It’s a question that lingers: What happens when Earth’s atmosphere becomes a little too cozy? In our quest to understand climate change, the greenhouse effect emerges as a pivotal phenomenon. As temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, decoding the science behind the greenhouse effect becomes vital. It underpins not just the warming of our planet but also many intricate interactions within our global ecosystem.
Let’s embark on a journey through the essential workings of this natural process. To fully grasp the greenhouse effect, we should first examine the role of greenhouse gases and how they contribute to our current climate crisis.
The Role of Greenhouse Gases: A Necessary Component?
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are a mix of naturally occurring and man-made components that trap heat in our atmosphere. These gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor—though many others exist in trace amounts. While the presence of GHGs is crucial for maintaining a hospitable Earth, the troubling escalation of their concentrations leads to serious repercussions.
Imagine a warm blanket on a chilly night, wrapping you in comfort. This analogy holds true for GHGs; they help to retain solar energy, enabling the Earth to maintain a temperate climate conducive to life. Without the greenhouse effect, our planet would be a frigid wasteland, devoid of the diverse ecosystems we know today.
However, with the past century’s unprecedented industrial growth, human activities have increased the level of GHGs dramatically, particularly through burning fossil fuels and deforestation. Simply put, we’ve turned a cozy blanket into an oppressive comforter—one that’s raising our global temperature and leading to climatic extremes. The balance that once allowed life to flourish is tipping toward a precarious and dangerous edge.
How Does the Greenhouse Effect Work?
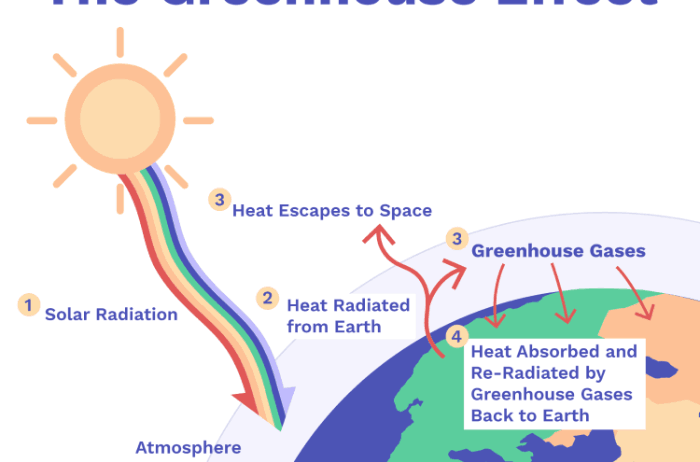
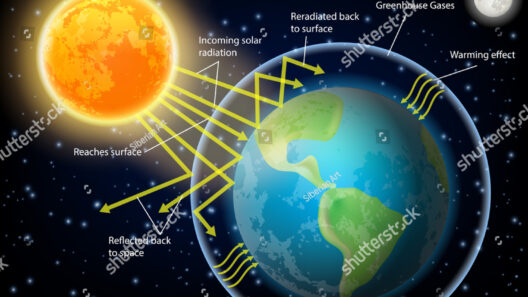
A scientific marvel lies at the heart of the greenhouse effect: the intricate dance of solar radiation and heat retention. The Earth receives energy primarily from the Sun, in the form of shortwave radiation. Some of this energy is reflected back into space, while the remainder is absorbed by the Earth’s surface. This absorbed energy warms the land and oceans, facilitating photosynthesis and maintaining weather patterns.
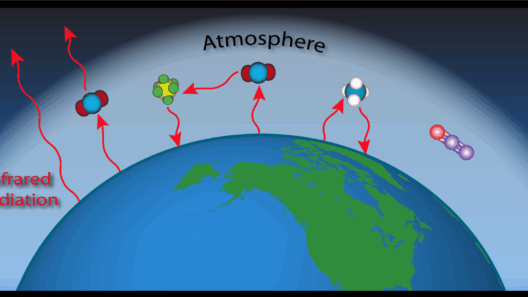
Once this shortwave radiation has been absorbed, the Earth radiates energy back into the atmosphere as longwave (infrared) radiation. Herein lies the crux of the greenhouse effect: certain gases, particularly CO2 and methane, possess the capability to absorb and re-emit this infrared radiation. This process subsequently warms the atmosphere, creating a natural heating system for our planet.
While this phenomenon is essential for life, it is the amplification of GHGs that leads to excessive warming, causing chain reactions that produce unforeseen environmental consequences. And so we return to the opening question: what happens when this balance is disrupted? Let’s analyze the multi-tiered ramifications.
A Cascade of Consequences: From Melting Ice Caps to Altered Ecosystems
Climate change paints a picture fraught with peril and uncertainty. The ramifications of an imbalanced greenhouse effect are vast and deeply interconnected. One of the most observable phenomena is the accelerated melting of polar ice caps and glaciers. As these immense landforms retreat, they contribute to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities and entire nations.
Beyond the threat of flooding, the melting ice contributes to a feedback loop. As ice diminishes, less sunlight reflects away, which means more solar energy is absorbed by the darker ocean waters, further exacerbating temperature hikes. In essence, we find ourselves trapped in an insidious cycle—a momentum of warming that seems difficult to halt.
Moreover, ecosystems globally are suffering from climate-induced stressors. As temperatures rise, many species are forced to adapt, migrate, or face extinction. This loss of biodiversity has cascading effects on food chains, ecosystem services, and the resilience of our environment to withstand climatic fluctuations. Ponder this: must we sacrifice the planet’s inhabitants for the so-called necessity of development?
Solutions on the Horizon: A Call to Action
The burgeoning understanding of the greenhouse effect offers a glimmer of hope amidst the chaos. Advances in renewable energy, sustainable agricultural practices, and conservation efforts present us with valuable tools to combat climate change. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing carbon sinks, we can begin to reverse trends that propel warming.
Transitioning to a carbon-neutral economy demands innovation and systemic change—an endeavor that requires collective political will, societal commitment, and individual responsibility. Imagine a community where solar panels adorn rooftops, where local produce is valued, and where conservation practices flourish. The challenge lies before us: can we transform our current trajectory into a sustainable future?
In reflection, the greenhouse effect serves as a cautionary tale about our planet’s fragile equilibrium. It reveals both the complexity of our climate systems and the critical need for concerted action. Humanity’s insatiable desire for growth must be tempered with a commitment to stewardship, as we remain stewards of not just this generation but countless future ones. As we grapple with the intricacies of the greenhouse effect, we must consider not only our immediate needs but the legacy we choose to create for the Earth.