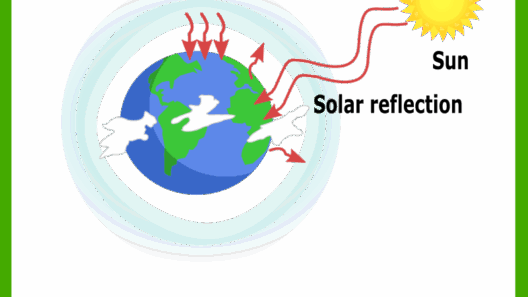
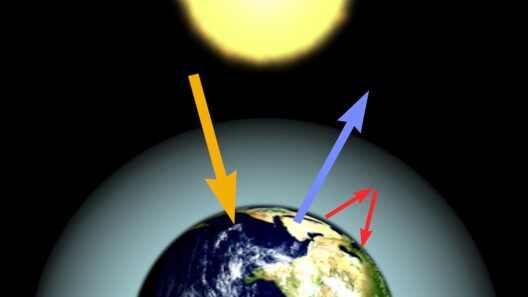
Understanding the Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is an intrinsic and natural phenomenon that serves as the very linchpin of life on Earth. It is the mechanism by which certain gases, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and water vapor (H2O), trap heat in the atmosphere, creating a warm environment that sustains myriad ecosystems. Without this crucial effect, Earth would be inhospitable, with average temperatures plummeting far below what is necessary for sustaining life. This potent wonder of nature provokes a plethora of questions and observations, intricately interwoven into our understanding of planetary habitability.
Despite its essential function, the greenhouse effect is often misunderstood and misconstrued as a negative force. It is vital to delve deeper into its positive contributions, unraveling the complexities that lead to a greater appreciation of this highly intricate climatic system.
The Delicate Balance of Atmospheric Components
At the heart of the greenhouse effect lies a delicate equilibrium among various atmospheric components. Sunlight permeates the atmosphere, causing the Earth’s surface to absorb energy and subsequently re-radiate that energy in the form of infrared radiation. Herein lies the function of greenhouse gases; they absorb and emit this radiation, effectively insulating the planet. The natural abundance of these gases is crucial for maintaining an average global temperature of approximately 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius). In the absence of this protective blanket, temperature averages would drop drastically, plunging to about -0 degrees Fahrenheit (-18 degrees Celsius).
These gases include essential elements of our atmosphere, like CO2 and CH4, which are produced through both natural processes—such as respiration, decomposition, and volcanic activity—and human activities, like burning fossil fuels and deforestation. A careful examination reveals that the greenhouse effect is not solely a product of anthropogenic influences; rather, it is an enduring feature of our planetary system that has evolved over eons.
Symbiosis With Biodiversity
The greenhouse effect profoundly influences biodiversity. It helps delineate diverse habitats, which in turn provide various ecological niches from arid deserts to lush rainforests. Each habitat thrives due to the specific climate conditions fostered by this insulative layer of greenhouse gases. In regions prone to cold temperatures, the greenhouse effect enables survival strategies employed by various species. For instance, many animals and plants undergo adaptations to cope with seasonal variations, which would be exacerbated in a world devoid of this warming mechanism.
For flora, the greenhouse effect permits the flourishing of phototrophic life forms, especially those found in temperate regions. Warmer climates mean extended growing seasons, allowing for a more diverse array of plant species. This, in turn, provides sustenance for herbivorous animals and subsequently the carnivores that feed on them. There exists an intricate web of interdependence, indicating that the greenhouse effect is pivotal not just for temperatures, but for the entire tapestry of life.
Climate Regulation and Weather Patterns
In addition to supporting life, the greenhouse effect plays a critical role in climate regulation. It influences weather patterns, atmospheric circulation, and precipitation levels across the globe. The warmth that is retained via greenhouse gases leads to the creation of favorable conditions for a variety of climatic phenomena. For instance, it is imperative for the maintenance of the hydrological cycle, driving evaporation and facilitating cloud formation. Rainfall, which is essential for agriculture and water supply, is inextricably linked to these temperature distributions.
However, as human activities exacerbate the greenhouse effect by increasing the concentration of these gases, the balance becomes skewed. Climate change, driven by anthropogenic emissions, raises global temperatures and shifts weather patterns, which can have dire consequences for ecosystems and human populations. Understanding this nexus between the greenhouse effect and climate dynamics is crucial for implementing effective mitigative strategies to harness its benefits while safeguarding our planet’s health.
Moving Toward Sustainable Practices
Efforts to preserve the natural greenhouse effect must be paired with initiatives aimed at reducing excess emissions. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, fostering sustainable agriculture, and enhancing carbon sequestration are endeavors that can aid in mitigating the adverse effects of heightened greenhouse gases. Promoting an awareness of the collective responsibility to balance our impact with Earth’s natural systems is of paramount importance.
Ultimately, the greenhouse effect stands as a testament to the complexities of the Earth’s climate system. By understanding its significance and nurturing this delicate balance, we open doors to a more sustainable future, one that ensures the continued habitability of our planet for generations to come. By viewing the greenhouse effect through a lens of appreciation rather than a lens of concern, we can foster a holistic respect for natural processes and engage in dialogue that values Earth’s ecological integrity.
In conclusion, while the greenhouse effect encompasses a myriad of challenges primarily linked to climate change, its foundational role in promoting life on our planet cannot be overstated. Recognizing that we inhabit a finely tuned ecosystem intricately connected to natural laws is both humbling and empowering. The journey toward understanding and protecting this balance is the cornerstone of fostering a more ecologically sustainable world.