Energy conservation is a term that encapsulates a range of practices aimed at reducing energy consumption through using less energy service. It embraces not just the strategies we employ but also the philosophy behind making conscious choices that mitigate the impact of our energy use on the environment. As the global community grapples with climate change, resource depletion, and sustainable living, understanding energy conservation’s definition and significance becomes paramount.
Understanding Energy Conservation
To fully grasp energy conservation, it is essential to explore its fundamentals. At its core, energy conservation involves minimizing the amount of energy used to provide the same level of energy service. This can be achieved through mechanical, behavioral, and technological means. Examples include switching off lights when not in use, utilizing energy-efficient appliances, and investing in renewable energy sources such as solar and wind.
The root cause of energy conservation lies in the recognition that energy is not unlimited. Non-renewable resources, primarily fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, harbor finite quantities. Their continued consumption not only threatens their availability but also exacerbates environmental degradation. Conservation efforts identify ways to repurpose energy use without curtailing daily life activities while maintaining comfort and convenience.
The Crucial Role of Energy Conservation in Environmental Sustainability
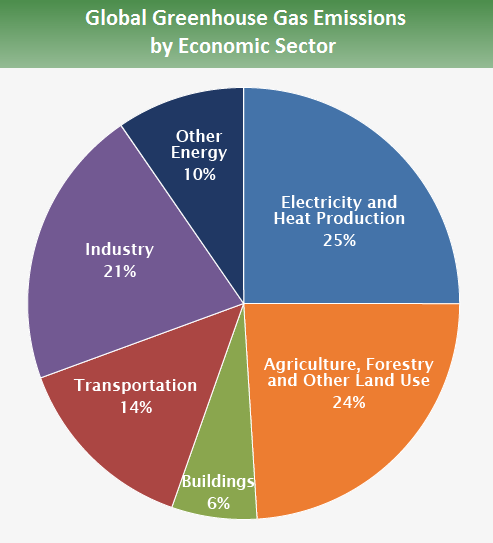
Energy conservation plays a pivotal role in environmental sustainability. The burning of fossil fuels produces greenhouse gases, mainly carbon dioxide, which contribute significantly to global warming and climate change. By conserving energy, we can reduce the demand for fossil fuel combustion, thereby reducing emissions that harm our atmosphere.
Moreover, the extraction and consumption of fossil fuels are often laden with perilous environmental consequences—oil spills, habitat disruption, and sprawling industrial landscapes all underscore the ecological cost of our current energy consumption patterns. Energy conservation assists in mitigating these negative impacts. By promoting practices such as the use of public transportation or cycling instead of driving, we reduce air pollutants and easing congestion in urban areas.
Additionally, conserving energy can alleviate pressure on our natural resources. For instance, lower energy demand can lead to reduced water consumption in power plants, helping to address water scarcity in many regions. Each kilowatt-hour saved not only lessens our energy bills but also impacts our water supply and ecosystems positively.
Economic Benefits of Energy Savings
Beyond the environmental implications, the economic rationale for energy conservation is compelling. The rising cost of energy has made it increasingly necessary for households and businesses to seek efficient alternatives. The immediate advantage of energy conservation is the reduction in electricity bills. Energy-efficient appliances, for example, may have higher upfront costs, but their reduced energy use leads to substantial savings in the long run.
In addition to individual savings, energy conservation can foster broader economic growth. By investing in energy efficiency, we can stimulate job creation in various sectors, including manufacturing, construction, and renewable energy. Initiatives such as home retrofitting programs or energy audits encourage skill development and workforce expansion while supporting local economies.
Moreover, increasing energy efficiency helps stabilize electricity prices. By decreasing demand, less need arises for new power plants, leading to lower capital investments for energy production. This stabilization ultimately shields consumers from wild price fluctuations in the energy market.
Promoting Energy Conservation: Strategies for Individuals and Communities
Creating a culture of energy conservation requires active participation from individuals, families, communities, and governments. Engaging in energy-efficient practices hinges not only on awareness but also on accessible strategies. Here are several methods to facilitate conservation at various levels.
1. **Adopting Energy-Efficient Technology**: Embrace appliances that have the Energy Star label or are known for their efficiency ratings. These technologies significantly consume less energy without compromising output.
2. **Educating and Involving Communities**: Awareness campaigns at the community level can drive collective action. Neighborhood initiatives promote sharing resources, like communal gardens or tool-sharing programs. Host workshops on energy-saving behaviors and simple changes that have a significant impact.
3. **Implementing Smart Solutions**: Utilize smart home technologies such as programmable thermostats or energy monitoring systems. These can adjust energy use in real-time based on actual need rather than fixed habits.
4. **Supporting Renewable Energy Initiatives**: Encourage the use of solar panels or wind turbines within your community. Collective buy-in on renewable projects can lower costs and provide clean energy alternatives for broader consumption.
5. **Policy Advocacy**: Citizens should advocate for policies encouraging energy conservation, such as incentives for energy-efficient home improvement or comprehensive energy audits for businesses.
Final Thoughts: The Future of Energy Conservation
As we forge ahead into an uncertain future, energy conservation stands as a beacon of hope. It not only offers a pathway towards sustainable living but also emphasizes the interconnectedness of our choices and the environment. Each action, no matter how small, contributes to a larger collective effort towards conserving our precious resources.
Ultimately, embracing the principles of energy conservation signifies a commitment to a healthier planet, economic resilience, and a sustainable future. As individuals and communities become more informed and engaged, the cumulative impact can lead us towards achieving a more sustainable and equitable world.