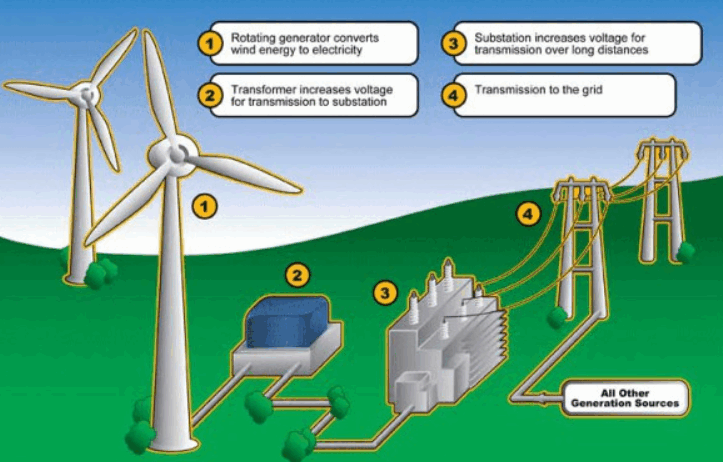
Wind energy stands as one of the most promising forms of renewable energy, harnessing the natural movement of air to generate electricity. As societies begin to pivot towards sustainable energy solutions amid the climate crisis, understanding the fundamentals of wind energy becomes imperative. This article delves into what makes wind a valid and essential aspect of renewable energy, its environmental benefits, technological advancements, and future potential.
Wind energy is considered renewable because it draws upon an inexhaustible resource—the wind. The sun’s heat causes temperature variations across the Earth’s surface, which in turn creates wind patterns. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, wind power is sustainable and generates energy without depleting natural resources. With advancements in technology and increasing efficiency, wind energy is evolving into a robust solution for providing clean power to homes, businesses, and industries globally.
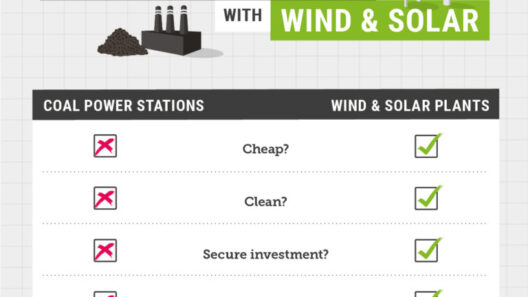
One of the principal characteristics that differentiates wind energy from conventional energy sources is its minimal environmental footprint. The expansion of wind farms has demonstrated a remarkable capability to generate electricity cleanly and efficiently. Turbines operate silently, and their presence atop hills or in open fields often does not require extensive land alteration. Unlike coal or natural gas plants, the processing and combustion of fossil fuels are not necessary when utilizing wind as an energy source, significantly reducing air and water pollution.
Moreover, the life-cycle emissions associated with wind power are substantially lower than those tied to fossil fuels. While the manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of wind turbines entail some energy consumption and resources, the energy produced over their operational lifespan far outweighs these initial investments. This efficiency contributes to lowering overall greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
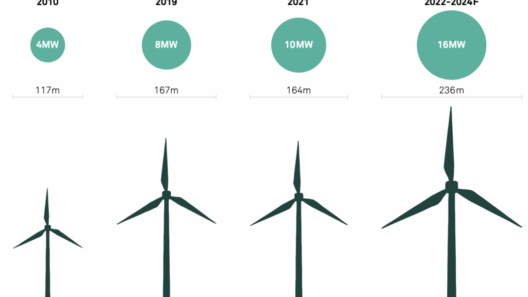
In recent years, technological advancements have propelled wind energy into the limelight. The engineering surrounding turbine design has transformed, leading to larger and more efficient models capable of harvesting energy even in lower wind conditions. The advent of smart grid technology and energy storage solutions enhances the viability of wind energy by allowing excess power to be stored for later use. This, in turn, addresses one of the prominent challenges facing renewable energy: the inconsistency of resource availability. Wind is not always blowing, thus incorporating energy storage methods ensures a reliable and steady power supply.
Beyond technological advances, economic growth and job creation are key aspects of wind energy that merit attention. The wind sector has seen substantial investment, stimulating local economies and creating numerous jobs. From engineering and installation to maintenance and research, this burgeoning field requires diverse skill sets. Communities near wind farms often benefit through local tax revenues and lease payments, further incentivizing the expansion of wind energy in rural areas, which are ideal for the establishment of wind farms.
As governments worldwide commit to reducing carbon footprints and transitioning towards renewable energy, wind energy plays a pivotal role in achieving these ambitious targets. Countries like Denmark, Spain, and the United States have set benchmarks for wind energy contributions to their overall power supply. National policies supporting renewable energy, including tax incentives and grants, encourage innovation and drive competitive pricing. As the industry matures, wind energy has continued to achieve grid parity, offering prices that compete favorably with traditional energy sources.
Integrating wind energy with other renewable sources, such as solar and hydroelectric power, can further optimize energy systems. This holistic approach allows for a diversified energy portfolio that can enhance reliability while maximizing the benefits of each type of renewable energy. For instance, during periods of lower wind activity, solar energy can fill the void, ensuring continued energy supply. Such coordination can foster a resilient energy infrastructure geared towards sustainability and energy independence.
Public perception of wind energy has also evolved over time. Initially, concerns surrounding the visual impact on landscapes, noise generated by the turbines, and potential effects on wildlife emerged. However, extensive research has alleviated many such concerns. Modern turbine designs have become more aesthetically pleasing, and collaborative efforts with environmental organizations have helped mitigate risks to avian populations. Raising awareness about the extensive benefits of wind energy has fostered acceptance and support from communities, paving the way for further development.
Looking to the future, the potential for wind energy appears boundless. Offshore wind farms are gaining momentum, capitalizing on more robust wind resources available in ocean environments. Floating wind technology enables turbines to be placed in deeper waters, expanding the geographical reach of wind energy generation. As energy demands increase in the wake of urbanization and population growth, scaling up wind infrastructure seems essential to meet future energy needs sustainably.
Furthermore, as the world confronts the monumental challenges posed by climate change and resource depletion, wind power emerges as not simply an option, but a necessity. It epitomizes a critical pathway towards reducing reliance on fossil fuels, cutting greenhouse gas emissions, and securing a cleaner, sustainable future. In summary, wind energy’s role in sustainable energy transcends mere generation; it intertwines with economic growth, technological advancement, and ecological preservation. By embracing and investing in wind power, societies can pave the way for a resilient and sustainable energy landscape that cherishes both human and environmental prosperity.