With the escalating concerns surrounding climate change and the pursuit of sustainable energy sources, wind energy has emerged as a pivotal player in the global transition towards renewable energy. Highways are often seen merely as conduits for automobiles, but they present an untapped, significant opportunity for wind energy conservation and utilization. This essay explores innovative green solutions to conservatively harness wind energy in highway environments, delving into the practicality and feasibility of various approaches.
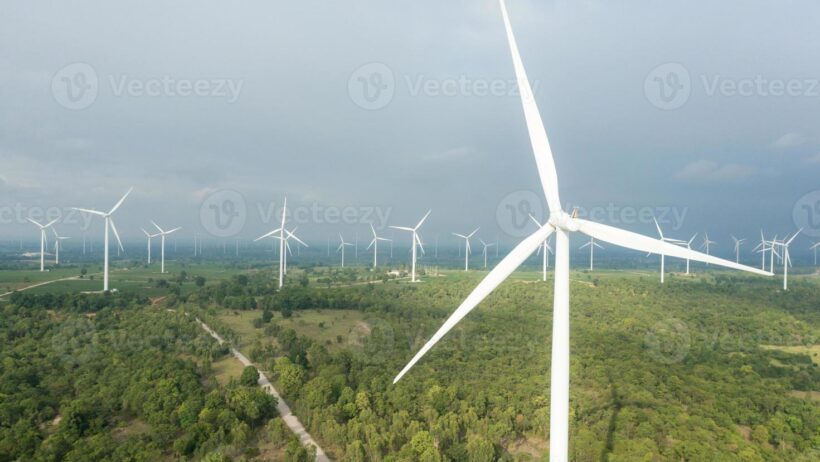
First and foremost, understanding the mechanics of wind energy is crucial. Wind energy, fundamentally, arises from the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface by solar radiation. This uneven heating engenders air movement, generating kinetic energy that can be converted into electrical energy via wind turbines. Highways often afford vast swathes of land, typically characterized by minimal obstructions that disrupt airflow patterns. Thus, highways can be an ideal platform for the strategic placement of wind turbines.
One primary solution is the integration of micro wind turbines along highway medians and shoulder areas. These small-scale turbines can be strategically affixed to roadside infrastructure, such as sound barriers or light poles. The winds generated by high-speed vehicles can act as a catalyst for increased energy production, maximizing the conversion of kinetic energy. Furthermore, micro turbines are less intrusive than traditional towering wind turbines, preserving highway aesthetics while effectively contributing to energy generation.
In addition to micro wind turbines, another innovative solution is the installation of vertical axis wind turbines (VAWT) along highways. Unlike traditional horizontal axis turbines, which require specific wind directions for optimal performance, VAWTs can harness wind from any direction. This adaptability is particularly advantageous on highways, where wind patterns can be erratic due to the proximity of vehicles and surrounding structures. VAWTs can be mounted near entrance and exit ramps, where wind currents may be stronger. Their compact and versatile design makes them a practical option for urban and suburban landscapes.
Moreover, utilizing wind energy to power electrical systems embedded within highways can serve as an efficient means of energy conservation. For instance, wind energy can power electric vehicle (EV) charging stations located strategically along highways. As the demand for EVs escalates, facilitating accessible and sustainable charging options is paramount. The incorporation of wind turbines to offset the energy requirements of these charging stations would not only reduce reliance on fossil fuels but also enhance the overall sustainability of transportation infrastructures.
Additionally, innovative concepts such as wind energy harvesting from pavement surfaces are gaining traction. Some researchers advocate for specialized pavement materials embedded with piezoelectric elements, capable of generating electricity as vehicles traverse over them. The wind-induced kinetic energy could be synergistically combined with this approach, creating a multifaceted energy generation system along highways. This dual strategy can substantially bolster energy conservation efforts while also potentially decreasing the carbon footprint associated with road maintenance and construction.
When contemplating the scale of implementing wind energy solutions, it is imperative to factor in the ecological implications. Wind turbines must be carefully positioned to minimize negative impacts on wildlife, particularly avian populations. As such, conducting thorough environmental assessments prior to installation is crucial. Additionally, public sentiment plays a key role in the acceptance of wind energy projects. Engaging local communities in discussions about potential benefits, such as job creation and reduced emissions, will foster a greater understanding and facilitate support.
To effectively demonstrate the potential of wind energy solutions along highways, successful case studies should be highlighted. For instance, countries like Denmark and Germany have implemented comprehensive wind energy solutions in urban and rural areas, resulting in significant energy savings and emission reductions. Drawing parallels to their initiatives can inspire and encourage the adoption of similar projects in other regions. Local governments and transport agencies can benefit from the insights gained through such real-world applications, ensuring that implementation is realistic and beneficial.
It is also vital to consider financial mechanisms that can drive the adoption of wind energy solutions on highways. Public-private partnerships, grants, and subsidization from governmental bodies can provide the necessary capital to launch innovative projects. This collaborative approach not only mitigates financial risk but also fosters a shared commitment to environmental sustainability. Promoting policies that encourage the utilization of renewable energy infrastructure will lead to broader societal acceptance and greater investment.
Finally, embracing technological advancements can further streamline the implementation of wind energy solutions. Automated monitoring systems can ensure that wind turbines are functioning optimally, while data analytics can provide insights into energy production and consumption patterns. Incorporating smart technology can maximize efficiency and enhance the predictive capabilities of energy generation systems. As digitalization permeates various sectors, its integration within wind energy solutions can revolutionize highway energy conservation efforts.
In conclusion, highways represent a promising frontier for wind energy conservation and innovative green solutions. By integrating micro wind turbines, vertical axis turbines, and energy-harvesting pavement technologies, the potential to augment energy production significantly increases. The implication of these solutions extends beyond merely seizing a renewable resource; they underscore a broader commitment to environmental stewardship. As society grapples with the pressing realities of climate change, embracing these innovative approaches on highways is not just an opportunity but an obligation. The convergence of sustainable practices within the context of transportation infrastructures can ultimately pave the way toward a greener and more resilient future.