In an era characterized by increasing discussions on climate change and environmental awareness, it might be beneficial to pause and consider the greenhouse effect in a more nuanced light. It’s easy to view this phenomenon solely through the lens of its negative ramifications. However, is there a playful paradox to ponder upon? Could the very mechanism that contributes to climate change also be fundamentally essential to life as we know it on Earth?
The greenhouse effect, often vilified for its contribution to global warming, is a natural atmospheric phenomenon that plays a pivotal role in regulating the Earth’s temperature. It is imperative to understand the vital importance of this heat retention mechanism, as it underpins the very existence of life on Earth. Let’s delve into this phenomenon and explore why the greenhouse effect is not just a villain in the narrative of climate change, but, in fact, a crucial element for life.
The Fundamentals: How the Greenhouse Effect Works
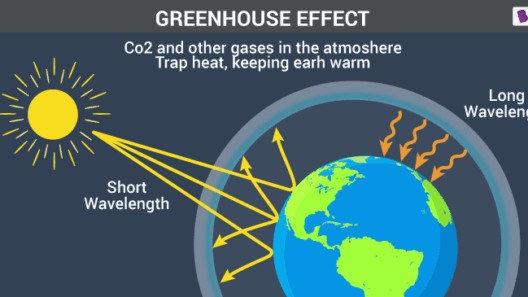
To comprehend the significance of the greenhouse effect, one must first grasp the mechanics behind it. In simplest terms, the greenhouse effect occurs when the Sun’s energy reaches the Earth. Some of this energy is absorbed, warming the land and oceans. Subsequently, the Earth re-radiates this heat back into space in the form of infrared radiation. However, certain gases in the atmosphere, known as greenhouse gases (GHGs) – primarily carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor – trap some of this heat, preventing it from escaping into the cosmos.
Imagine the atmosphere as a finely tuned thermal blanket. This insulating layer warms the planet to a level that is just right for sustaining life. Without it, the Earth would be a frigid place, with average temperatures plummeting to approximately -18 degrees Celsius (0 degrees Fahrenheit). With no warmth retained, the abundance of life we witness today would be an impossibility.
Vital for Life: The Role of Heat Retention
The greenhouse effect facilitates the establishment of a habitable climate. Think of the diverse ecosystems — jungles, deserts, tundras — each flourishing within its own climatic niche attributed to a balanced greenhouse effect. Heat retention plays a paramount role in a variety of processes essential for life.
The water cycle, for instance, is intricately linked to temperatures maintained by the greenhouse effect. It aids in the evaporation of water, forming clouds, and eventually precipitating as rain. This natural irrigation system nourishes crops, maintains freshwater reserves, and supports exquisite biodiversity. Moreover, without this precious heat retention, Plants would struggle to photosynthesize efficiently. The role of temperature in biochemical reactions is critical, making the greenhouse effect indispensable for agricultural stability and food security.
The Melting Pot: Diversity and Adaptability
Indeed, the greenhouse effect supports not only life’s existence but also its richness and diversity. A warm planet fosters a versatile array of habitats, ensuring that various species — from polar bears in the Arctic to tropical fish in coral reefs — can thrive. This ecological diversity is critical as it enhances ecosystem resilience, allowing nature to adapt to fluctuations and disturbances.
The challenge, however, lies in striking a balance. While the greenhouse effect is essential for a warm and vibrant planet, anthropogenic activities have intensified it to unprecedented levels, leading to global warming and climate catastrophes. The rude awakening of extreme weather patterns and rising sea levels illustrates that it’s not the greenhouse effect that is the antagonist; instead, it is the excessive accumulation of greenhouse gases due to human actions that amass threats to our planet’s delicate equilibrium.
Embracing Sustainability: Harmonizing Nature and Humanity
Given that the greenhouse effect is fundamentally beneficial, a transformative approach toward sustainability is paramount. This necessitates innovative strategies to mitigate undesirable emissions while preserving the essential functions of the greenhouse effect.
Promoting renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydroelectric systems can reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Implementing sustainable agricultural practices not only increases food security but also sequesters carbon in soils. Reforestation and afforestation campaigns restore habitats, enhancing biodiversity while capturing carbon. The challenge lies in fostering widespread acceptance of these practices in governance, industry, and lifestyle choices.
As humanity grapples with climate change, a vital question emerges: “How can we retain the benefits of the greenhouse effect while curbing its adverse impacts?” Finding this equilibrium is a collective responsibility that invites every individual, community, and government to reflect on their ecological footprint.
Conclusion: The Necessity of Balance
In summation, the greenhouse effect is an intrinsic element of our planet’s environmental fabric. It imbues our world with warmth and sustains the plethora of ecosystems that thrive within it. While it indeed poses modern challenges, understanding its intricacies allows us to navigate climate change with a sense of purpose and responsibility. By embracing sustainable practices, we have the opportunity to safeguard this vital process, ensuring a balanced and thriving planet for generations to come. The question remains, how will humanity respond to this challenge? The answer will define the future of life on Earth.