Understanding the intricacies of our planet’s climate system unveils a fundamental concept: the greenhouse effect. While often labeled as a harbinger of climate change, the greenhouse effect is pivotal in sustaining life on Earth. The necessity of greenhouse gases in maintaining our planet’s warmth cannot be overstated.
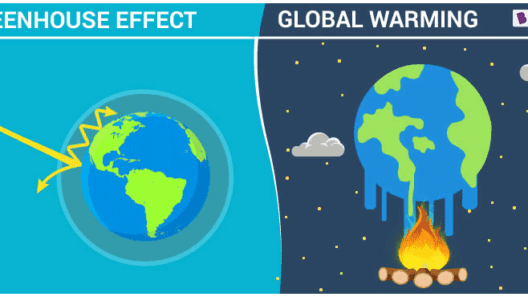
At its core, the greenhouse effect occurs when certain gases in our atmosphere, known as greenhouse gases, trap heat. This phenomenon results in the retention of thermal energy, preventing it from escaping back into the cosmos. The natural occurrence of this effect keeps our Earth at a habitable temperature.
To comprehend the paramount importance of greenhouse gases, we must delve into their roles, mechanisms, and the delicate balance they maintain for life on our planet.
The Role of Greenhouse Gases: Building Blocks of Life
Greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor, are integral to the Earth’s temperature regulation. Imagine these gases as a protective blanket enveloping the planet, absorbing and re-radiating heat. Without this thermal insulation, our Earth would average a frigid temperature of approximately -18°C (0°F). Instead, it boasts a comfortable average temperature of about 15°C (59°F).
Plants, oceans, and soils naturally release and absorb greenhouse gases. Plants, through photosynthesis, play a crucial role in sequestering CO2, which is vital not only for maintaining Earth’s temperature but also for nurturing life forms reliant on plant growth. These gases contribute to photosynthetic processes, which produce the oxygen necessary for animal life.
Water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas, also plays a significant role in weather patterns and climate variability. Although it does not directly result from human activity, its response to climate changes exacerbated by anthropogenic emissions underscores the complexity of global warming.
The Mechanism Behind the Greenhouse Effect: A Cosmic Dance
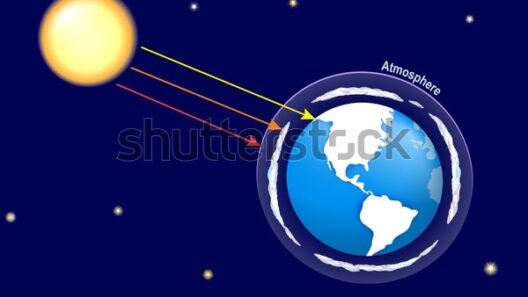
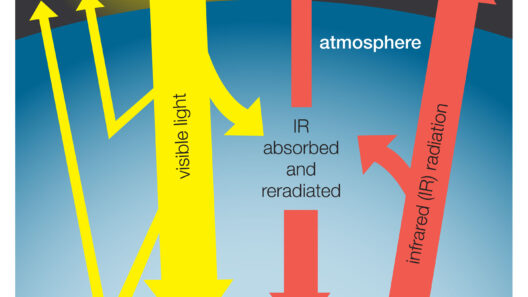
The process by which greenhouse gases maintain warmth involves a fascinating interplay between solar radiation and Earth’s surface. Incoming solar radiation penetrates the atmosphere, heating the Earth’s surface. As this heat is re-emitted in the form of infrared radiation, greenhouse gases trap a portion of it. This natural phenomenon is akin to a dance, where gases oscillate between absorption and emission, ultimately sustaining the Earth’s climate equilibrium.
Yet, the equilibrium established by natural processes can be disrupted. Anthropogenic activities, notably the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial practices, have resulted in an unprecedented surge in greenhouse gas concentrations. The delicate balance maintained over millennia is under threat as CO2 levels have risen significantly, raising concerns regarding global warming and climate stability.
Climate Regulation and its Effects on Biodiversity
The greenhouse effect is not merely a scientific concept; it is a vital determinant of biodiversity and ecosystems. The warmth generated by greenhouse gases fosters diverse climatic zones, which host distinct flora and fauna. Without the greenhouse effect, ice caps would be more extensive, and many life forms would struggle to survive in the inhospitable climates.
Moreover, the greenhouse effect facilitates vital ecological processes. It regulates agricultural cycles, influencing growing seasons and crop yields. Plants depend on a specific temperature range for photosynthesis, growth, and reproduction. As temperature fluctuations become more extreme due to climate change, agricultural practices are challenged, threatening food security.
The World’s Crystalline Balance: The Interplay of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors
Amidst the undeniable necessity of greenhouse gases, their overabundance presents a paradox. As anthropogenic emissions escalate, the very phenomenon that sustains life is at risk of exacerbating global warming. It is crucial to discern between the beneficial effects of naturally occurring greenhouse gases and the adverse consequences of excess emissions due to human activities.
To mitigate the impacts of climate change, significant efforts must be directed towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Incorporating sustainable practices, fostering renewable energy sources, and enhancing carbon sequestration techniques can help maintain a balance that upholds the natural greenhouse effect while curtailing the influences of climate change.
Conclusion: The Striking Balance of Nature
In summation, the greenhouse effect serves as a double-edged sword—the lifeblood of our planet that necessitates prudent stewardship. Greenhouse gases perform an indispensable function in sustaining warmth and fostering biodiversity. Yet, the need for moderation is imperative.
As stewards of the environment, we must cultivate an understanding of the greenhouse effect that transcends alarmism, embracing a holistic view of atmospheric health. To preserve our planet and its intricate web of life, we must ensure that the beneficial greenhouse effect remains intact while detracting elements induced by human activity are curbed.
Ultimately, fostering awareness and initiating dialogues surrounding greenhouse gases will engender a deeper appreciation for their role in our ecosystem—a role that, when meticulously balanced, nourishes the vibrant tapestry of life that flourishes on Earth.