The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that plays an indispensable role in maintaining the delicate equilibrium that sustains life on Earth. Without it, our planet would be inhospitable, with average temperatures plummeting to levels that could not support complex organisms. The atmospheric layers composed of greenhouse gases (GHGs) not only facilitate temperature regulation but also create an environment conducive to life as we know it. Let us delve into the multifaceted nature of the greenhouse effect and appreciate its vital importance to our planet.
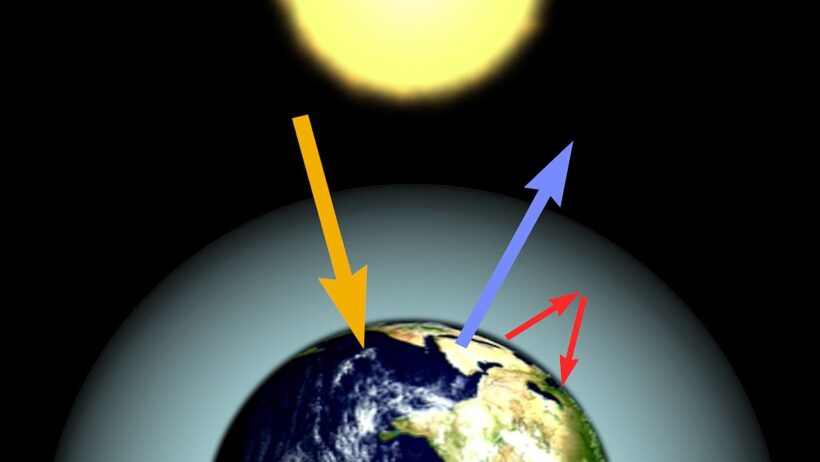
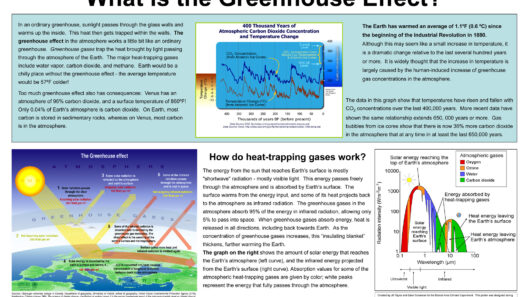
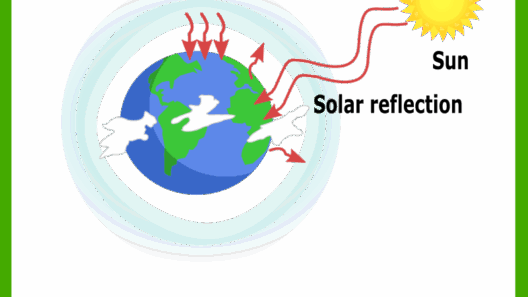
To grasp why the greenhouse effect is necessary, one must first understand the role of greenhouse gases. These gases, which include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor (H2O), interact with sunlight. When solar radiation reaches Earth, some of it is reflected back into space, while a significant portion is absorbed by the surface, warming the planet. Subsequently, Earth radiates this energy in the form of infrared heat. Greenhouse gases capture and re-emit some of this heat, preventing it from escaping to the outer atmosphere. This intricate dance of energy between the Earth and its atmospheric constituents establishes a stable climate, essential for the survival of flora and fauna.
The initial question arises: What would happen in the absence of the greenhouse effect? A planetary scenario devoid of such gases would result in a catastrophic drop in surface temperatures. In fact, scientists estimate that, without greenhouse gases, the Earth’s average temperature would plummet to approximately -18°C (0°F), making it a frigid wasteland. This stark contrast underscores the necessity of a balanced greenhouse effect, vital for ensuring temperatures remain within the narrow range conducive to life.
Another paramount aspect of the greenhouse effect is its role in sustaining liquid water, a fundamental prerequisite for life. The presence of GHGs helps maintain a warm enough environment for water to exist in all three states: solid, liquid, and gas. Water—known as the universal solvent—is critical for biochemical reactions and cellular functions, serving as a linchpin in the intricate web of life. Thus, the greenhouse effect indirectly influences terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, dictating where life can thrive.
Furthermore, consider the aesthetic appeal of a planet bustling with life, lush landscapes, and diverse ecosystems. The greenhouse effect engenders climatic conditions that enable the flourishing of vegetation, which, in turn, populates the Earth with intricate food webs. The interplay of sunlight, temperature, and moisture initiates the growth of plants, creating fertile grounds for herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores alike. Through photosynthesis, plants convert solar energy into chemical energy, fundamentally linking several trophic levels and establishing a foundation for life on Earth.
Moreover, greenhouse gases contribute significantly to the complexity of climate systems. Varied concentrations of these gases lead to fluctuations in weather patterns, which can result in distinct climates that foster biodiversity. Tropical rainforests thrive under humid and warm conditions, while arid deserts manifest in regions with minimal rainfall and extreme temperatures. The diversity of climates shaped by the greenhouse effect enables species to adapt and evolve, offering a mesmerizing tapestry of life forms. Each organism plays a unique role, establishing relationships that drive ecological balance and resilience.
As we reflect on the necessity of greenhouse gases, it becomes critically important to acknowledge the equilibrium required for sustainability. The modern industrial era has ushered in an era of unprecedented GHG emissions, resulting in an enhanced greenhouse effect and consequently, global warming. The implications of climate change are profound, threatening the very existence of numerous species and dismantling the intricate relationships that bind ecosystems. The battle against anthropogenic climate change is not solely about preserving our planet’s beauty but also about ensuring the survival of future generations and maintaining environmental integrity.
In conclusion, the greenhouse effect is not merely a scientific term; it encapsulates a complex interaction that underpins life on Earth. It is a fundamental force that regulates temperatures, sustains liquid water, and fosters rich biodiversity. However, human activities have disrupted this delicate system, leading to consequences we must urgently address. As stewards of this planet, it is our responsibility to safeguard the equilibrium that the greenhouse effect provides. By promoting sustainability and implementing measures to reduce GHG emissions, we can maintain the aesthetic allure and ecological viability of our home for generations to come. Let us embrace this challenge not only for ourselves but for the myriad forms of life that depend on this wondrous planet.