual impact are also notable considerations. Critics often raise concerns regarding the aesthetic implications of wind farms on landscapes, as well as the sound produced by the turbine blades. Addressing these concerns requires thoughtful planning and community engagement to ensure that the benefits of wind energy are appreciated alongside its physical presence.
Moreover, the impact on wildlife, particularly birds and bats, necessitates ongoing research and innovative designs that mitigate adverse effects. Developers are increasingly adopting bird-friendly technologies and strategic placement of turbines to minimize disruption to local ecosystems.
A Future Driven by Wind Energy
In conclusion, wind power energy embodies a synthesis of ecological prudence and technological ingenuity. As countries worldwide strive to reduce carbon emissions, investments in wind energy are likely to flourish. The mechanical processes that convert wind into electricity underscore a profound understanding of physics and engineering, demonstrating how harnessing natural forces can yield viable and sustainable energy solutions.
Society’s growing fascination with wind energy reflects a deeper commitment to prioritizing environmental sustainability. As advancements continue to unfold, the future of wind energy holds promise for cleaner, greener, and more resilient energy systems, sustaining not only the present but also future generations.