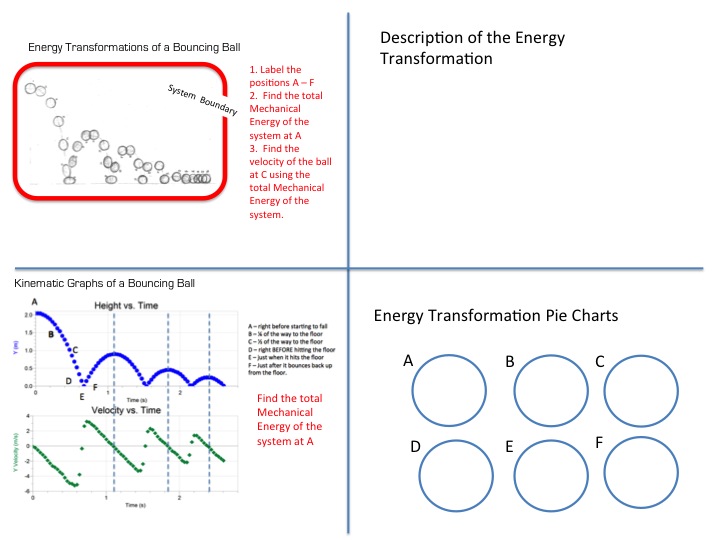
The law of conservation of energy is a fundamental principle in the realm of physics, positing that energy cannot be created or destroyed but can only be transformed from one form to another. This unyielding rule serves as the backbone for numerous scientific disciplines and remains pivotal not only in our understanding of physical processes but also in our appreciation of ecological systems and sustainability efforts.
Understanding the implications of energy conservation can illuminate various aspects of both theoretical physics and practical applications in everyday life. This article delves into the essence of the conservation of energy, its multifaceted significance, and its profound impact on various scientific and natural phenomena.
Beyond the mere statement of its definition, it is crucial to explore the broader dimensions of energy types, real-world applications, and the panoramic influence it exerts on environmental sustainability.
Exploring the Concept of Energy Transformation
At its core, the law of conservation of energy articulates that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant. This notion invites contemplation on the diverse forms through which energy manifests. There exists kinetic energy, captured in the motion of objects, and potential energy, often stored within systems poised for movement or change.
Thermal energy, associated with heat, and chemical energy, which resides in the bonds of molecular compounds, are equally significant. These transformations illustrate that while energy can shift forms—such as from potential to kinetic during a fall—the overall quantity of energy remains unchanged.
This concept finds striking illustrations in mechanical systems, such as a pendulum swinging back and forth. Here, energy continually converts between kinetic and potential forms. When the pendulum reaches its apex, potential energy peaks while kinetic energy hits a nadir. Conversely, as it descends, kinetic energy swells at the potential energy’s expense. This dance of energy embodies the essence of conservation.
The Prevalence of Conservation of Energy Across Disciplines
Interestingly, the conservation of energy transcends mere theoretical physics; it permeates various scientific disciplines, including biology and chemistry. For instance, in biological systems, the intricate processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration conform to the energy conservation principle. Plants capture solar energy and convert it into chemical energy, while organisms utilize this chemical energy for growth and metabolism.
In chemistry, the principles behind thermodynamics are deeply rooted in energy conservation. Endothermic and exothermic reactions epitomize this dynamic, marking a constant exchange of energy that abides by this law. Chemical bonds break and form, yet the total energy remains balanced, underscoring the robustness of this principle across various scientific realms.
The influence of energy conservation also extends to engineering and technology. Renewable energy technologies, particularly those harnessing solar, wind, and hydroelectric energy, epitomize the practical applications of energy transformation in achieving sustainable lifestyles. By understanding energy conservation, engineers can craft systems that optimize energy usage and minimize waste, driving innovations in efficiency that are crucial for a sustainable future.
Environmental Implications of Energy Conservation
Moreover, the law of conservation of energy bears profound implications on ecological systems and initiatives aimed at combating climate change. The principles of energy conservation inform sustainable practices that promote resource efficiency, highlighting the need to evaluate our energy consumption patterns.
By recognizing how energy flows through ecosystems, humans can develop more effective conservation strategies. For instance, understanding the energy dynamics within food webs reveals how energy is transferred between trophic levels, thereby emphasizing the importance of biodiversity in sustaining ecological balance.
Furthermore, the challenges posed by energy consumption and waste underscore the urgency of transitioning to a circular economy. This model emphasizes resource recovery and continual use, where energy efficiency becomes paramount. It encourages industries to minimize waste, recycle materials, and conserve energy, reinforcing the essence of energy conservation in a world increasingly concerned with environmental integrity.
Challenges and Opportunities in Energy Conservation
The implications of the conservation of energy extend into the societal framework, inspiring innovation while also posing challenges. The pressing need for conserving energy in light of dwindling resources, and the escalating concerns over climate change, challenges scientists, engineers, and policymakers alike.
This dynamic tension between energy demand and environmental responsibility demands novel technologies and collective behavioral adjustments. The rising momentum surrounding alternative energy sources illustrates a shifting paradigm where energy conservation is not merely a theoretical concept but a practical necessity, interwoven with global socioeconomic strategies.
Encouraging citizen engagement in energy conservation initiatives can foster a culture of sustainability. Programs advocating for energy-efficient practices, such as reducing electricity consumption or utilizing public transport, can fundamentally alter how communities approach energy resourcefulness.
In conclusion, the law of conservation of energy is a cornerstone of scientific understanding with extensive implications across various fields—be it physics, biology, or environmental science. Acknowledging the continuous flow of energy in its myriad forms not only aids our comprehension of physical phenomena but also reinforces our responsibility toward sustainable practices. By embracing this principle, societies can navigate the challenges of resource consumption and environmental stewardship more effectively, paving the way for a sustainable future.