Our planet’s oceans are a vital part of the Earth’s system, meticulously intertwined with climatic patterns and ecological stability. Observations over the past century indicate a steady rise in sea levels, captivating the attention of scientists and environmentalists alike. The reasons behind this phenomenon are multifaceted, stemming from a combination of climate change, glacial melting, and even terrestrial dynamics. Delving into the science of rising oceans reveals the intricate tapestry of natural and anthropogenic forces at play.
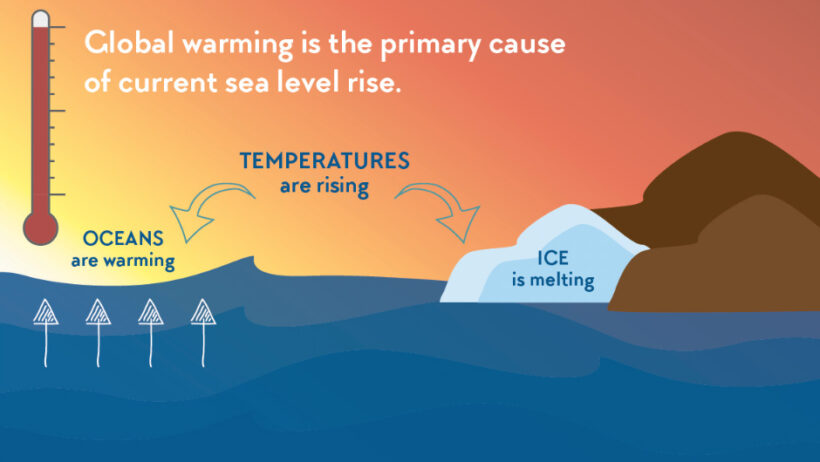
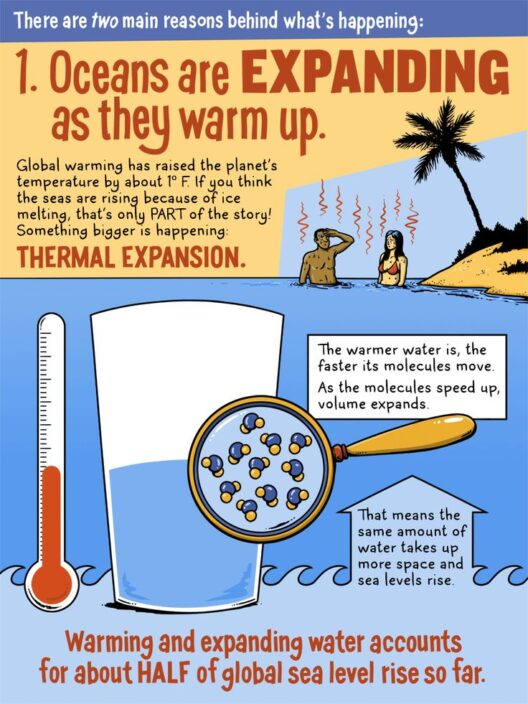
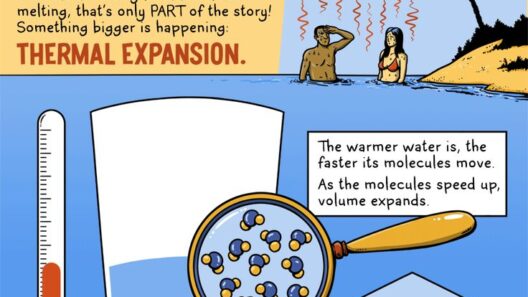
Understanding the factors contributing to sea-level rise necessitates a look at thermal expansion. Water, like most substances, expands as it warms. The incessant rise in global temperatures, largely spurred by anthropogenic activities, results in the warming of the oceans. According to scientific consensus, as the planet’s average temperature increases, the oceans absorb a significant amount of this heat, leading to thermal expansion. This process is responsible for nearly half of the total observed sea-level rise since the late 19th century. The challenge lies not only in mitigating climate change but also in comprehending the long-term implications of rising water levels for coastal communities.
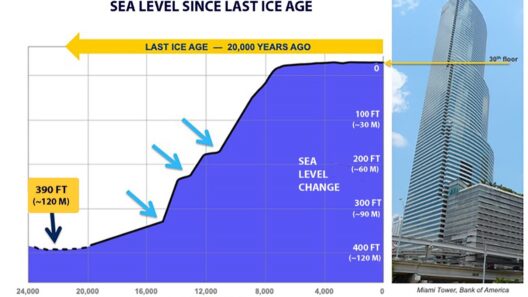
Shifting the focus to the polar regions unveils a startling reality. Polar ice caps, particularly those in Greenland and Antarctica, serve as vast reservoirs of freshwater. However, they have become increasingly vulnerable to climatic fluctuations. With rising global temperatures, the rate of glacial melting has accelerated alarmingly. The Greenland Ice Sheet, for example, has been losing approximately 280 billion tons of ice annually. Similarly, studies indicate that Antarctica is shedding ice at an accelerated rate, contributing to an additional significant rise in sea levels. The interconnection between temperature increases and glacial dynamics underscores the complex relationship between Earth’s systems and climate change.
Another significant aspect of sea-level rise is the contribution of terrestrial water storage. As global temperatures rise, weather patterns become increasingly erratic. Droughts and heavy precipitation events intensify, depleting and redistributing water resources across the planet. Groundwater depletion, particularly in arid regions, exacerbates the situation as water extraction lowers land elevation, causing additional subsidence. Notably, cities like New Orleans and Jakarta are experiencing land subsidence, compounding the effects of rising sea levels. This phenomenon exemplifies how human activities, such as groundwater extraction and urban development, can unwittingly contribute to the challenges posed by rising oceans.
The repercussions of rising sea levels extend beyond mere coastal flooding. Ecosystems are under siege; saltwater intrusion into freshwater aquifers disrupts local water supplies and threatens agricultural viability. Coastal habitats, including mangroves and salt marshes, face submergence, leading to the loss of biodiversity and the ecosystem services they provide. Additionally, the risk of increased storm surges and heightened erosion poses a significant threat to coastal infrastructure, necessitating a reevaluation of urban planning and management strategies in vulnerable areas.
In light of these realities, it becomes imperative to consider potential mitigation strategies. Global efforts such as the Paris Agreement aim to curb greenhouse gas emissions, thereby addressing the root causes of climate change. However, adaptation strategies must also be paramount in planning for future sea-level rise. This includes investigating innovative solutions for coastal infrastructure, such as elevated buildings, seawalls, and natural buffers like restored wetlands. Policymakers must collaborate with scientists, urban planners, and community organizers to formulate sustainable approaches that prioritize both human safety and environmental integrity.
Education and awareness are key in rallying public support for initiatives addressing rising sea levels. By shedding light on the science behind this pressing issue, we can cultivate a collective sense of responsibility. Engaging communities in conservation efforts, promoting sustainable practices, and advocating for climate-resilient policies are integral steps in navigating this crisis. Science, once understood, drives action; the complexities of climate change and rising oceans become catalysts for sustainable innovation and community resilience.
In conclusion, the intricate causes behind the rising seas are a testament to the interconnectedness of the Earth’s climate systems. Thermal expansion, glacial melt, and terrestrial dynamics not only elucidate the science of rising oceans, but they remind us of our collective responsibility to foster a sustainable future. As we confront the myriad challenges posed by climate change, the necessity for informed action becomes all the more pertinent. Understanding the nuances of sea-level rise lays the foundation for creating resilient communities that can adapt to a world shaped by the forces of nature and human impact alike.