Wind power is an increasingly prominent form of energy among renewable resources, harnessing the natural movement of air to generate electricity. Defined simply, wind energy is the conversion of wind currents into electrical energy using turbines. This phenomenon is not merely a modern marvel but represents an ancient practice, with windmills used for centuries for tasks such as grinding grain and pumping water. However, the contemporary approach to wind energy exemplifies a growing demand for sustainable and clean sources of power, making it a crucial asset in global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Wind power is categorized as a renewable resource because it is generated from naturally replenishing sources — specifically, wind. Geographic locations with consistent wind patterns provide ideal conditions for the installation of wind turbines, and advancements in technology continue to enhance the efficiency and output of these systems. This aspect, coupled with the inexhaustible nature of wind, underscores the promise of wind energy as a mainstay in the transition to cleaner energy solutions.
In understanding wind power more intricately, it is vital to delve into its operational mechanisms, advantages, and challenges faced in the scope of renewable energy.
Mechanics of Wind Power: How It Works
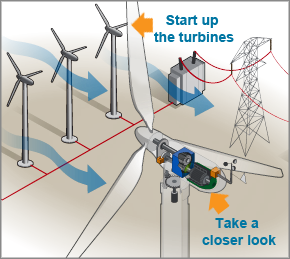
The operational process of wind power begins with the interaction between wind and turbines. A wind turbine consists of large blades, typically three, which are attached to a rotor. When the wind blows, it exerts force upon these blades, causing the rotor to spin. This mechanical movement is then converted into electrical energy through a generator housed within the turbine structure. The entire conversion process can be succinctly described through the principles of electromagnetic induction, which highlights how mechanical energy is transformed into electrical energy.
Modern wind turbines are designed to operate efficiently across various wind speeds. Variable pitch control and advanced sensor technology allow these turbines to adjust accordingly, optimizing energy generation while minimizing wear and tear on mechanical components. Moreover, wind farms, which are clusters of interconnected turbines, are strategically located in areas with favorable wind conditions to maximize energy production.
The Spectrum of Wind Energy: Types and Technologies
Wind energy is not monolithic; it encompasses various forms and technologies tailored to different environments and needs. Primarily, wind energy can be classified into two main categories: onshore and offshore wind energy. Onshore wind farms are situated on land, utilizing available open spaces to tap into local wind currents. These installations can range from small, community-level projects to vast, utility-scale operations capable of powering thousands of homes.
Contrarily, offshore wind energy capitalizes on the more potent and consistent winds found at sea. Offshore turbines are uniquely designed to withstand harsh maritime conditions, often positioned on floating platforms or fixed foundations on the seabed. This form of wind energy generation tends to result in a higher capacity factor than its onshore counterparts due to reduced turbulence and ample open space for turbine deployment.
Another emerging technology in the wind energy spectrum is the vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT). Unlike the traditional horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWT), VAWTs can capture wind from any direction and can be integrated into urban environments, albeit they are generally less efficient than HAWTs. Continued research and development in wind turbine technology focus on innovation and efficiency, pushing the boundaries of what is possible within this renewable resource.
Advantages of Embracing Wind Energy
The benefits of wind energy are manifold, making it an attractive option for both energy producers and consumers. Primarily, wind power is lauded for its minimal environmental impact compared to fossil fuels; it produces no air pollutants or greenhouse gas emissions during operation, contributing significantly to global efforts against climate change. Additionally, once a wind farm is established, the cost of maintaining and operating turbines is relatively low, resulting in competitive electricity pricing, particularly in regions with ideal wind resources.
Moreover, the installation and operation of wind turbines foster job creation, from manufacturing to maintenance, thereby invigorating local economies. The renewable aspect of wind energy means that it is not subject to the same volatility of supply and demand as fossil fuels. As wind power becomes increasingly cost-effective, nations are recognizing its potential for energy independence and security.
Challenges and Considerations in Wind Energy Adoption
Despite its numerous advantages, the adoption of wind energy is not without challenges. Intermittency represents a significant concern; wind does not blow uniformly, leading to fluctuations in energy generation. This necessitates the integration of energy storage systems and backup power to ensure a reliable electricity supply. Furthermore, the aesthetic and ecological impacts of wind farms must be carefully assessed, as turbine placement can affect local landscapes and wildlife, sparking debates within communities.
Future Directions for Wind Power Integration
As technology continues to evolve, the future of wind power holds exciting possibilities. Innovations such as advanced energy storage, improved turbine designs, and smart grid technologies are set to enhance the operational efficiency and reliability of wind energy systems. Additionally, integrating wind energy with other renewable resources — such as solar and hydroelectric systems — can create a more balanced and sustainable energy portfolio, supporting efforts to combat climate change on a broader scale.
In summary, wind power represents a cornerstone of renewable energy, offering a sustainable pathway to meet the escalating energy demands of our world. Its numerous benefits, coupled with growing technological advancements, underscore its critical role in shaping a cleaner, more sustainable future. Embracing wind energy not only addresses current environmental challenges but also invigorates economies and promotes a diverse energy landscape essential for a resilient global community.