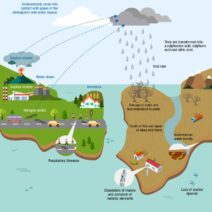
Climate change is an ever-looming specter that has begun to shape the natural world in myriad ways, profoundly impacting not only ecological systems but also the reproductive behavior of wildlife. As the global climate shifts, so too do the pressures faced by various species—altering their breeding cycles, migratory patterns, and even the composition of populations. This complex interplay requires understanding the ways in which climate change disrupts the delicate balance of animal reproduction.
An essential aspect of reproductive behavior in animals is timing. Many species have evolved to synchronize their breeding activities with environmental cues, such as temperature and food availability. Seasonal changes are critical markers; for example, many birds initiate nesting around the onset of spring when temperatures rise and food sources become abundant. However, climate change has dramatically destabilized these seasonal cues. Warmer temperatures can lead to earlier springs, which in turn prompts birds to breed sooner than usual. If these birds lay eggs before food sources are sufficiently abundant, it could jeopardize the survival of the young. Thus, understanding this temporal mismatch is crucial as it can drive population declines.
Furthermore, the phenomenon of phenological shifts—the timing of life cycle events—has become increasingly evident. A prime example can be found in migratory birds. These species often travel thousands of miles to breed in the northern latitudes, relying on predictable weather patterns. Climate change has altered these patterns, resulting in unpredictable migration timings. Birds may arrive at breeding grounds either too early or too late, resulting in lost opportunities for successful reproduction. The disconnect between the timing of migration and breeding is critical as mismatched schedules can lead to reduced reproductive success.
Additionally, changes in habitat due to climate change can also result in altered reproductive behaviors. Species that are already on the brink of extinction due to habitat loss face even greater reproductive pressures when their environments shift. For instance, amphibians with specific habitat requirements for breeding, such as clean water bodies, can experience drastic changes in reproductive success as their habitats become unsuitable. Droughts, flooding, and temperature extremes can all contribute to the degradation of these necessary environments, leading to lower reproductive rates.
Climate change does not just affect the timing and location of reproduction; it can also have physiological implications for not only breeding success but also the health of future generations. Elevated temperatures can be particularly harmful during crucial developmental phases. For some species, such as sea turtles, incubation temperatures have a direct impact on the sex ratio of hatchlings. Warmer temperatures can lead to skewed sex ratios, with a predominance of females, eventually jeopardizing breeding populations. This phenomenon highlights the importance of temperature regulation in reproductive success across the animal kingdom.
Moreover, altered weather patterns can lead to increased stress on animal populations. Extreme weather events—such as hurricanes, wildfires, and prolonged droughts—can result in stress that adversely affects reproduction. Stress in animal populations can manifest in various ways, including altering hormone levels associated with reproduction and causing behavioral changes that reduce mating opportunities. Stress-induced factors play a significant role in community structures, ultimately leading to diminished reproductive outcomes.
Notably, climate change also catalyzes shifting predator-prey dynamics, which can have cascading effects on reproductive behavior. As prey species adapt to changing environments, predator species often find themselves facing a mismatch in their hunting strategies and prey availability. These food web disruptions can lead to a decrease in reproductive opportunities, as predators may struggle to find enough food to sustain themselves and their young. The local extinction of certain prey species can lead to predators facing starvation, thereby impacting their reproductive success.
Insects, too, illustrate the complexities of climate change’s impact on reproduction. Many insect species are critical pollinators, and their reproductive patterns are heavily influenced by temperature and plant phenology. As climate change alters the life cycles of plants, it can create a mismatch in the availability of flowers and the emergence of adult insects. A decline in pollinator populations can have profound consequences for the reproductive success of flowering plants, leading to further implications for entire ecosystems.
Mitigation strategies are essential to counteract the repercussions of climate change. Conservation efforts aimed at protecting habitats and implementing restoration plans are vital. Creating wildlife corridors can assist in facilitating species migration and enhancing genetic diversity. Additionally, monitoring programs that track phenological changes in animal behavior can provide data necessary for adaptive management strategies.
In conclusion, the cascading effects of climate change on animal reproductive behavior are complex and multifaceted. By shifting climatic conditions, species faces challenges that threaten their reproductive timing, habitat suitability, physiological health, and interactions within their ecosystems. As environmental stewards, our obligation is to acknowledge these changes and implement strategies that promote sustainability and biodiversity. Recognizing the urgency of these issues is the first step towards fostering a harmonious coexistence with the wildlife that shares our planet.