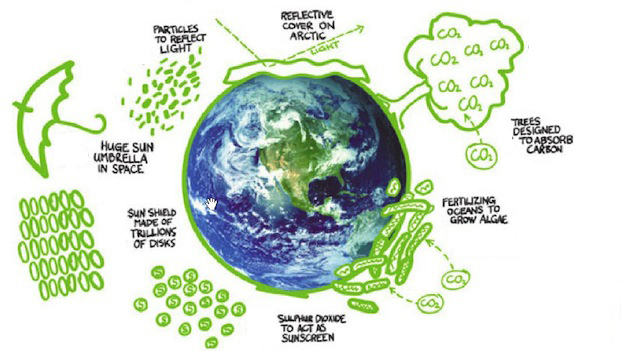
Global warming is an impending crisis demanding immediate intervention. As average global temperatures continue to rise, the call for innovative solutions to combat climate change is louder than ever. But how do scientists plan on stopping this phenomenon? With a plethora of cutting-edge solutions in the pipeline, the scientific community is engaging in a multifaceted approach to address this extraordinary challenge.
The first point of discussion is carbon capture and storage (CCS), a technology gaining traction as a viable method of reducing atmospheric carbon dioxide. CCS involves capturing carbon emissions from sources like power plants and industrial facilities before they can enter the atmosphere. Once captured, the carbon is transported and sequestered in geological formations deep underground. Interestingly, this process not only curbs emissions but can also be complemented by utilizing captured carbon dioxide to enhance oil recovery, effectively turning a potential pollutant into an economically advantageous resource.
Next on the horizon is direct air capture (DAC), a pioneering technology that extracts CO2 directly from the ambient air. By employing large-scale machines equipped with chemical processes to filter incoming air, scientists can isolate carbon from the atmosphere, a procedure akin to carbon scrubbing but on a grand scale. How about that? In a world that continually pumps carbon into the air, a solution that actively removes it is as revolutionary as it sounds. However, challenges remain in terms of energy consumption and infrastructure required for scaling DAC operations globally.
Turning our attention to renewable energy sources, there is an increasing emphasis on harnessing solar power. Photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into electricity are becoming progressively efficient and economical. Moreover, scientists are investigating solar fuels, which mimic photosynthesis to convert sunlight directly into chemical fuels like hydrogen. This not only provides an alternative to fossil fuels but also demonstrates the remarkable potential of utilizing nature’s own processes for innovative energy solutions. Yet, how do we incentivize widespread adoption of these technologies in a market still so reliant on traditional energy sources?
Wind energy is another titan in the renewable sector. With the ability to produce electricity without emitting harmful pollutants, wind power is rapidly on the rise. Innovative designs, such as vertical-axis wind turbines, are being developed to optimize energy capture even in low-wind areas. The integration of energy storage solutions, like large-scale batteries, can even out the intermittent nature of wind energy, making it a reliable power source. What might be stopping us from completely embracing wind as a mainstream energy provider? Regulatory hurdles and financial constraints remain prominent obstacles.
Next, the discussion shifts to bioengineering and synthetic biology. The manipulation of microorganisms to produce biofuels, bioplastics, and other sustainable materials may offer breakthroughs that transform industries. By creating microbes that digest waste or generate energy-rich resources, scientists can engineer solutions that actively reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. Can engineered organisms clean our planet? It’s an intriguing proposition, but the safety, ecological consequences, and ethical considerations regarding genetic modifications raise significant questions.
As alarming as global warming is, adaptations in agricultural practices cannot be overlooked. Climate-resilient crops, engineered for enhanced sustainability and productivity, are on the forefront of innovation. By employing genetic modification and selective breeding techniques, scientists are developing crops that can withstand changing weather patterns and pests more effectively. The use of precision agriculture practices, including satellite and drone technology, facilitates the efficient use of resources. Will this be enough to keep up with the growing global food demand in the face of climate change? It raises a crucial point regarding food security and the welfare of millions.
Furthermore, forests play a significant role in mitigating climate change. Reforestation and afforestation are being promoted rigorously. Programs to restore damaged ecosystems not only sequester carbon but also preserve biodiversity. Governments and organizations are actively investing in large-scale forest planting initiatives, recognizing that their restoration has undeniable benefits. Nevertheless, as we advance in these efforts, a burning question arises: how do we ensure that these projects are sustainable and equitable for all communities involved?
Moving on, we encounter the realm of geoengineering, a controversial and futuristic approach. Proposed interventions to manipulate the Earth’s climate system promise impressive yet daunting possibilities. One such method entails solar radiation management (SRM), which seeks to reflect a portion of solar energy back into space. While it could theoretically result in immediate cooling, concerns surrounding the potential unintended consequences loom large. Is there a possibility of playing god with our climate? One can only hope that thorough exploration of these concepts is matched with careful ethical consideration.
In summary, the scientific community is leaving no stone unturned in its quest to halt global warming. From carbon capture technologies to innovative agricultural practices, the array of potential solutions reflects a collective recognition of the urgency of this crisis. However, the journey towards a sustainable future is fraught with complexities. It poses existential questions about energy consumption, ethical decision-making, and socio-economic equity. Addressing climate change is not solely a scientific pursuit but a global endeavor requiring a united front. We must harness our creativity, intellect, and commitment to chart a course toward a more sustainable world. The challenge is immense, yet the pathways are illuminated with possibility.