The Earth’s atmosphere, enveloping us like a cocoon, plays a vital role in maintaining the planet’s temperature. This delicate balance, however, is being severely disrupted by human activity, most notably through what is referred to as the enhanced greenhouse effect. To grasp the implications of this phenomenon, we must delve into its intricacies, implications, and the stark reality of its impact on our planet.
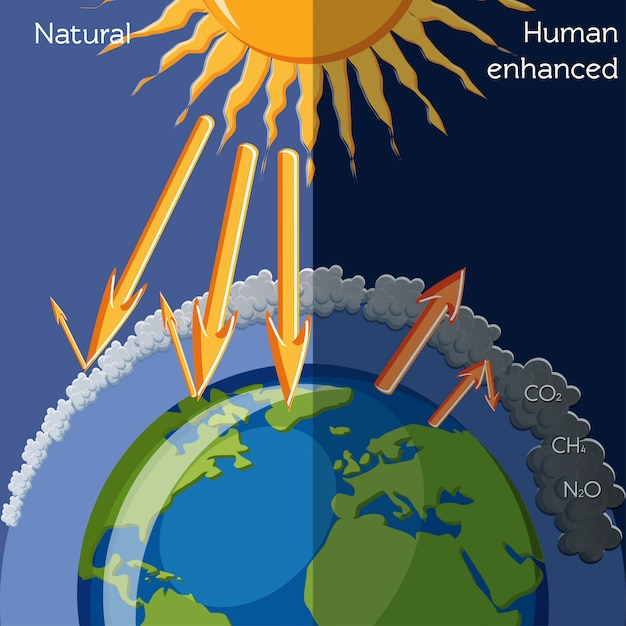
At its core, the greenhouse effect is a natural process where certain gases in the atmosphere trap heat from the sun, preventing it from escaping back into space. Think of these gases as the Earth’s thermal blanket — they keep us warm enough to thrive. However, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, have significantly intensified this effect, leading to what is termed the enhanced greenhouse effect.
This augmentation occurs as a direct result of increased concentrations of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. The metaphorical blanket is now thicker, causing the Earth to warm at an alarming rate. This escalation is not merely a scientific anomaly; it reverberates through ecosystems, climate patterns, and human livelihoods globally.
The Culprits: Human Activities and Their Consequences
The industrial era heralded unprecedented advances in technology and quality of life. However, it also marked the beginning of a relentless pursuit of resources that has pushed our planet to its limits. The combustion of fossil fuels for energy has released billions of tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere since the late 1800s. This carbon footprint has contributed to a drastic rise in atmospheric CO2, exceeding levels deemed stable for millennia.
Additionally, deforestation, often described as the lungs of our planet being choked, exacerbates the situation. Trees are nature’s champions in absorbing CO2; their removal not only releases stored carbon but also diminishes our capacity to absorb future emissions. Agriculture, particularly livestock production, further amplifies the enhanced greenhouse effect by emitting substantial amounts of methane, a gas over twenty times more potent than CO2 in its initial impact. The synergy of these human-driven actions propels us into a perilous trajectory of climate change.
Climate Consequences: A Global Reckoning
The repercussions of the enhanced greenhouse effect are already manifesting. Climate change, an umbrella term encompassing rising global temperatures, erratic weather patterns, and sea level rise, stands as a testament to the damage wrought by human actions. As a result, we are witnessing unprecedented phenomena such as more frequent and severe hurricanes, prolonged droughts, and rising temperatures that challenge the familiar rhythms of nature.
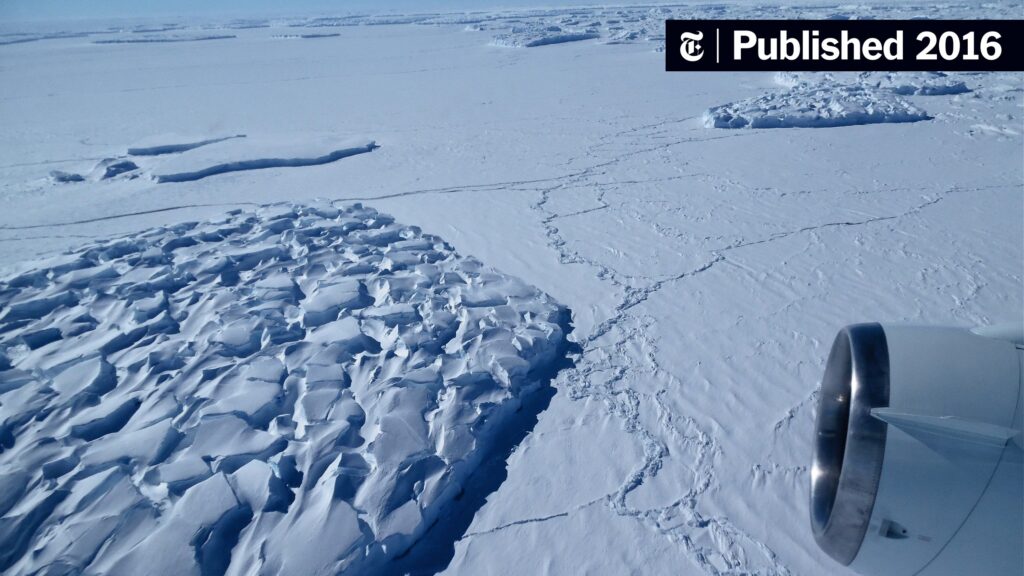
Moreover, the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers poses an existential threat to coastal cities worldwide. As these glaciers recede, they do not merely mirror the warming world; they usher in a potential humanitarian crisis, displacing populations and threatening food and water sources. Freshwater resources, often taken for granted, are diminishing, compounding social and economic disparities across the globe. In this context, global warming is not merely an environmental issue; it is a harbinger of social upheaval on an unprecedented scale.
Vision Forward: Mitigating the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
In the face of daunting challenges, there exists a flicker of hope — an opportunity to pivot towards sustainable practices capable of mitigating the enhanced greenhouse effect. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, offers a promising pathway. These technologies harness the inexhaustible power of nature without imposing the burdens that fossil fuels do. Innovations in energy efficiency also play a crucial role; simple changes in how we consume energy can collectively yield monumental impacts.
Reforestation initiatives, enforcing stringent logging regulations, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices are pivotal steps toward restoring the balance we have disrupted. Furthermore, fostering a culture of conservation and encouraging individuals to reduce their carbon footprints through lifestyle choices can empower communities to become active participants in the battle against climate change.
Global governance and cohesive policy frameworks also play indispensable roles. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, exemplify the collective responsibility that transcends borders, urging nations to commit to measurable reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. Only through unified action can humanity hope to reverse the tide of climate change and transition towards resilience.
The enhanced greenhouse effect serves as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of human activity and environmental sustainability. As we stand at a pivotal crossroads for our planet, we can choose to embrace innovative solutions and responsible stewardship of natural resources. The future of the Earth hangs in the balance, waiting for our decisive actions today to forge a sustainable tomorrow.
Ultimately, recognizing the human-centric origins of the enhanced greenhouse effect is crucial as we navigate this pivotal juncture. It is an urgent call to action for individuals, communities, and leaders alike to acknowledge their role as stewards of the Earth, tasked with nurturing its delicate ecosystems and ensuring a viable legacy for future generations.