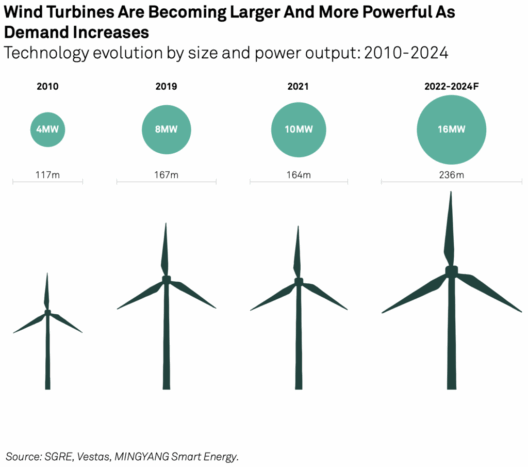
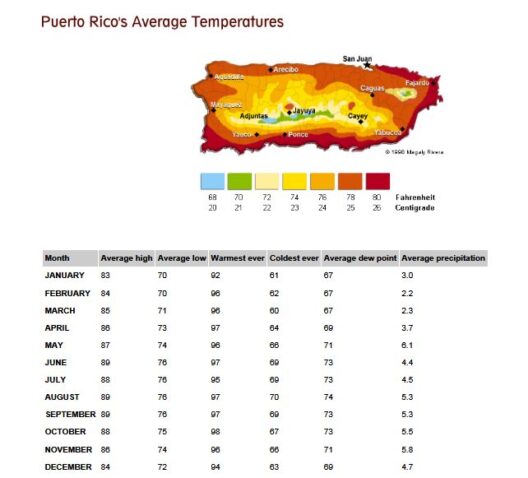
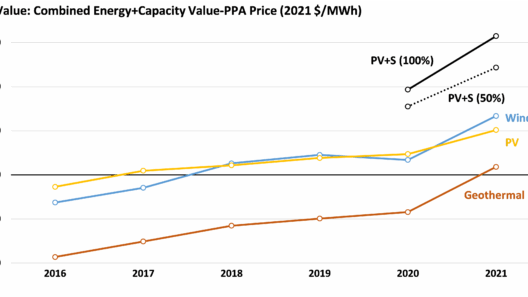Wind energy has emerged as a popular alternative to fossil fuels, often lauded for its potential to mitigate climate change. However, while the benefits are frequently emphasized, it is imperative to scrutinize the adverse environmental and economic implications associated with wind power. This exploration seeks to dissect the downsides of wind energy, providing a comprehensive understanding of why some argue its adoption is not without significant consequences.
This examination delves into three main areas of concern: the ecological ramifications, the impact on local economies, and the energy reliability issues. Each of these facets warrants careful consideration to inform a holistic perspective on wind energy.
Environmental Consequences: The Untold Story
While wind turbines generate clean energy and produce no direct emissions, their production and operation involve substantial environmental costs. The construction of wind farms entails land alteration, which can disrupt local ecosystems and biodiversity. The ecological footprint left by the sprawling installations may endanger habitats, particularly in sensitive areas. This habitat loss, often overlooked in the push for renewable energy, poses a grave risk to wildlife, especially avian populations, which are notoriously affected by turbine collisions.
Moreover, the manufacturing process for wind turbines requires significant amounts of rare-earth materials. Extracting these minerals often leads to environmental degradation through habitat destruction and pollution. The mining processes not only damage the land but also generate toxic waste that can contaminate soil and waterways, raising concerns about the sustainability of wind energy as a genuinely green alternative.
Noise pollution is another environmental consideration that accompanies the advent of wind farms. The whirring noise produced by turbine blades can have detrimental effects on human health and wildlife behavior. Communities that live in proximity to these installations report disturbances, indicating that noise levels have become a significant source of conflict and concern.
Local Economic Impact: Analyzing the Costs and Benefits
The economic arguments for wind energy often foreground job creation and investment in local communities. However, the reality may not be as straightforward. The energy transition toward wind power has the potential to disrupt traditional economic structures. For communities that rely on fossil fuel industries, the shift towards wind energy may lead to job losses and economic downturns, creating a dichotomy that is challenging to reconcile.
Additionally, local governments may experience increased costs associated with the maintenance of wind farms and their infrastructural demands. The influx of infrastructure, while beneficial for some, often leads to increased traffic and wear on local roads. This necessitates further public expenditure to maintain these routes, potentially straining municipal budgets.
Furthermore, there is the issue of land use. Wind farms can require vast tracts of land, which can misalign with agricultural needs or other forms of land utilization. This generates tension among landowners, whose livelihoods may be jeopardized by the encroachment of wind turbine installations. The conflict between renewable energy projects and agricultural practices poses a quandary for policymakers who must balance energy demands with the need to support local economies.
Energy Reliability: The Stability Dilemma
Another pressing concern regarding wind energy lies in its reliability. Wind power is inherently intermittent, relying on the fluctuating nature of wind. This leaves energy grids vulnerable to supply disruptions. The inconsistency necessitates reliance on backup systems, often powered by fossil fuels, to compensate during periods of low wind activity. Such a situation undermines the very objective of transitioning to renewable energy sources, as fossil fuel reliance persists, counteracting the environmental benefits of wind power.
Moreover, energy storage systems essential for balancing demand and supply are not yet sufficiently developed to handle the variability associated with wind energy generation. While technological advancements are underway, the current limitations in energy storage may hinder the efficiency and reliability of wind power as a primary energy source.
Conclusion: A Balanced Perspective
Wind energy is frequently championed as a panacea for our energy woes, offering a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices. However, the environmental and economic concerns outlined here necessitate a more nuanced approach to its implementation. From ecological disruptions and economic dislocation to reliability challenges, the adoption of wind energy is fraught with complications that demand rigorous scrutiny.
The pursuit of renewable energy must be pursued with caution, weighing the potential benefits against the inherent drawbacks. Future energy strategies should incorporate a balanced mix of diverse energy sources, ensuring that sustainable development does not come at the expense of environmental integrity and economic stability. Only through such careful deliberation can we hope to navigate the complexities of transition toward a truly sustainable energy future.