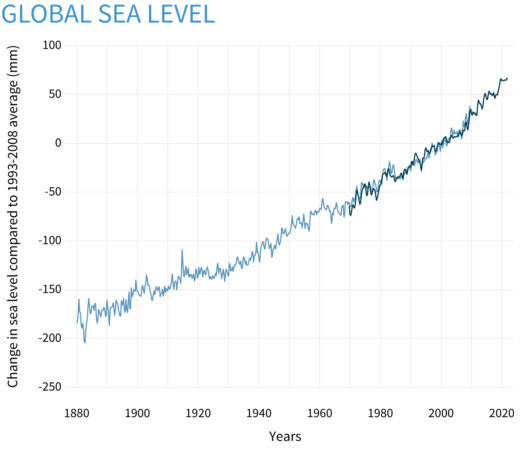
The phenomenon of rising sea levels is one of the most pressing environmental threats facing our planet today. As global temperatures rise due to climate change, the consequences of melting ice caps and increasing ocean temperatures become more apparent. Understanding why rising sea levels are detrimental requires an examination of the multifaceted impacts they have on ecosystems, human settlements, and global economies.
In this exploration, we will delve into the various implications of rising oceans, highlighting key areas of concern and illuminating the urgent need for proactive measures.
Understanding the Causes of Rising Sea Levels
To grasp the severity of rising sea levels, it is essential to understand the underlying causes. Primarily, sea level rise results from two main phenomena: thermal expansion of seawater and the melting of glaciers and polar ice sheets.
Thermal expansion occurs as seawater heats up, causing it to expand and occupy more volume. With global temperatures consistently on the rise, the oceans are absorbing most of this excess heat. Consequently, even a slight increase in temperature can lead to significant sea-level surges.
The second cause involves the influx of freshwater from glaciers and ice sheets into the oceans. Major ice reserves in Greenland and Antarctica store vast quantities of water. As these icy behemoths melt at an alarming rate, they contribute to rising sea levels. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has solemnly reported that sea levels could rise by more than a meter by the end of the century if current trends continue, making it imperative to act swiftly.
Destructive Impacts on Coastal Communities
The immediate victims of rising sea levels are coastal communities. With approximately 40% of the world’s population residing within 100 kilometers of the coast, increased flooding puts millions at risk. Inundation of low-lying areas, increased frequency of storm surges, and erosion of shorelines create an existential threat to these communities.
As seawater intrudes upon freshwater sources, the phenomenon known as saltwater intrusion renders drinking water supplies unusable. This vulnerability exacerbates existing tensions and inequalities, often displacing marginalized communities first. Historic cities and cultures are at risk, as landmarks and ecosystems are swallowed by encroaching waters.
Economic Ramifications of Rising Seas
The economic ramifications of rising sea levels are severe and far-reaching. Coastal cities are economic powerhouses, contributing significantly to national GDPs. The destruction of infrastructure, real estate, and tourism industries generates staggering financial losses. As businesses adapt to these changes, costs related to adaptation and emergency response will escalate, heightening the economic strain on governments and communities.
Furthermore, industries reliant on marine resources, such as fishing and aquaculture, face jeopardy as shifting ecosystems disrupt delicate balances. As habitats transform and species migrate, local economies tied to these industries will suffer. Fisheries struggling to adapt may lead to job loss and food insecurity, contributing to broader economic instability.
The Ripple Effect: Global Ecosystem Disruption
The ecological consequences of rising sea levels are equally concerning. Coastal wetlands, mangroves, and coral reefs act as crucial buffers against storm surges and provide habitats for countless species. However, as sea levels rise, these ecosystems face inundation, leading to habitat loss and diminishing biodiversity.
Wetlands are particularly susceptible, serving as nurseries for many marine species and providers of vital ecosystem services. If lost, the loss of fish populations and other marine life will have cascading effects on food webs and community livelihoods.
Moreover, coral reefs, already beleaguered by ocean acidification, face the dual threat of rising temperatures and sea levels. The degradation of coral reefs would not only result in loss of biodiversity but also erode coastal protection, exposing communities to increasingly violent storms and erosion.
Health Risks and Public Safety Concerns
The health risks associated with rising sea levels transcend the physical landscape. With flooding comes increased exposure to contaminated water sources, leading to outbreaks of waterborne diseases. Mosquito-borne illnesses may flourish in the warm, stagnant waters created by rising seas, further endangering public health.
Moreover, the stressors of displacement and loss of home can lead to profound psychological impacts, contributing to anxiety, depression, and social fragmentation. The burden of these potential health crises places an enormous strain on public health systems already stretched thin.
Finding Solutions: Adaptive Strategies and Global Cooperation
Confronting the daunting challenges posed by rising sea levels necessitates innovative thinking and global cooperation. Developing comprehensive strategies for coastal resilience is paramount. This includes investing in infrastructure to protect vulnerable areas, implementing sustainable land-use planning, and restoring wetlands and natural buffers.
International collaboration plays a critical role in addressing this global issue. Sharing knowledge, technology, and resources ensures that nations can adapt more efficiently and equitably to rising sea levels. Investing in renewable energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions remains crucial in curtailing the future impact of climate change and, consequently, slowing the rate of sea-level rise.
Conclusion: Urgency of Action
The dangerous impacts of rising oceans are evident across the globe, from increasingly severe flooding to biodiversity loss, economic turmoil, and public health crises. Proactive measures must be taken if we hope to protect vulnerable communities and ecosystems from these threats. In addressing climate change comprehensively and collaboratively, we can work toward a more sustainable future for all, safeguarding the planet for generations to come.