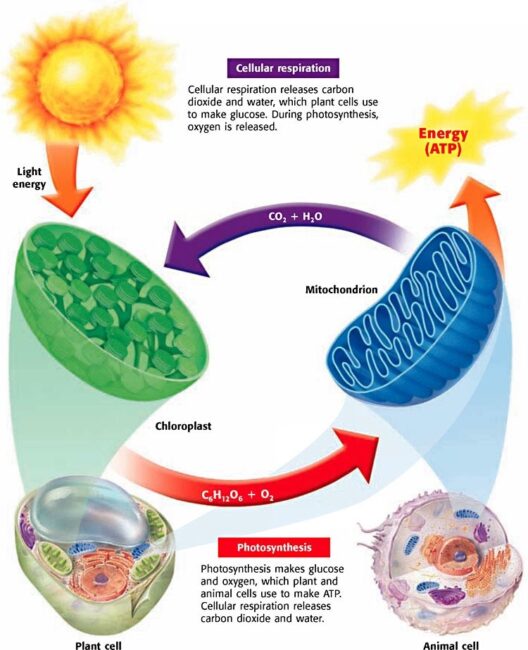
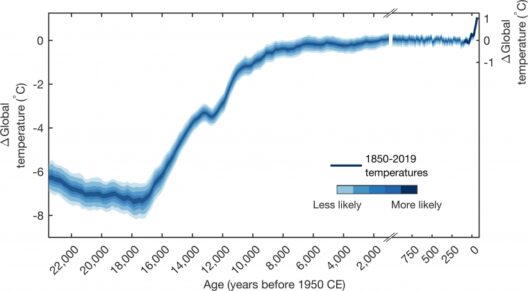
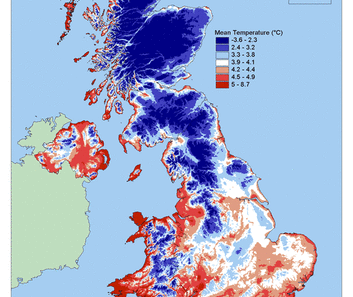
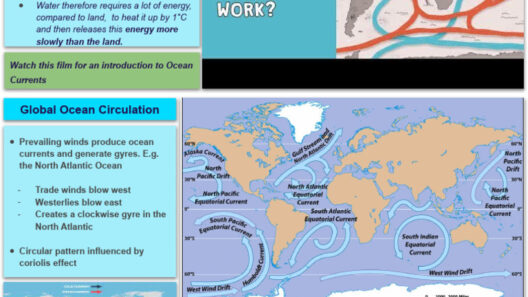
What if one day, humanity finds a way to traverse the overwhelming expanses of our solar system? Would we consider settling on a planet with a tempestuous climate, like Jupiter? Imagining life on the largest planet in our solar system may seem far-fetched, but understanding its atmospheric dynamics reveals crucial insights about both Jupiter and the nature of planetary climates. This exploration uncovers the stormy narratives written in the clouds of Jupiter and the implications they have not just for space exploration, but also for understanding climatic phenomena on Earth.
At a staggering distance of approximately 484 million miles from the Sun, Jupiter’s climate is radically different from what we experience on Earth. Dominated by colossal storms, frigid temperatures, and a complex meteorological tapestry, Jupiter’s atmosphere is an enigmatic realm that defies easy comprehension. The planet’s gaseous composition includes hydrogen, helium, methane, and ammonia, which engenders a diverse array of weather patterns. This unique make-up begs the question: how do these elements interact to produce the formidable storms and vibrant cloud bands observed through telescopes?
The majestic cloud bands of Jupiter are far more than mere visual spectacles. Known as zones and belts, they are manifestations of differential rotation and convection currents within the planet’s atmosphere. The equatorial region spins more rapidly than the poles, establishing a fluid dynamic that propels continuous currents. These currents give rise to the contrasting light and dark regions visible in images. The lighter zones, or “zones,” are characterized by higher altitudes and lower temperatures, while the darker “belts” reveal deeper, warmer regions. This stratification conjures imagery reminiscent of swirling cream in coffee — layers coalescing into forms both beautiful and chaotic.
However, the most captivating aspect of Jupiter’s climate is perhaps the ferocious storms that churn in its atmosphere. Among them, the Great Red Spot stands as a titan—an enormous, persistent hurricane that has raged for over 350 years. Spanning more than 16,000 kilometers, this gigantic tempest is larger than Earth itself. Its durability is a testament to Jupiter’s characteristic dynamics, where the interactions of high-speed winds and the vast reservoir of heat from the planet’s interior create an environment conducive to the formation of such leviathans. The swirling vortex of the Great Red Spot exemplifies not just a meteorological wonder but a harbinger of atmospheric resilience. It invites us to ponder: what can this extraterrestrial hurricane teach us about climate stability and change on our home planet?
Jupiter’s storms are driven by thermal energy rather than solar radiation, as the planet emits more heat than it receives from the Sun. This internal heat, coupled with the planet’s rapid rotation, produces intricate weather patterns that are often at odds with our terrestrial experiences. Notably, the planet’s temperature varies significantly with altitude, with temperatures plummeting to approximately -145 degrees Celsius in the upper atmosphere. The vertical layering results in atmospheric conditions where ammonia freezes at higher altitudes, creating clouds of ammonium hydrosulfide and other compounds. The interplay of these temperature gradients constructs a tapestry of unpredictable weather phenomena, beckoning deeper investigation.
Every aspect of Jupiter’s climate contributes to a continuous narrative of transformation. Winds gusting at speeds of up to 620 kilometers per hour demonstrate the ferocity and energy coursing through this behemoth. One might ponder how these phenomena correlate with our understanding of wind patterns on Earth — drawing parallels offers fascinating insights into the potential for chaos and stability across different planetary systems. Could analyzing a storm on Jupiter provide clues about cyclonic behaviors here at home? As we delve into such relationships, a challenge looms: what can scientists glean from Jupiter’s atmospheric complexities to mitigate the impacts of our changing climate?
While the clouds of Jupiter swirl with consequences yet to be fully understood, they also offer tantalizing opportunities for discovery. The exploration of Jupiter’s atmosphere—via spacecraft such as Juno—reveals data that can enhance our understanding of not only gas giants but also the dynamics governing planets across the cosmos. The intricate gravitational interactions within Jupiter’s system influence its moons and even its rings. By comprehensively studying these interactions, researchers can extrapolate theories about other extraterrestrial systems.
The examination of Jovian climate dynamics is not solely an academic exercise; its implications resonate profoundly with humanity’s experience on Earth. The study of storms, temperature variances, and atmospheric compositions can provide valuable lessons to address our pressing climate crisis. As scientists work tirelessly to track changing weather patterns and the extreme events that arise, the parallels with Jupiter’s unpredictability become a reminder of our planet’s own fragility. Thus, Jupiter acts as a mirror reflecting both the tumultuous nature of weather and the systems in place that govern life across the solar system.
Ultimately, exploring the climate of Jupiter instills a sense of wonder, curiosity, and urgency within us. The challenges posed by the planet’s mercurial atmosphere excite the imagination while underscoring the larger narrative of planetary science. A fascinating question arises: as humanity gazes into the heavy clouds on Jupiter, what reflections of our own climate dilemmas do we observe? As Earth continues to face unprecedented change, seeking knowledge from our cosmic neighbors may yet illuminate pathways toward a sustainable future.