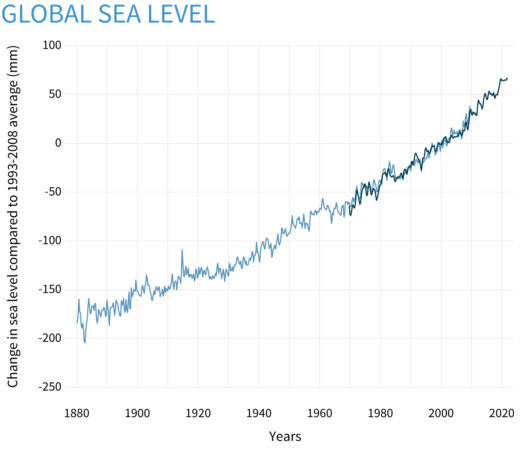
The phenomenon of rising sea levels is underpinned by a multitude of interconnected factors. Understanding these causes is imperative, not just for scientists but for anyone who resides near coastlines or has a vested interest in the future of our planet. This article will delve into the primary contributors to rising ocean levels, including thermal expansion, glacial melting, and anthropogenic influences, elucidating how these processes interplay to exacerbate the challenges faced by coastal regions worldwide.
Understanding the science behind sea level rise is critical. The Earth’s oceans are vast and dynamic systems that respond to climatic changes with remarkable sensitivity. As temperatures rise, both the oceanic and terrestrial systems are impacted significantly. This discussion will explore how these processes contribute individually and collectively to the troubling trend of rising sea levels.
Elements of Thermal Expansion
One of the fundamental processes driving sea level rise is thermal expansion, a phenomenon that occurs when water heats up and expands. As global temperatures increase, so does the temperature of the Earth’s oceans. The interconnectivity of our environment means that even a slight rise in oceanic temperature can lead to a significant increase in volume.
The physics behind thermal expansion is relatively straightforward: warmer water occupies more space than colder water. This effect, although often subtle in the short term, can accumulate over the decades to noticeably increase ocean levels. Current models estimate that thermal expansion is responsible for about half of the observed rise in global sea levels since the late 19th century. The nuances and intricacies of oceanic warming underscore the importance of continuous monitoring and research to predict future impacts.
Melting Glaciers: The Ice That Shapes Our Oceans
The role of glacial melting cannot be overstated when discussing rising sea levels. Polar ice caps and glaciers worldwide are diminishing at an alarming rate due to elevated temperatures. The Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets, in particular, are significant contributors to rising sea levels. They hold vast amounts of freshwater, and their melting contributes directly to oceanic rise.
When glaciers melt, the water that was previously bound in ice is released into the oceans. This process is accelerated by a feedback loop; as ice sheets thin, they absorb more sunlight, leading to increased temperatures and further melting. Moreover, the instability of ice shelves surrounding the Antarctic Peninsula has raised concerns. The disintegration of these ice shelves, caused by warmer ocean currents, potentially opens the floodgates for even more substantial ice loss from the larger ice sheets.
The interconnectivity of glacial loss and oceanic dynamics emphasizes the critical need for comprehensive climate models that can accurately predict future scenarios. As glaciers continue to recede, their impact on sea levels will become increasingly pronounced, affecting millions of lives along coastal regions worldwide.
Anthropogenic Impacts: The Human Factor
Intriguingly, human activities have exacerbated the natural processes contributing to sea level rise. The combustion of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial practices have led to an upsurge in greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere. The resultant climate change not only warms our planet but also disrupts the delicate balance of natural systems. Urbanization and land reclamation in coastal areas further complicate matters, with the modification of natural drainage patterns contributing to localized sea level rise.
Additionally, groundwater extraction contributes to rising sea levels. When we extract water from aquifers, the land above can sink, effectively increasing the relative sea level. Groundwater depletion is a profound issue—especially in regions like South Florida and California—where over-extraction creates vulnerabilities in the face of rising tides.
The Responsibility of Governance and Global Collaboration
Addressing the complexities of rising sea levels transcends national borders; it necessitates global cooperation and governance. Countries must unite in their efforts to mitigate the factors exacerbating climate change. By transitioning to renewable energy sources, implementing sustainable land management practices, and investing in carbon capture technologies, significant progress can be achieved. Additionally, international support for vulnerable nations is crucial. Many areas faced with rising sea levels lack the resources and funding to adapt effectively.
Innovative engineering solutions can also play a pivotal role. This includes developing advanced coastal defenses, such as sea walls, tidal barriers, and sustainable mangrove restoration projects that can absorb storm surges naturally. The integration of nature-based solutions with traditional engineering methods provides a multifaceted approach to protecting coastal regions.
Collective Action for a Shared Future
The rise in sea levels is not a distant concern; it is a present reality that requires immediate action. The challenges posed by this phenomenon cannot be tackled by isolated efforts. Governments, organizations, and individuals must collaborate to foster sustainable practices and enact policies that prioritize our planet’s health.
In conclusion, as the intricacies of rising sea levels unfold, a clear understanding of the myriad causes—from thermal expansion and glacial melting to the multifaceted human impacts—becomes imperative. By galvanizing collective action and committing to sustainable practices, there is hope for the preservation of coastal habitats and the communities that inhabit them. The ocean and land are intricately linked; the health of one directly influences the vitality of the other. Thus, it is our shared responsibility to ensure a stable future for our planet and its inhabitants.