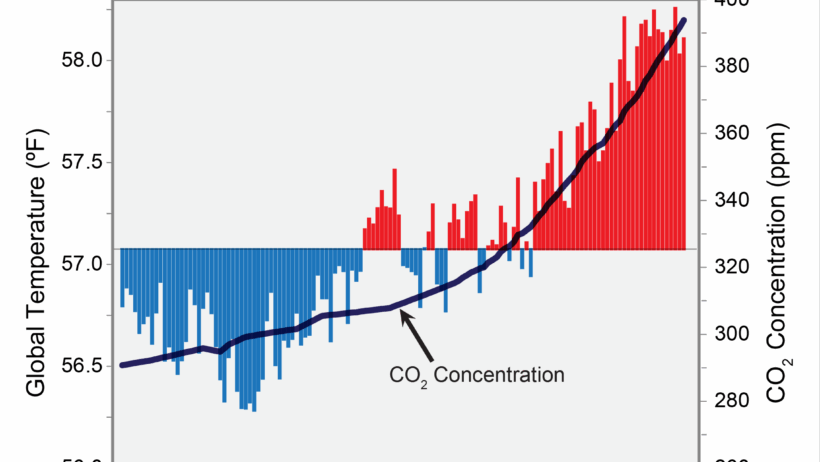
Global warming and sea level rise are twin phenomena intricately linked in the fabric of our planet’s climate system. As temperatures climb, the consequences unfurl in myriad ways, one of the most pressing being the elevation of ocean levels. Understanding why sea levels rise due to climate change illuminates the depth of the crisis we face and the urgency with which we must act.
Sea levels are not static; they fluctuate due to a variety of natural processes. However, anthropogenic climate change is accelerating these shifts. The compelling interplay between increasing temperatures and rising seas warrants a thorough examination.
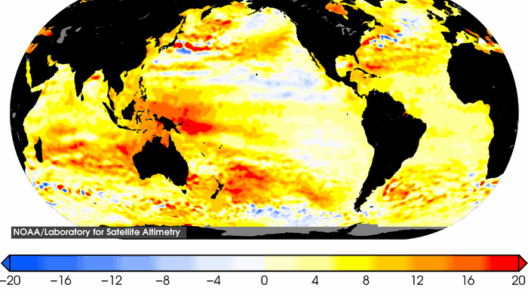
One of the primary drivers of rising sea levels is thermal expansion. When water heats, it expands; this phenomenon is governed by the laws of physics. The oceans absorb the majority of heat trapped by greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane. As the mean global temperature ascends, ocean temperatures follow suit. This thermal expansion contributes significantly to the rise in sea levels, accounting for about half of the observed increase.
But thermal expansion is only part of the story. The melting of glaciers and polar ice caps also plays a critical role in elevating sea levels. The vast ice sheets of Greenland and Antarctica are among the most significant reservoirs of frozen water on Earth. As global temperatures rise, these colossal formations succumb to melting, releasing freshwater into the ocean. This process is not merely a gradual trickle; it occurs at an alarming rate. Scientists have recorded that Greenland’s ice sheet is losing mass at a rate of approximately 280 billion tons per year, with Antarctica also contributing to the rising tide.
The cascading effects of melting ice extend beyond mere volume increase. The fresher water dilutes the ocean’s salinity, potentially disrupting marine ecosystems and ocean circulation patterns. As the perfect equilibrium of the oceans is altered, we could observe phenomena that further exacerbate sea level rise. For instance, the Gulf Stream, a major ocean current, could weaken, leading to additional shifts in water distribution and hence, sea levels.
Additionally, the groundwater extraction common in many coastal regions exacerbates sea level rise. As populations grow and urban areas expand, the demand for groundwater increases. When this water is pumped from aquifers, the land begins to sink—a process known as land subsidence. This human-induced factor compounds the impact of global warming, making areas more susceptible to flooding.
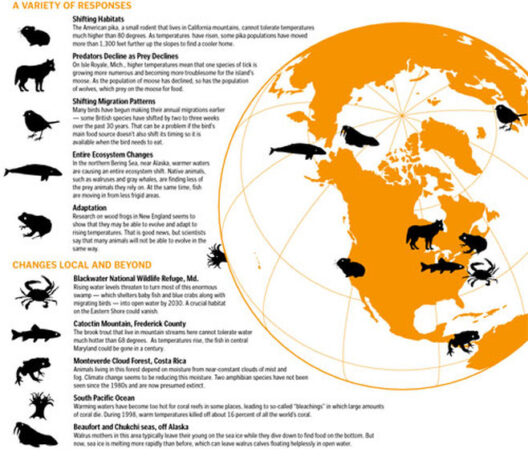
The implications of rising sea levels are profound. Coastal cities face existential threats as they contend with the prospects of chronic flooding, increased storm surges, and loss of habitat. Low-lying regions may become uninhabitable, forcing populations to relocate, which leads to socio-economic instability. The aesthetic appeal of once-bustling beach towns could fade into memories as they succumb to the relentless encroachment of tides.
What’s more, the ecological ramifications of rising sea levels are equally concerning. Wetlands, which serve as vital buffers against storms, are increasingly inundated. As saltwater intrudes, freshwater habitats are diminished, impacting myriad species that depend on these ecosystems. This alteration disrupts biodiversity and can lead to the loss of unique marine and coastal life, undoing centuries of ecological balance.
To address the existential crisis posed by rising sea levels, proactive measures must be taken. Mitigating climate change requires a multifaceted approach. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and implementing sustainable practices are pivotal in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Public policies should prioritize climate resilience, with investment in infrastructure capable of withstanding the new realities of a warming world.
Engineers and urban planners must design with foresight. Innovative solutions, such as creating natural barriers using restored wetlands, enhancing drainage systems, and building sea walls, can serve as protective measures against rising tides. Moreover, communities should engage in discussions about sustainable land use, recognizing that preserving natural habitats can serve dual purposes of safeguarding against flooding while maintaining biodiversity.
Education and awareness are critical. The more individuals understand the intrinsic connection between our actions and the health of the planet, the more motivated they will be to advocate for change. Grassroots movements have historically ignited policy shifts; leveraging this momentum is essential in the fight against climate change and rising sea levels.
In conclusion, the link between global warming and rising sea levels is undeniably complex and profound. As we witness the tangible effects of climate change, it becomes imperative to navigate this challenge with urgency and purpose. Our oceans, while magnificent and awe-inspiring, are not immune to the wrath of humanity’s choices. By understanding the intricacies of this environmental crisis, we can forge a path toward sustainability, resilience, and, ultimately, survival.