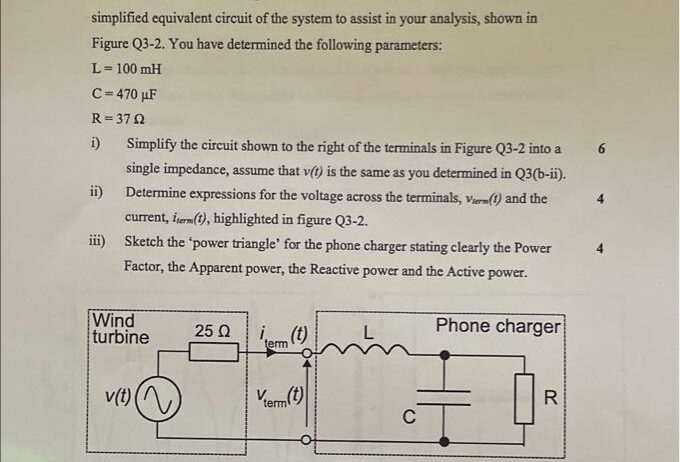
Wind power has emerged as one of the most compelling forms of renewable energy in our contemporary quest for sustainable solutions. Harnessing the invisible currents of air, wind energy demonstrates exceptional potential to mitigate climate change and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. What makes this clean energy source particularly intriguing is its graceful integration into the landscape where it flourishes. Vast fields of towering wind turbines punctuate the skyline, creating a juxtaposition of natural beauty and human ingenuity, capturing both our imagination and our hopes for a greener future.
At its core, wind energy is the result of solar radiation—not via burning fossil fuels but through the natural processes of the Earth’s atmosphere. As sunlight heats the Earth’s surface unevenly, air currents are generated, leading to wind. By converting the kinetic energy found in these currents into mechanical energy, we can harness this dynamic force to generate electricity. This phenomenon transcends mere generation; it calls us to rethink our relationship with the environment and our capabilities as innovators.
The aesthetic allure of wind farms is not to be overlooked. Long before we began utilizing wind for energy production, it served as a source of inspiration for artists, poets, and philosophers. These modern installations, far from being merely utilitarian structures, stand tall against the backdrop of rolling hills and open sky, symbolizing a forward-thinking mentality about energy production. The rhythmic rotation of turbine blades captures the imagination, evoking a sense of harmony between technology and nature.
Capturing the Essence of Wind: Mechanics of Wind Energy
Wind energy generation hinges on a fascinating choreography of components. When the wind blows, its force is captured by the blades of a wind turbine, which then convert the kinetic energy into rotational energy. This energy spins a rotor connected to a generator. As the rotor turns, it produces electricity that can be transmitted to the power grid. This elegant system is not confined to any one locale; it is adaptable, existing in offshore installations, tall towers on land, and even urban settings where sleek designs can complement city skylines.
Understanding the mechanics of wind energy also entails examining the types of wind turbines that are deployed. Most commonly used are horizontal-axis and vertical-axis turbines. Horizontal-axis turbines, most familiar to the public, are designed with two or three blades that rotate around a horizontal axis. In contrast, vertical-axis turbines exhibit a different structural grace, with blades that rotate around a vertical axis. Each design presents unique benefits and situational advantages, highlighting the ingenuity of engineers dedicated to maximizing wind energy efficiency.
The Environmental Impact: Wind Energy’s Green Credentials
One of the most compelling attributes of wind energy is its minimal ecological footprint. Unlike fossil fuel resources, which often contribute to carbon emissions and pollution, wind power generates electricity without any harmful byproducts—only clean air and tranquility. This distinction is vital as concerns about climate change grow more urgent. As the planet warms and weather patterns become increasingly erratic, transitioning to renewable energy sources like wind power is essential for fostering resilience within our communities.
Moreover, wind energy contributes to biodiversity conservation. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, wind power indirectly protects habitats that would otherwise be disturbed by drilling, mining, and pollution. The strategic placement of wind farms, often in previously disturbed or less biodiverse areas, can optimize land use while promoting a more sustainable energy model. Not embracing wind energy would mean forgoing a robust tool in our collective fight against climate change.
Challenges on the Horizon: Overcoming Obstacles in Wind Power
Despite the advantages, the path to maximizing wind power capacity isn’t devoid of challenges. Critics often cite concerns over noise generation, the effects on local wildlife, particularly birds and bats, and the visual impacts on scenic landscapes. These apprehensions are not to be dismissed lightly; they necessitate thoughtful planning and ongoing research to develop solutions that balance energy needs with environmental preservation. Technological advancements are continually improving turbine designs to mitigate wildlife risks, while community engagement can address aesthetic concerns and foster support for local projects.
The Future of Wind Energy: An Expansive Frontier
As we stand at a pivotal moment in our energy journey, the future of wind energy appears vibrant and full of potential. As technology advances, we can expect increased efficiency and cost reductions in wind energy systems. Innovations such as energy storage solutions and artificial intelligence for optimizing turbine performance are on the horizon. Such developments will not only enhance energy capture but also allow for better integration into smart grids, maximizing the potential of renewable sources.
Furthermore, the global investment in offshore wind farms is soaring, highlighting the untapped potential of harnessing wind where conventional land use may not be feasible. Harnessing wind over the vastness of oceans opens new doors for expansive energy generation without encroaching on terrestrial habitats, creating an elegant symbiosis with marine ecosystems.
In conclusion, wind energy stands as a beacon of hope and innovation in our quest for sustainable energy solutions. It is not merely an alternative; it represents a transformative shift in how we approach power generation. As we gaze upon the majestic turbines drawing energy from the landscape, we are reminded that harnessing nature’s gifts can lead to a cleaner, more resilient future. The intriguing characteristic of wind power lies not only in its technological elegance but also in its ability to inspire us to forge new pathways in our relationship with the Earth.